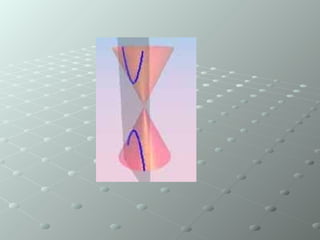
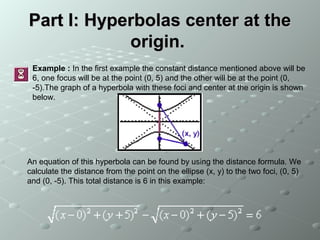
This document defines a hyperbola as the set of all points where the difference between the distances to two fixed points, called foci, is a constant. A hyperbola can be formed by slicing a cone with a plane parallel to the cone's vertical axis. An example hyperbola is shown with foci at (0,5) and (0, -5) and the points on the hyperbola satisfying the equation (x-0)^2/(4)^2 - (y-5)^2/(3)^2 = 1. Key features identified are the transverse axis connecting the foci, the distance a from the center to the foci, and the asymptotes that the branches approach but never reach