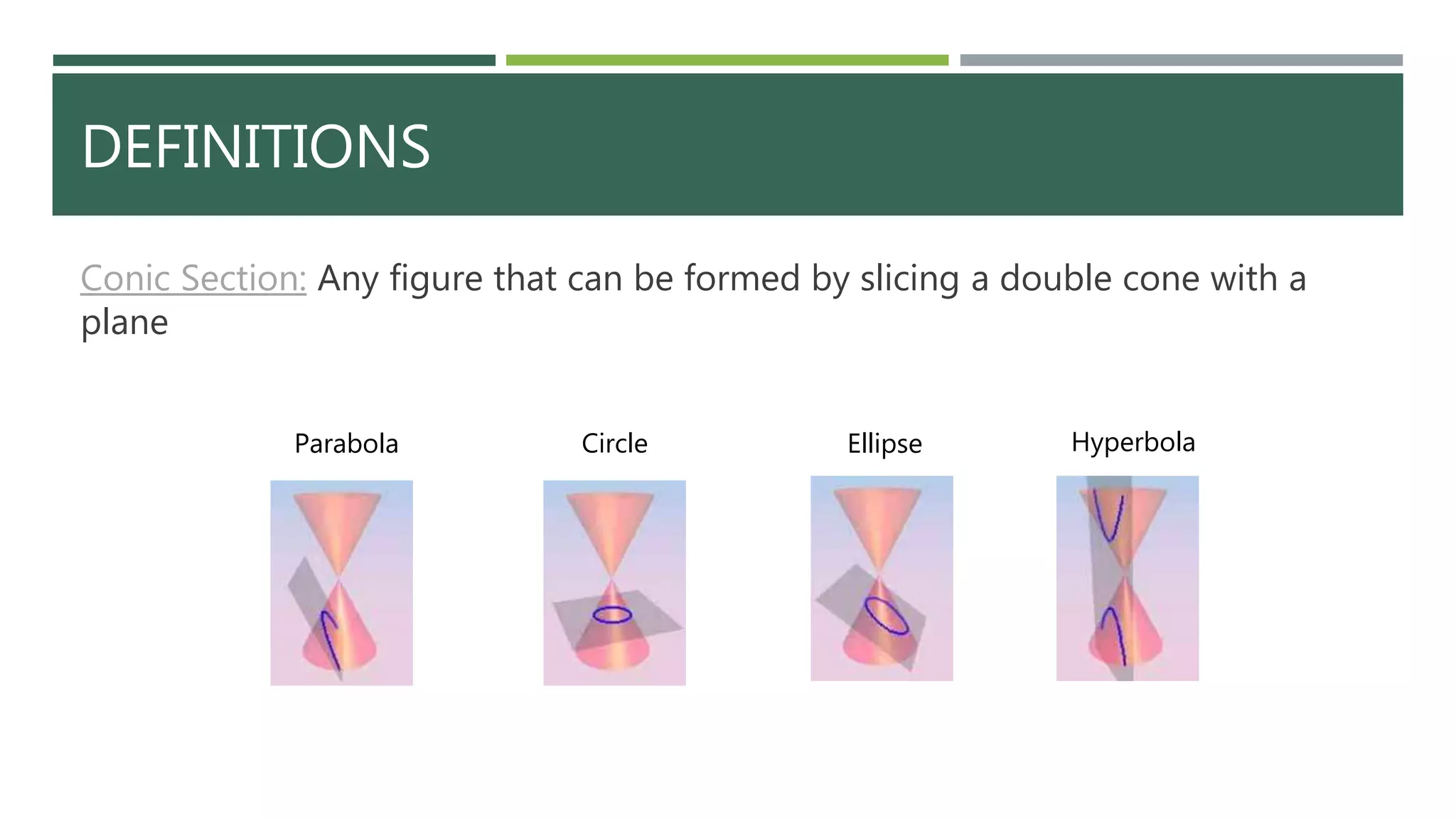
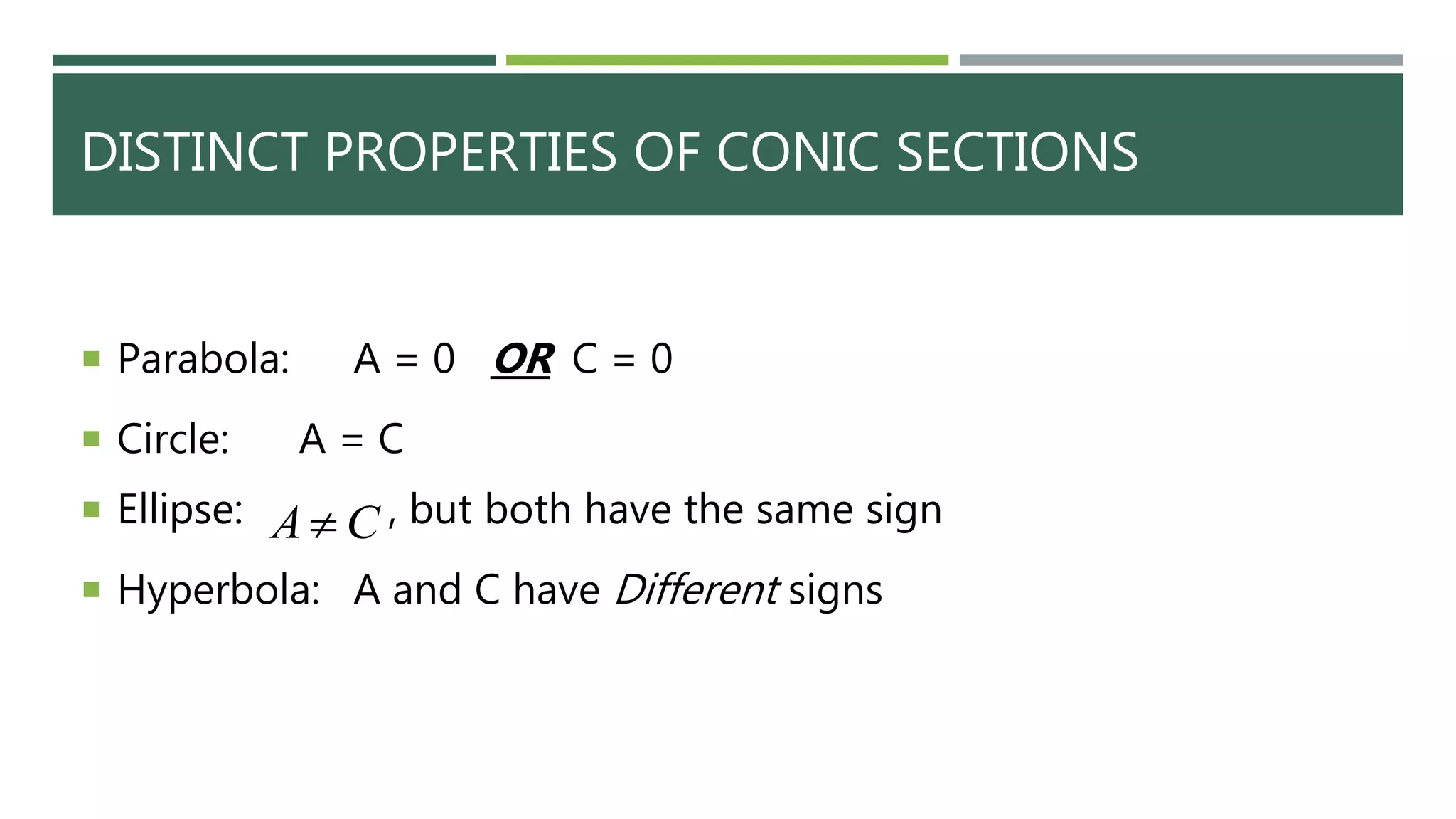
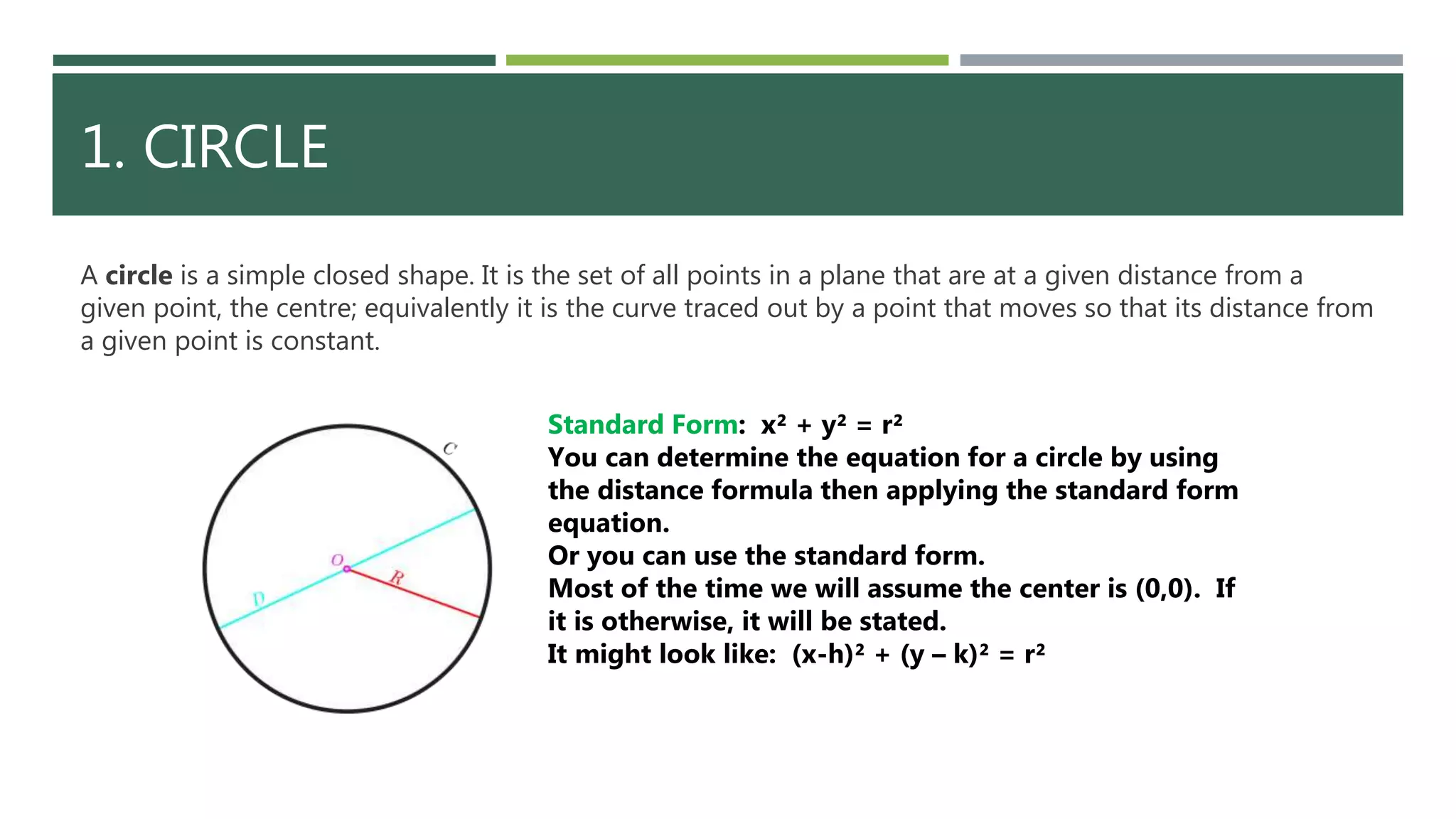
The document explains conic sections, which are figures formed by slicing a double cone with a plane, including definitions and properties of circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas. Each conic section has a specific standard equation and distinct characteristics, such as the constant distance in ellipses and hyperbolas. The document also provides equations for deriving these shapes based on given parameters.