Embed presentation
Downloaded 19 times
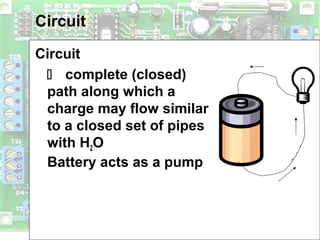
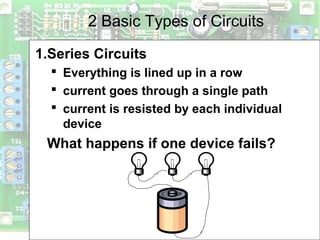
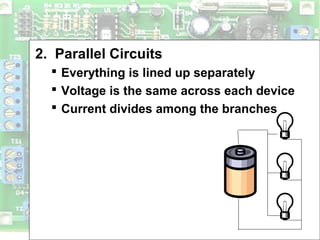
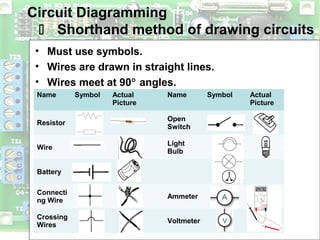
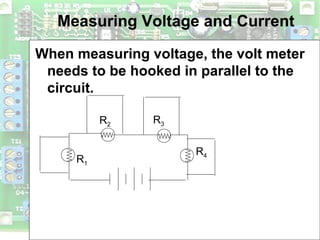
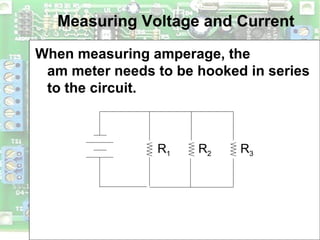
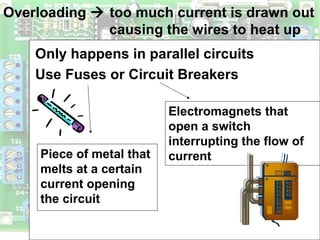
Electric circuits require a complete conductive path for charge to flow similarly to a closed pipe system. There are two basic types of circuits: series circuits where all components are lined up in a single conductive path and current is resisted at each component, and parallel circuits where the voltage is shared across branches while current divides among paths. Circuit diagrams use symbols to represent components like resistors, batteries, and wires to depict circuit layout and connections. Voltage is measured using a voltmeter connected in parallel across a component while current is measured using an ammeter connected in series within the conductive path. Overloading can occur in parallel circuits if too much current is drawn, which is prevented using fuses or circuit breakers.







