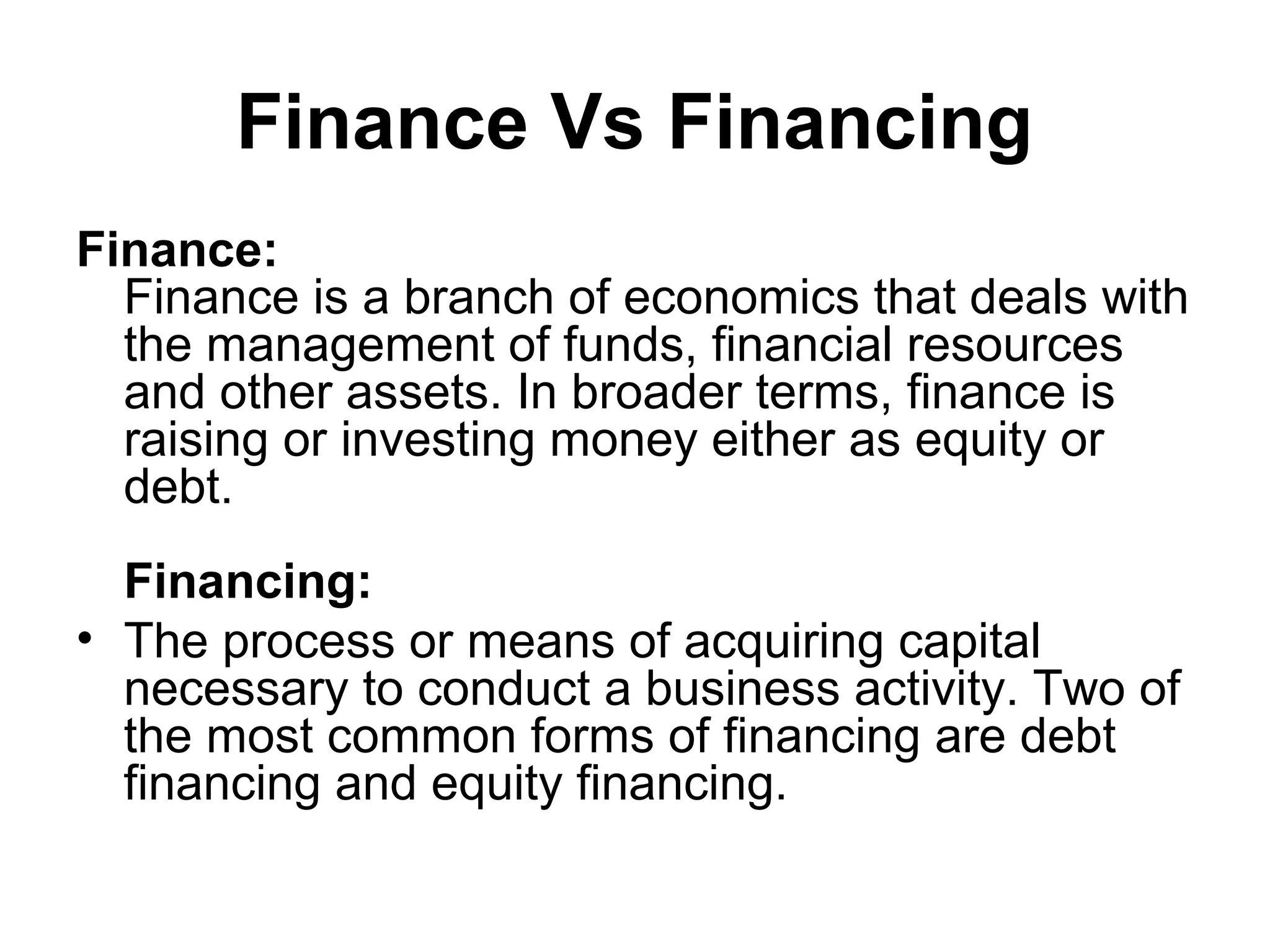
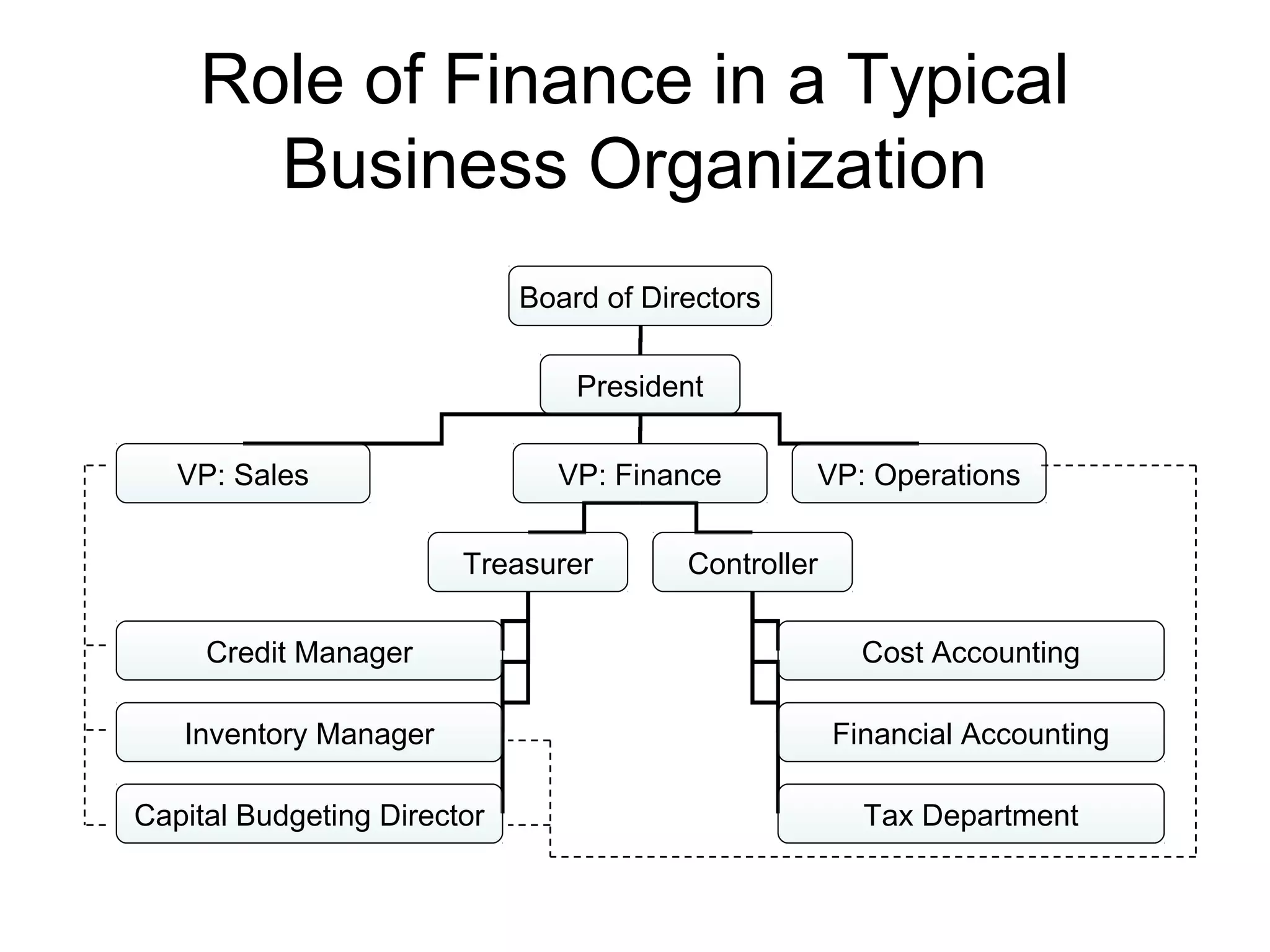
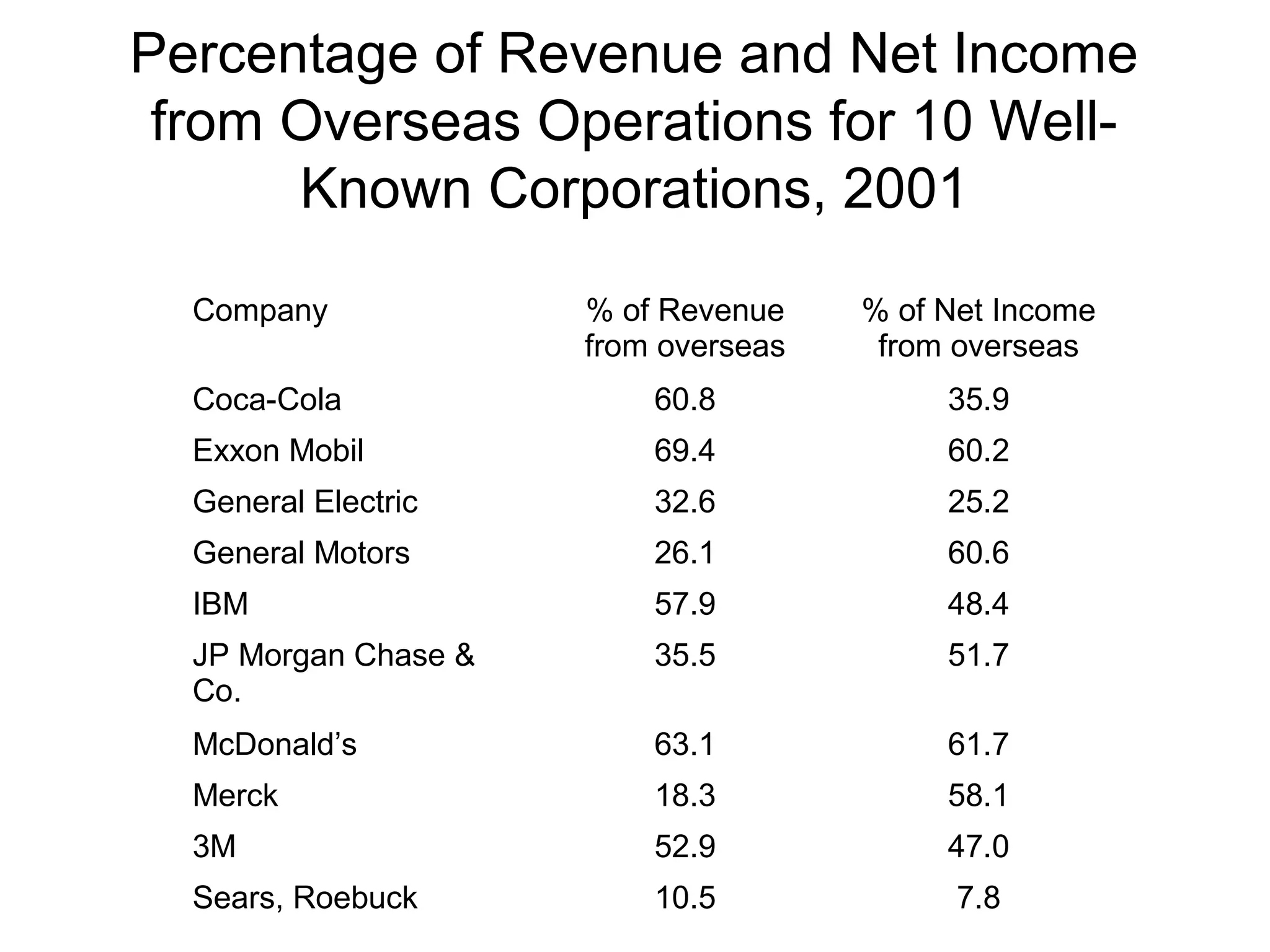
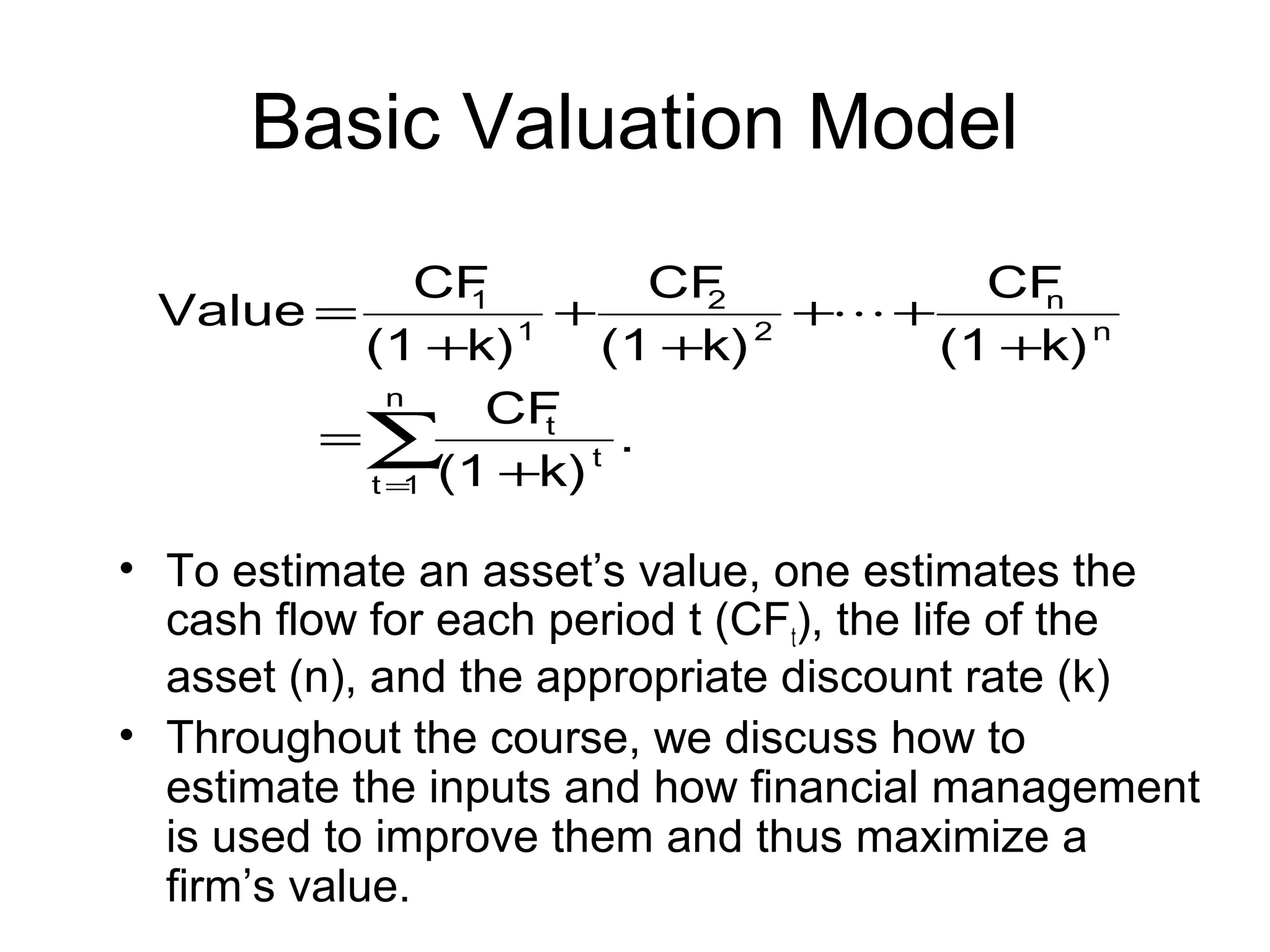
This document provides an overview of financial management. It discusses key topics such as the role of financial management in businesses, the scope and elements of financial management including investment, financial, and dividend decisions. It also covers related topics such as finance vs financing, careers in finance, financial institutions and capital markets, and financial management issues in the new millennium.