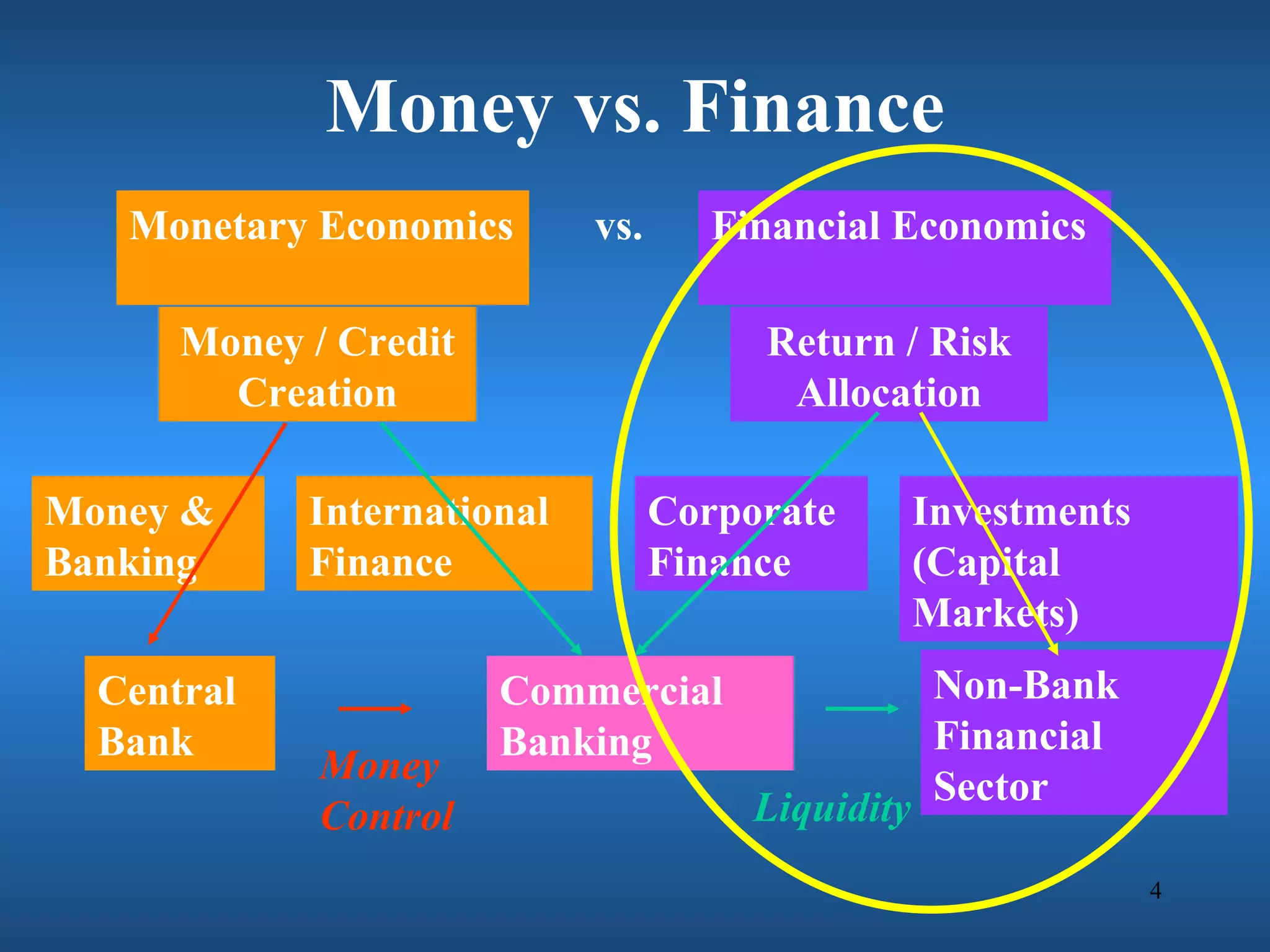
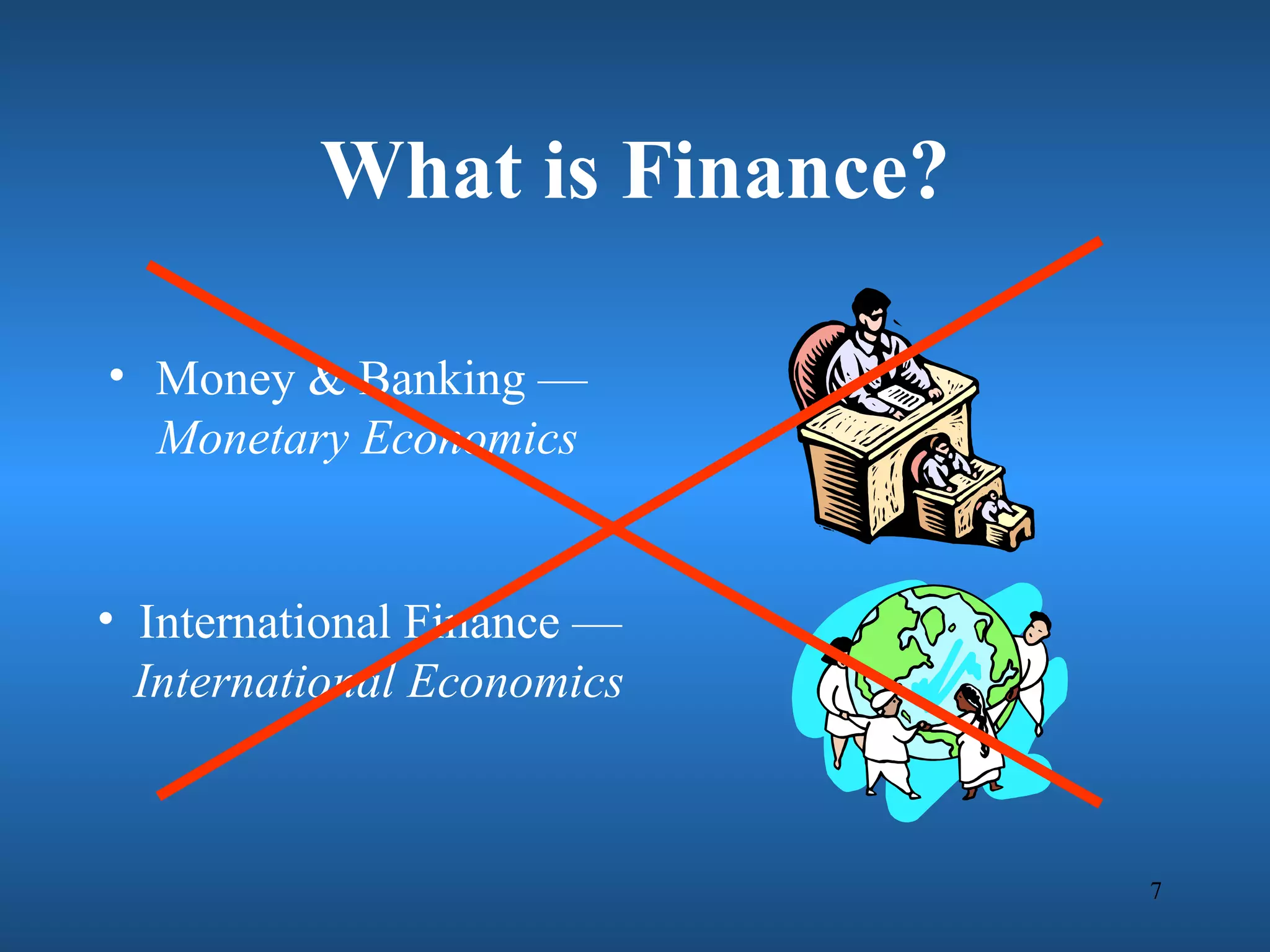
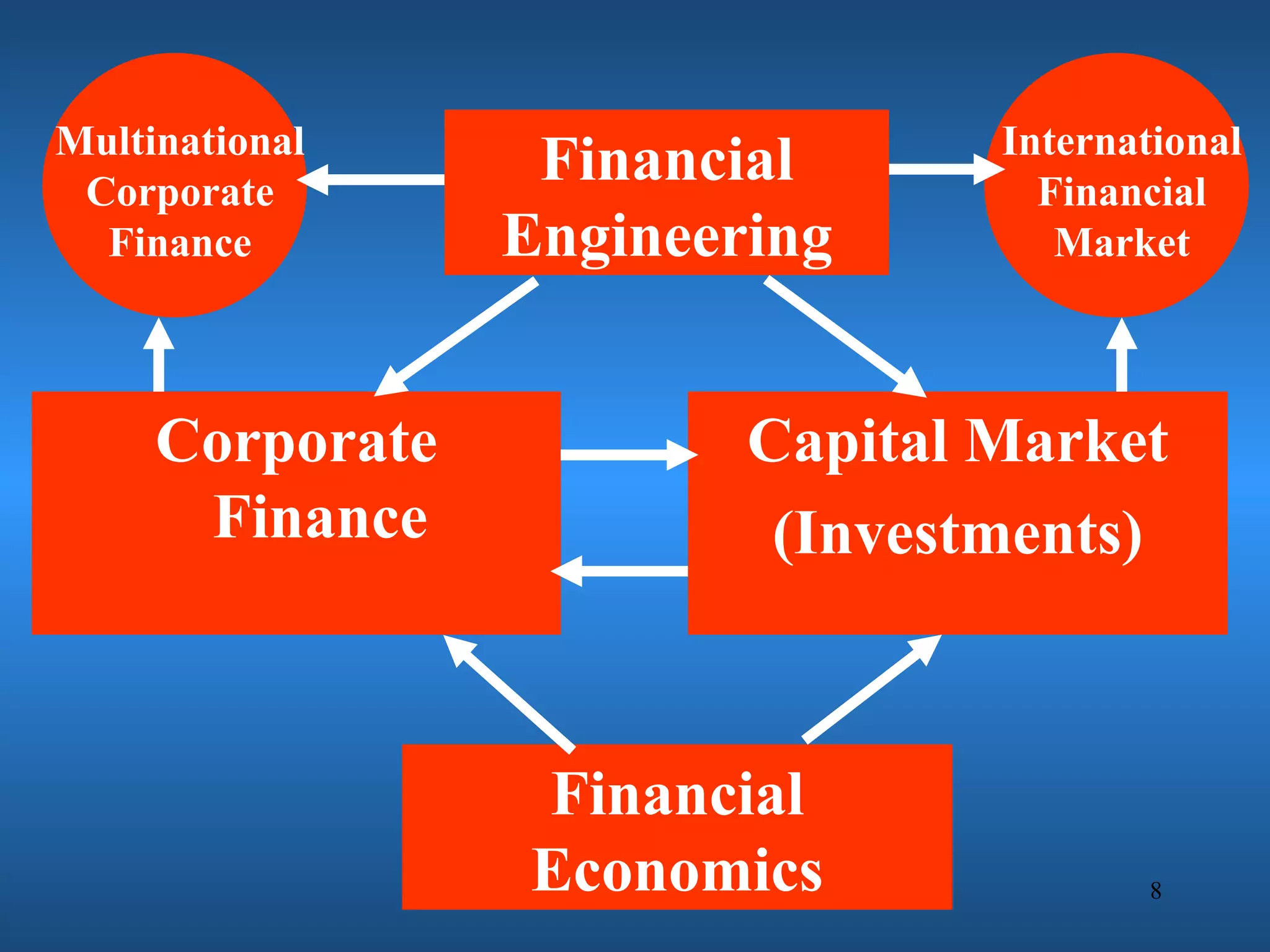
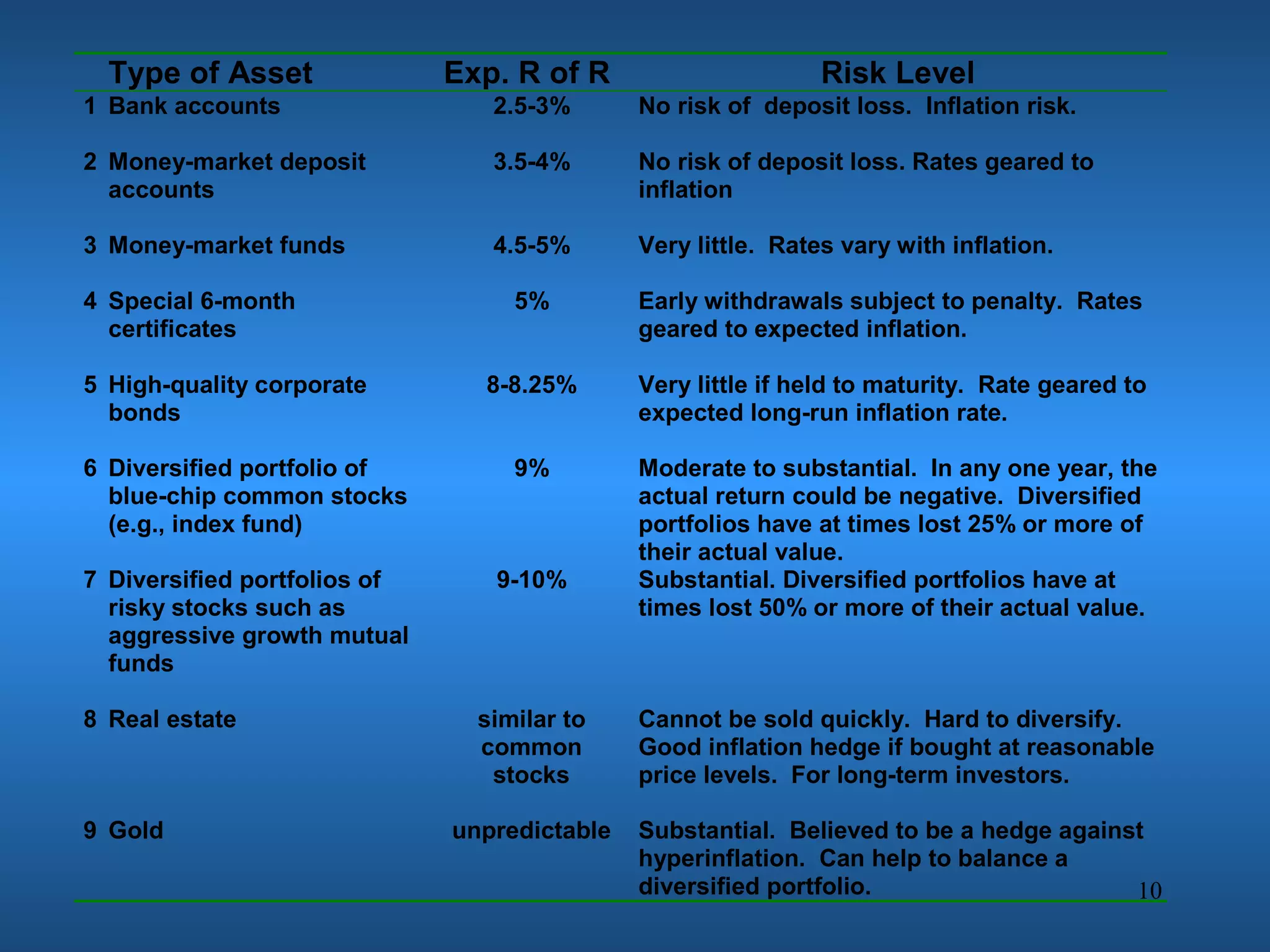
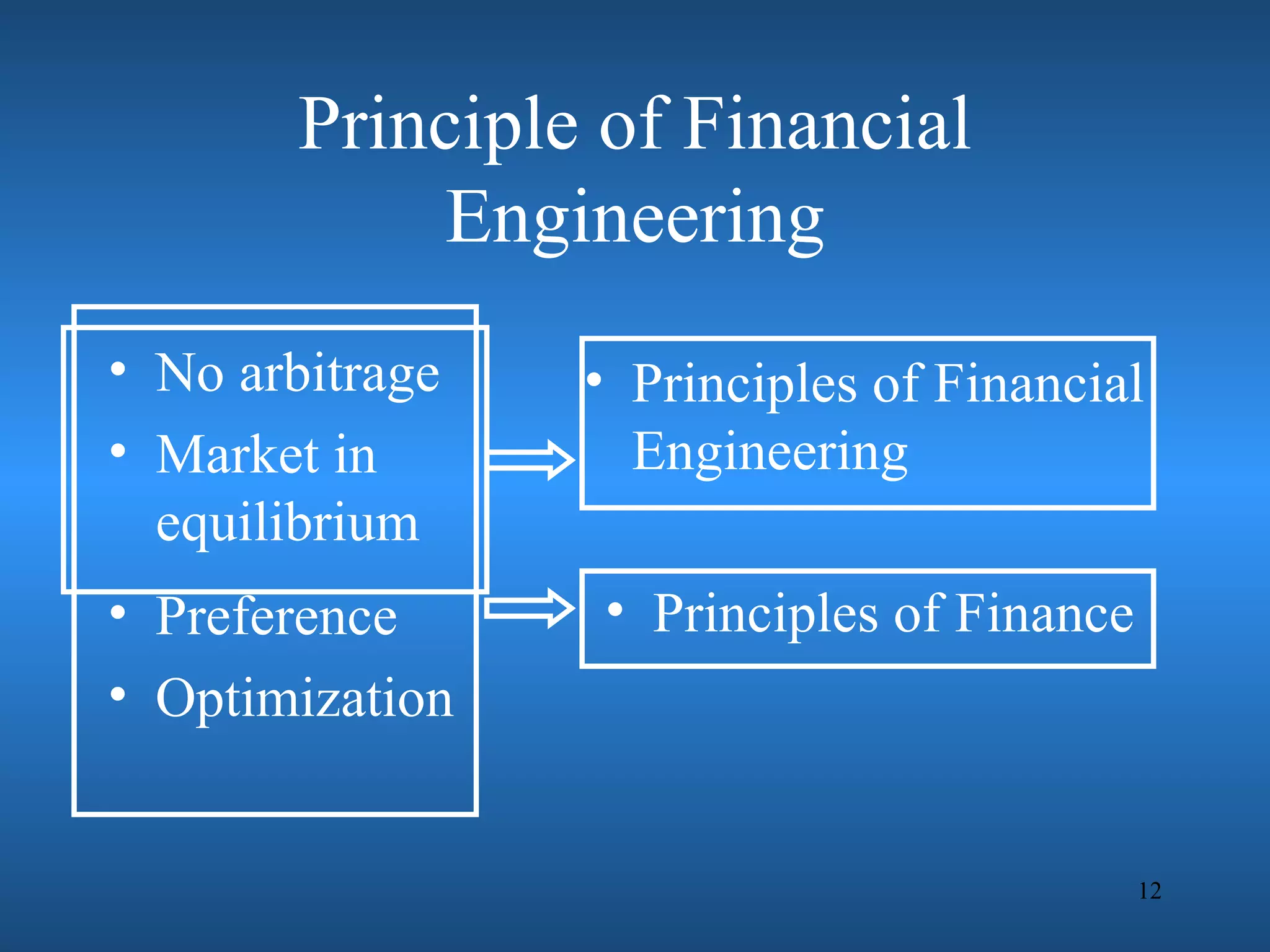
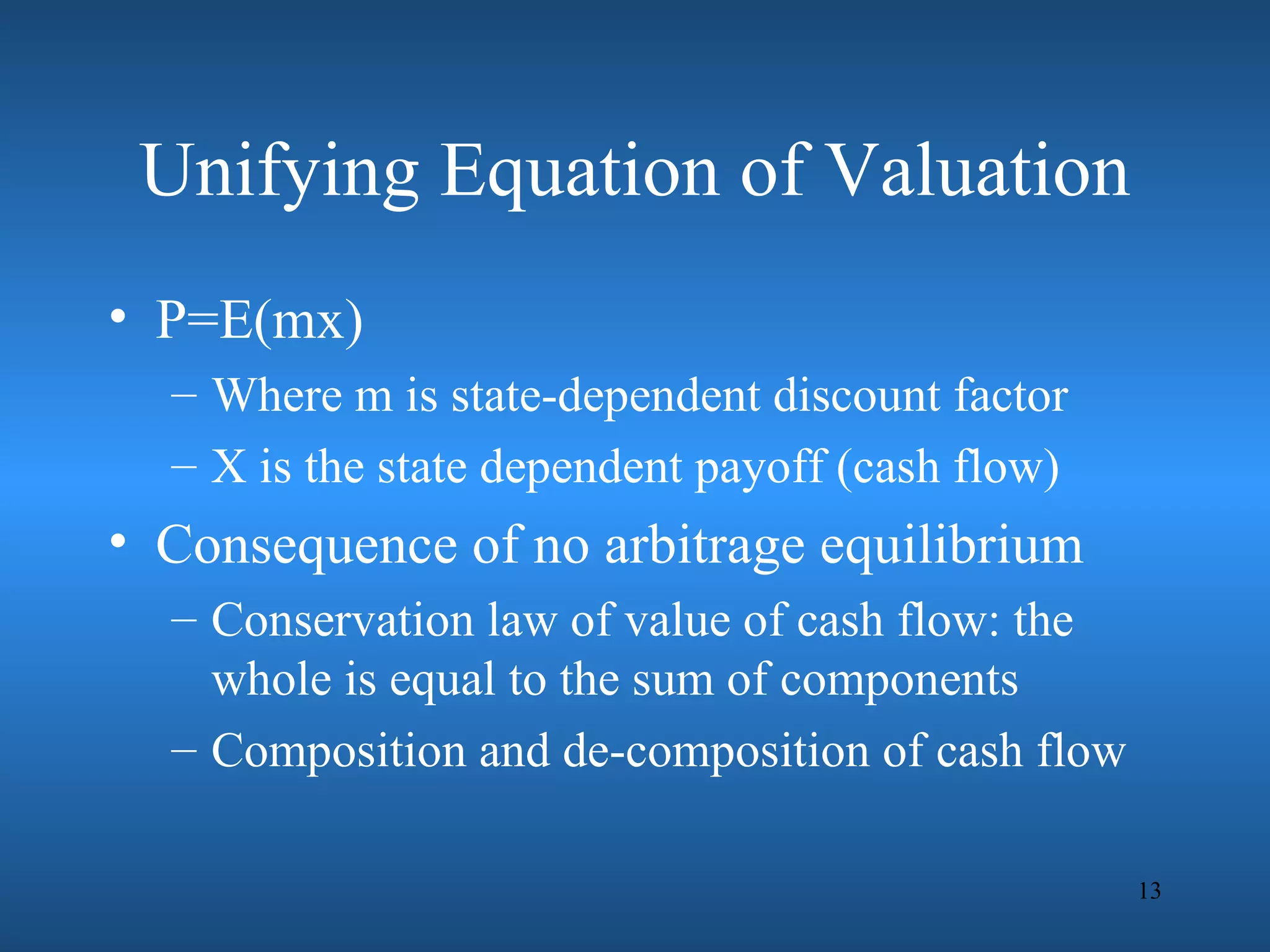
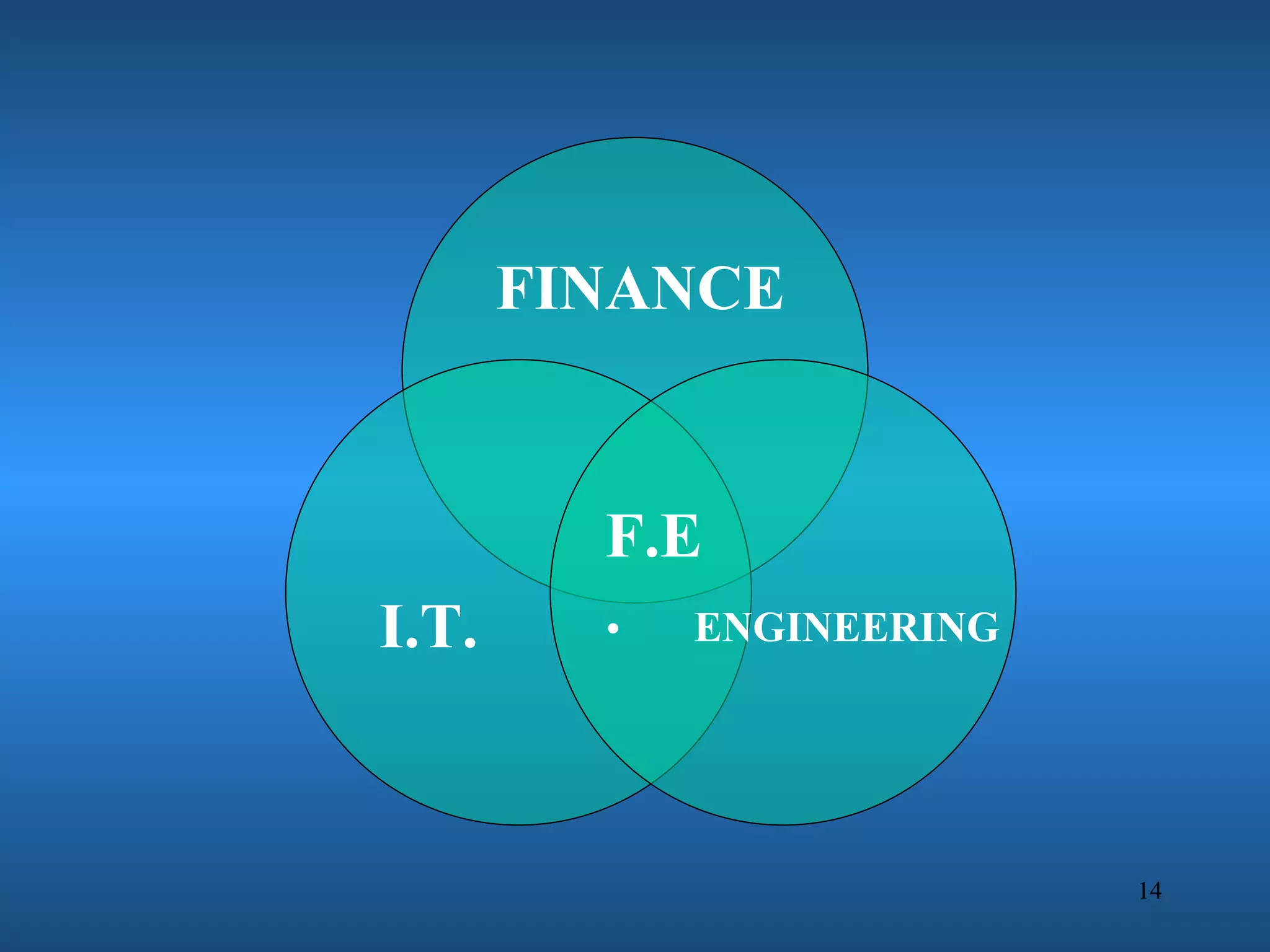
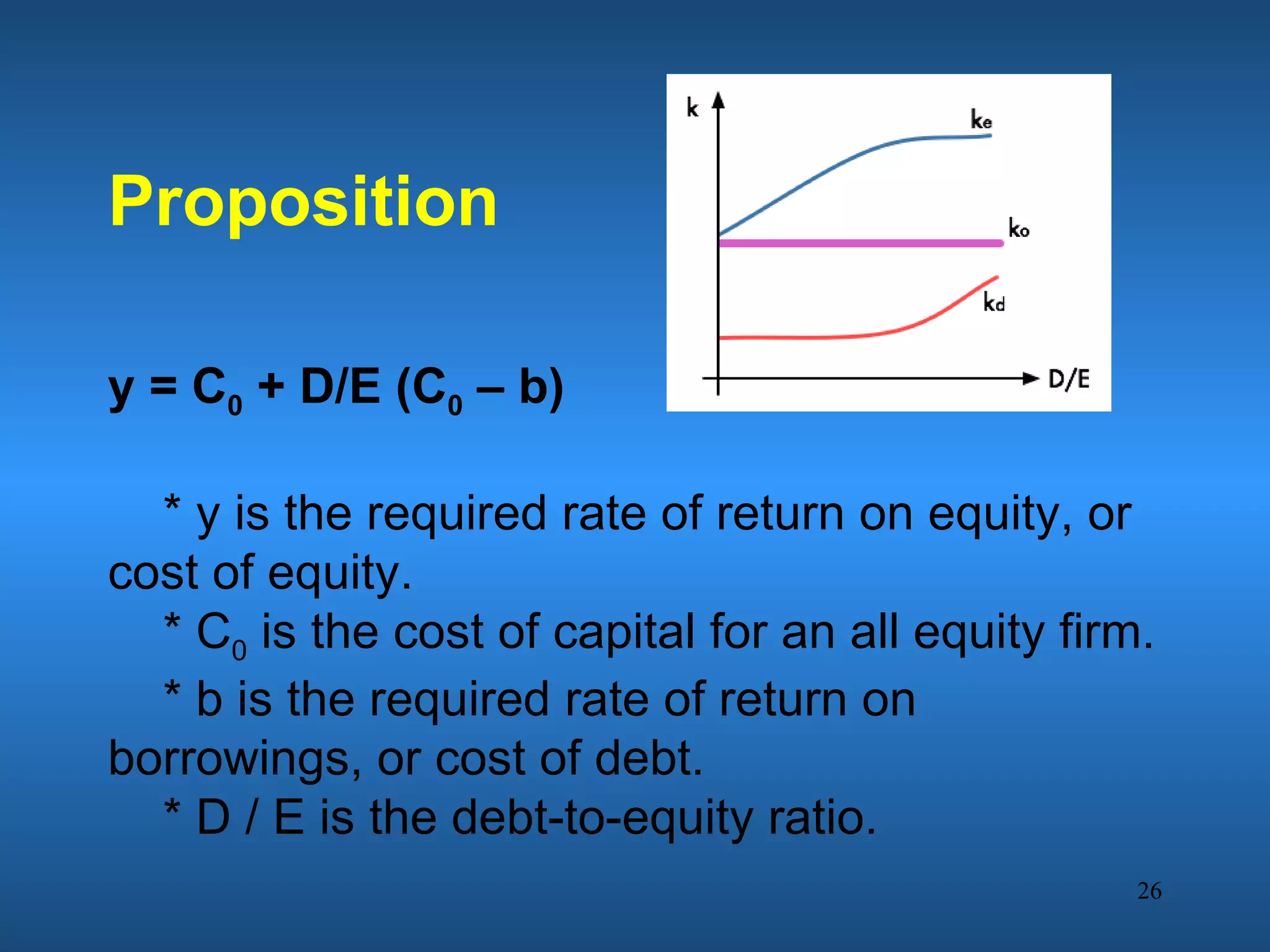
Financial engineering involves designing innovative financial instruments and processes to solve problems in finance. It applies theoretical finance and modeling to make pricing, hedging, and portfolio management decisions. Financial engineers bundle and unbundle securities to maximize profits using various assets. They are prepared for careers in areas like money and banking, corporate finance, investments, and financial markets.