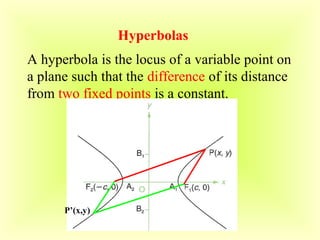
The document discusses the properties and definitions of conic sections: circles, ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas. It describes how each shape is formed based on the intersection of a plane with cones, providing equations and parameters related to their geometric properties. Additionally, it includes the general equations for tangents to conics and various forms of their standard equations.