This document discusses the math for series and parallel circuits.
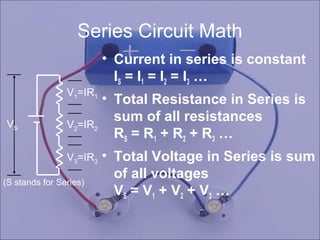
For series circuits, current is constant, total resistance is the sum of individual resistances, and total voltage is the sum of individual voltages.
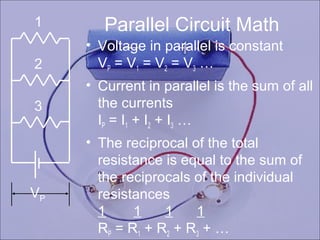
For parallel circuits, voltage is constant, total current is the sum of individual currents, and the reciprocal of total resistance equals the sum of the reciprocals of individual resistances.
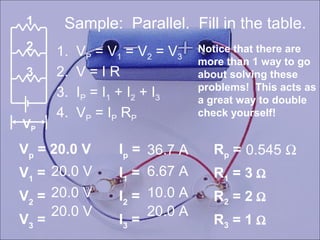
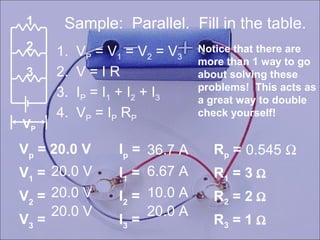
Sample problems are provided to demonstrate how to calculate current, voltage, resistance, and fill out tables for series and parallel circuits.