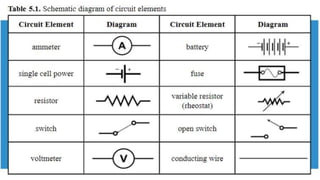
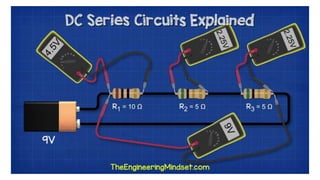
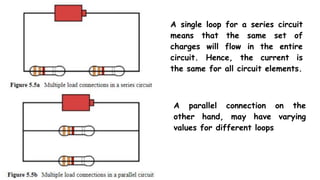
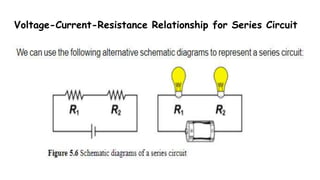
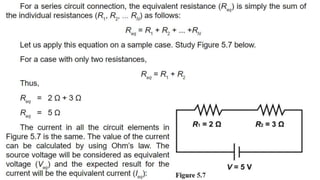
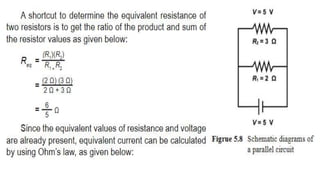
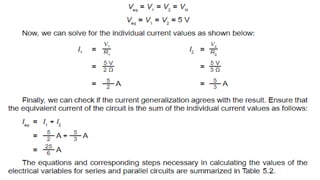
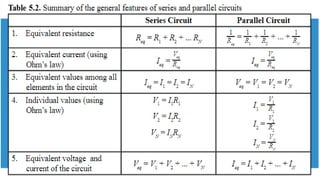
This document discusses direct current circuits and provides questions to test the reader's understanding. It covers topics like circuit diagrams, Kirchhoff's laws, capacitors, and experimental design. Key concepts explained include series and parallel circuits. In a series circuit, current is the same through all elements since there is a single path for charge flow. In parallel circuits, current can vary as there are multiple paths. The document also examines relationships between voltage, current, and resistance for both series and parallel circuits.