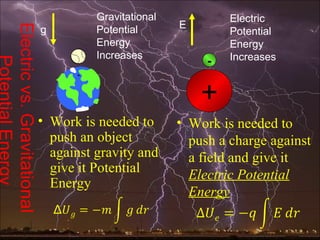
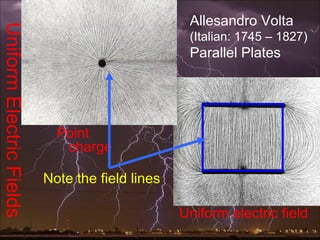
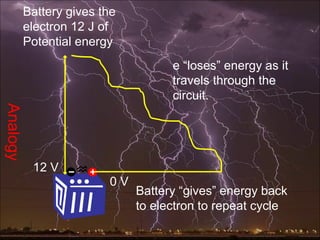
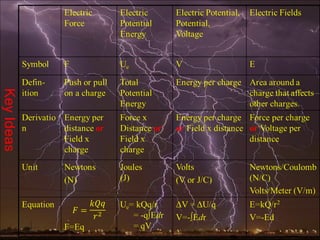
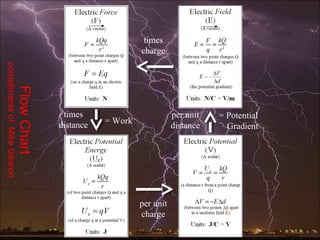
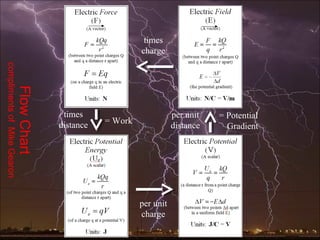
Electric potential energy, like gravitational potential energy, increases as an object is moved against an electric field. Voltage, also called electric potential, measures the electric potential energy of a charge and the work required to move it between two points in an electric field. Voltage is defined as the work done per unit charge to move an object from one point to another in a constant electric field. A battery supplies voltage that provides electric potential energy to charges moving through a circuit.