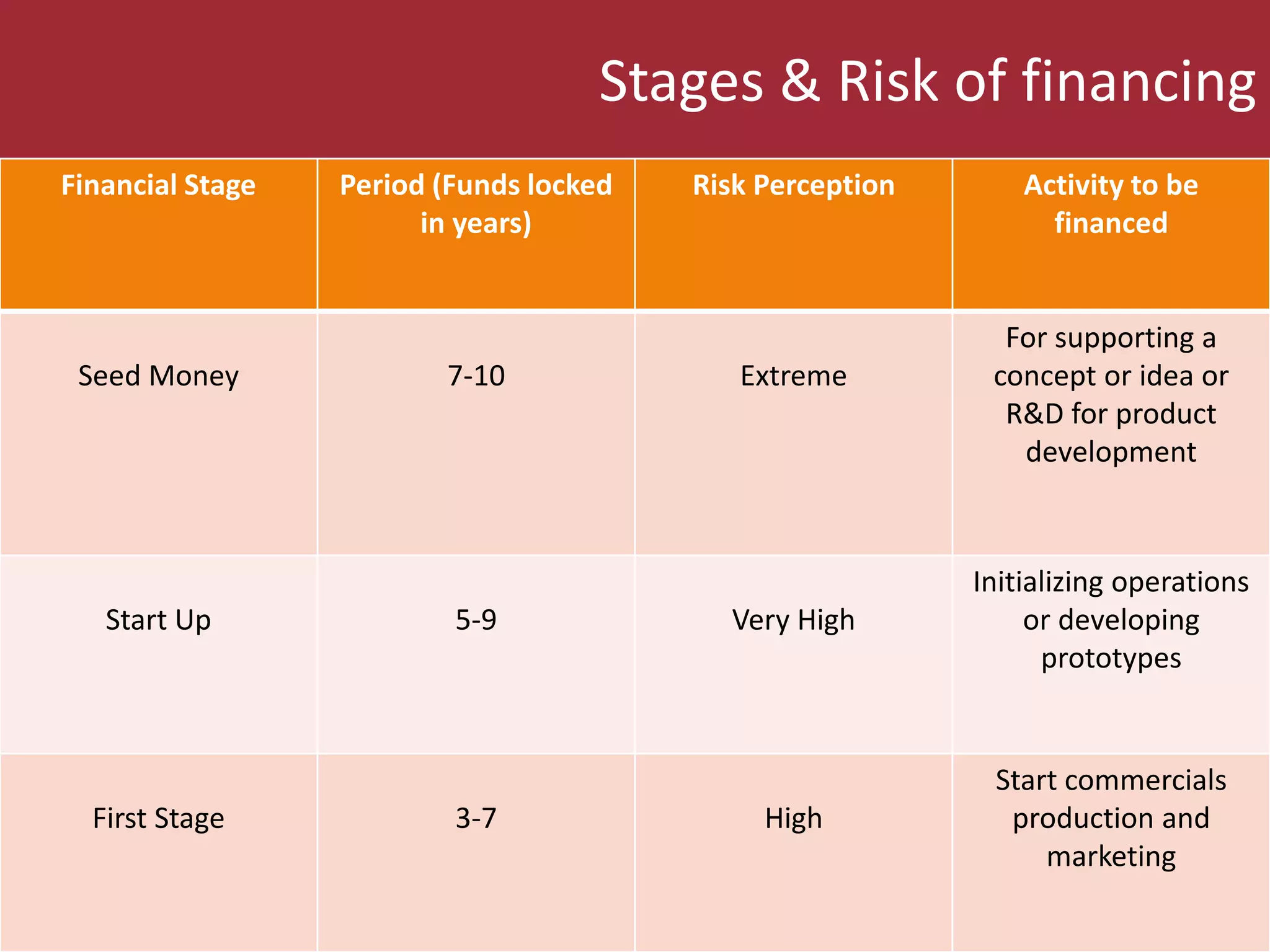
Venture capital refers to funds provided to startup companies and small businesses with growth potential. It involves long-term risk capital to finance high-risk technology projects. Venture capital is regulated in India by SEBI and involves investing in private companies, with at least 80% invested in venture capital firms. It provides benefits like large equity financing and expertise, but founders lose some autonomy and the application process is complex.