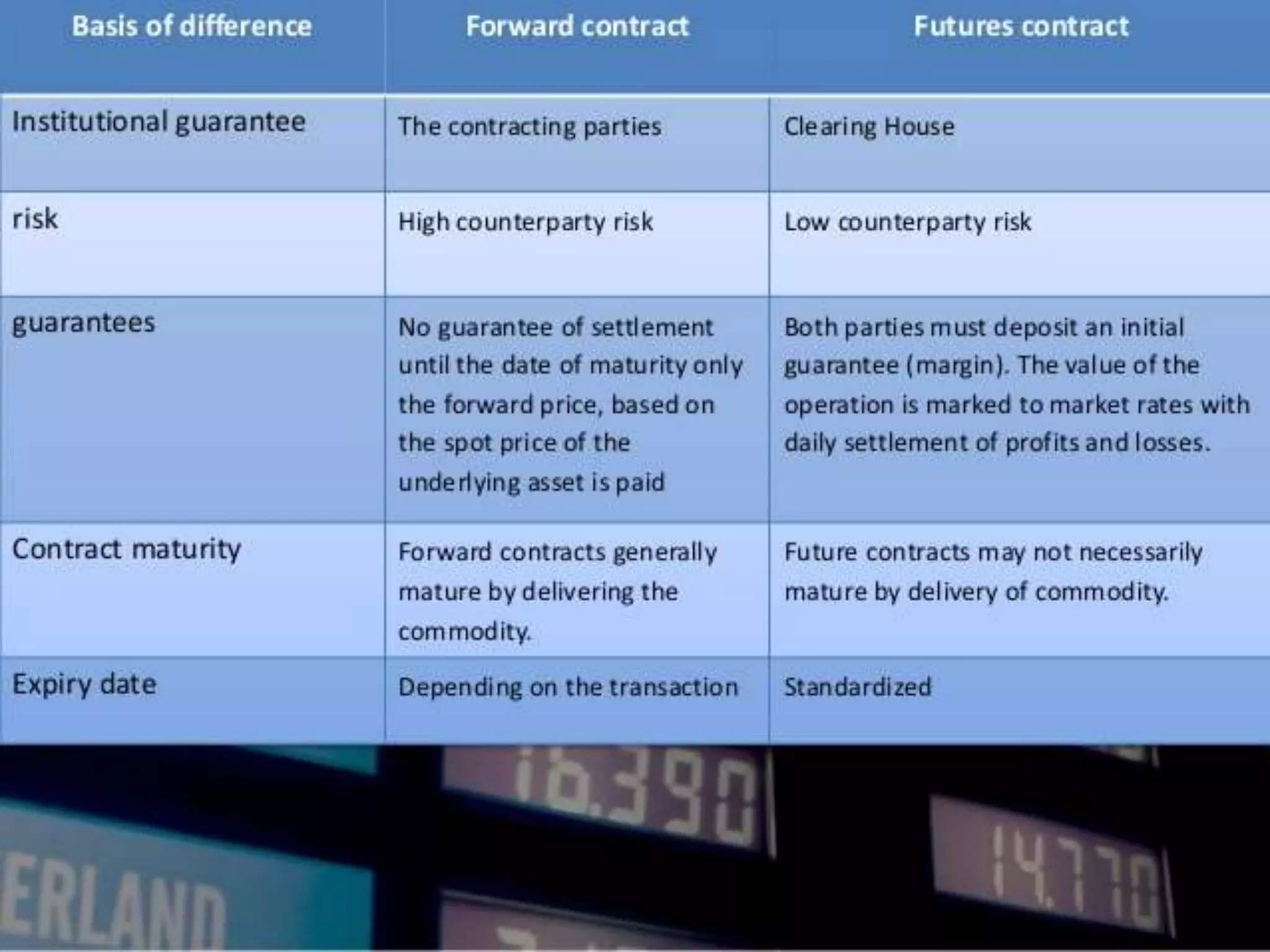
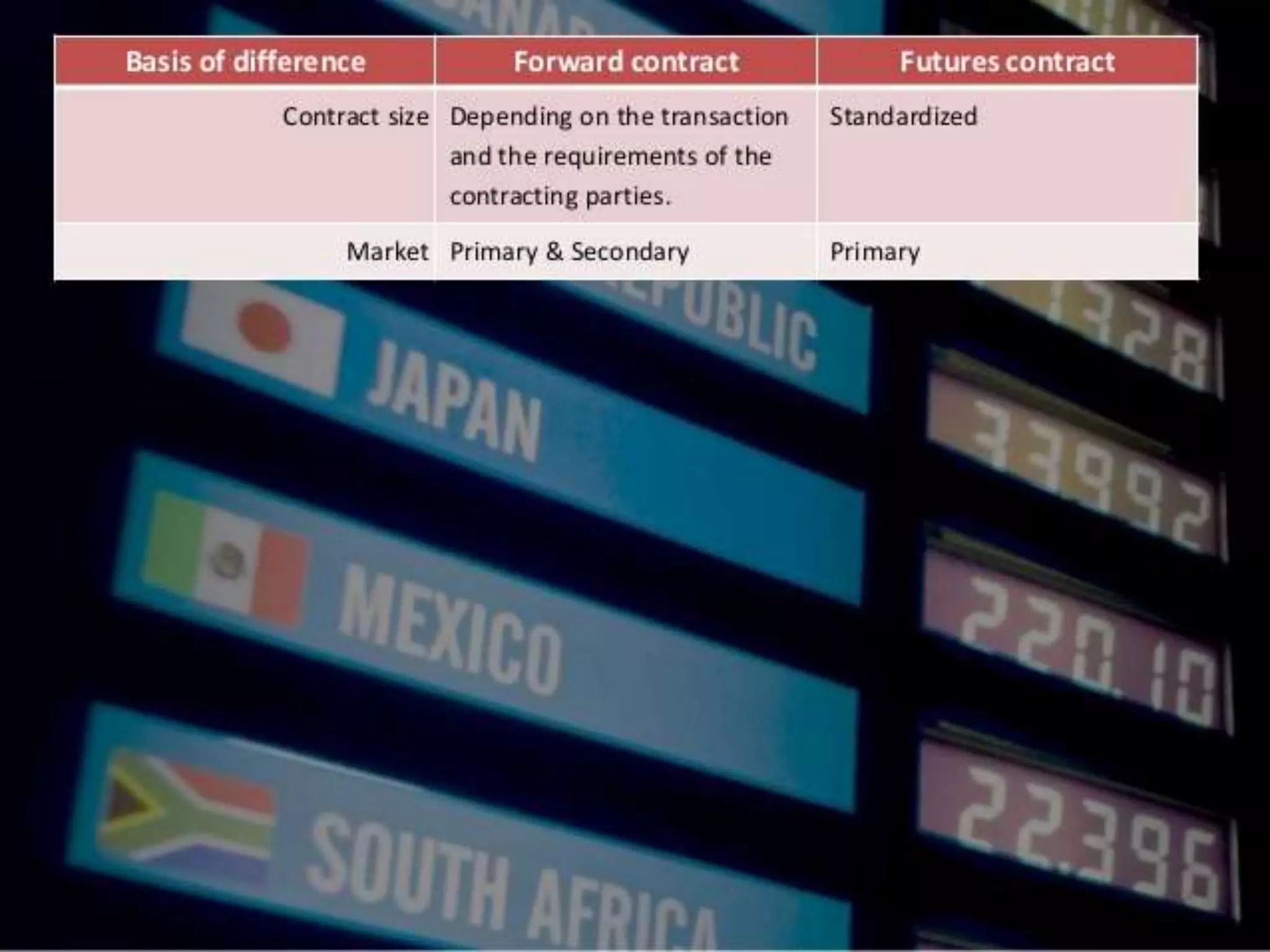
The document explains forwards and futures contracts, highlighting their differences and uses. A forwards contract is a customized, over-the-counter agreement for future delivery at a predetermined price, while a futures contract is a standardized, exchange-traded agreement with less counterparty risk. Features of futures include daily marking-to-market and various settlement methods, such as physical delivery, offsetting, and cash delivery.