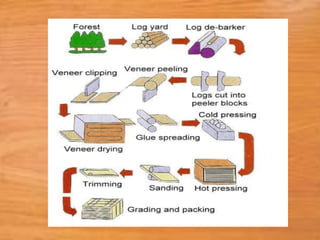
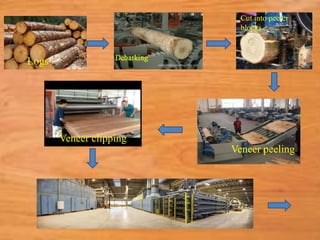
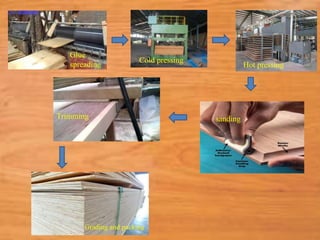
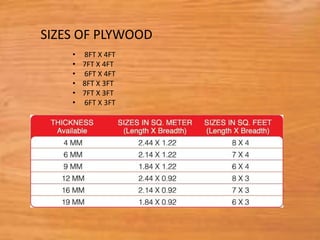
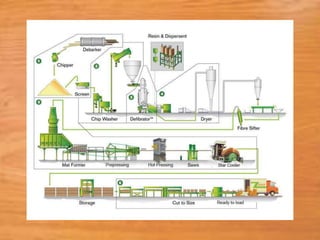
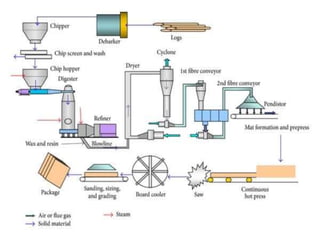
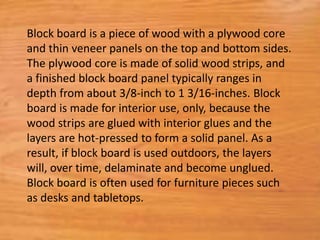
This document provides information about medium density fiberboard (MDF) including its production process, types, and advantages. MDF is made from compressed wood fibers, wax and resin. It is produced by refining wood materials into fibers, adding resin, forming mats, and pressing them at high temperature and pressure. The document describes the MDF production steps and lists its applications for interior uses due to its smooth, affordable and strong qualities.

![TOPICS
PLYWOOD
HIGH DENSITY BOARD[HDF]
MEDIUM DENSITY BOARD[MDF]
BLOCK BOARD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingmaterials-200602144153/85/Building-materials-2-320.jpg)