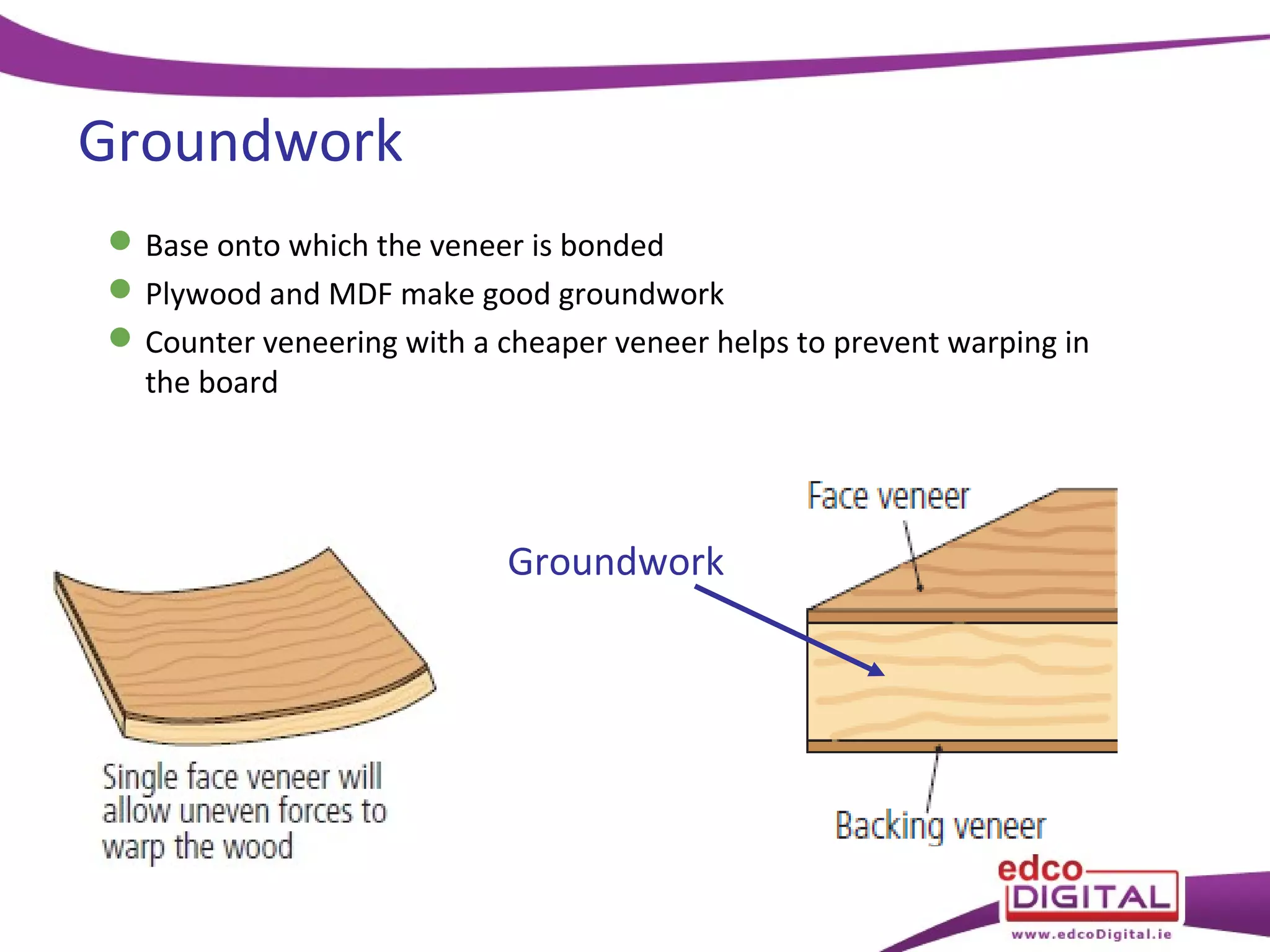
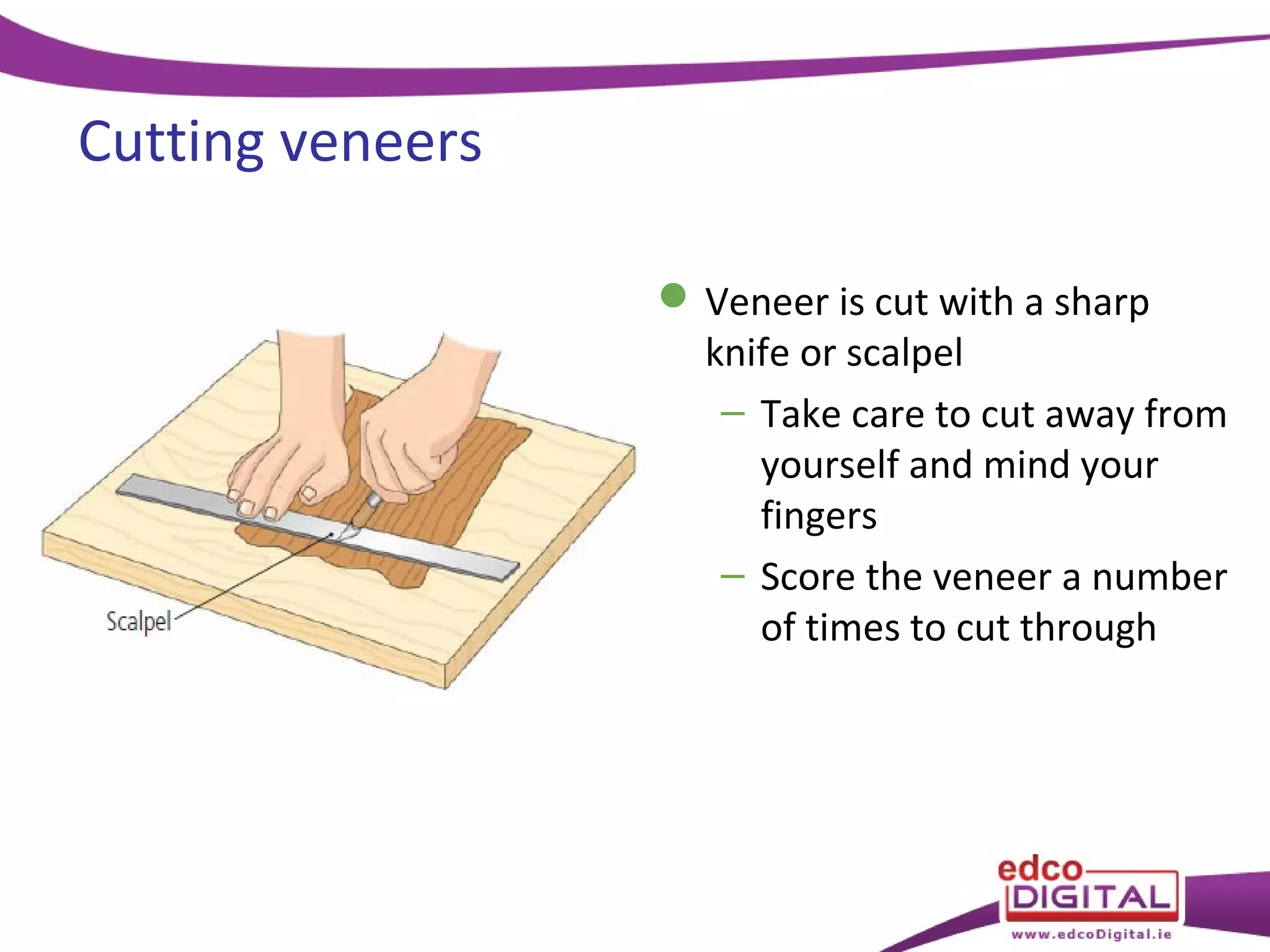
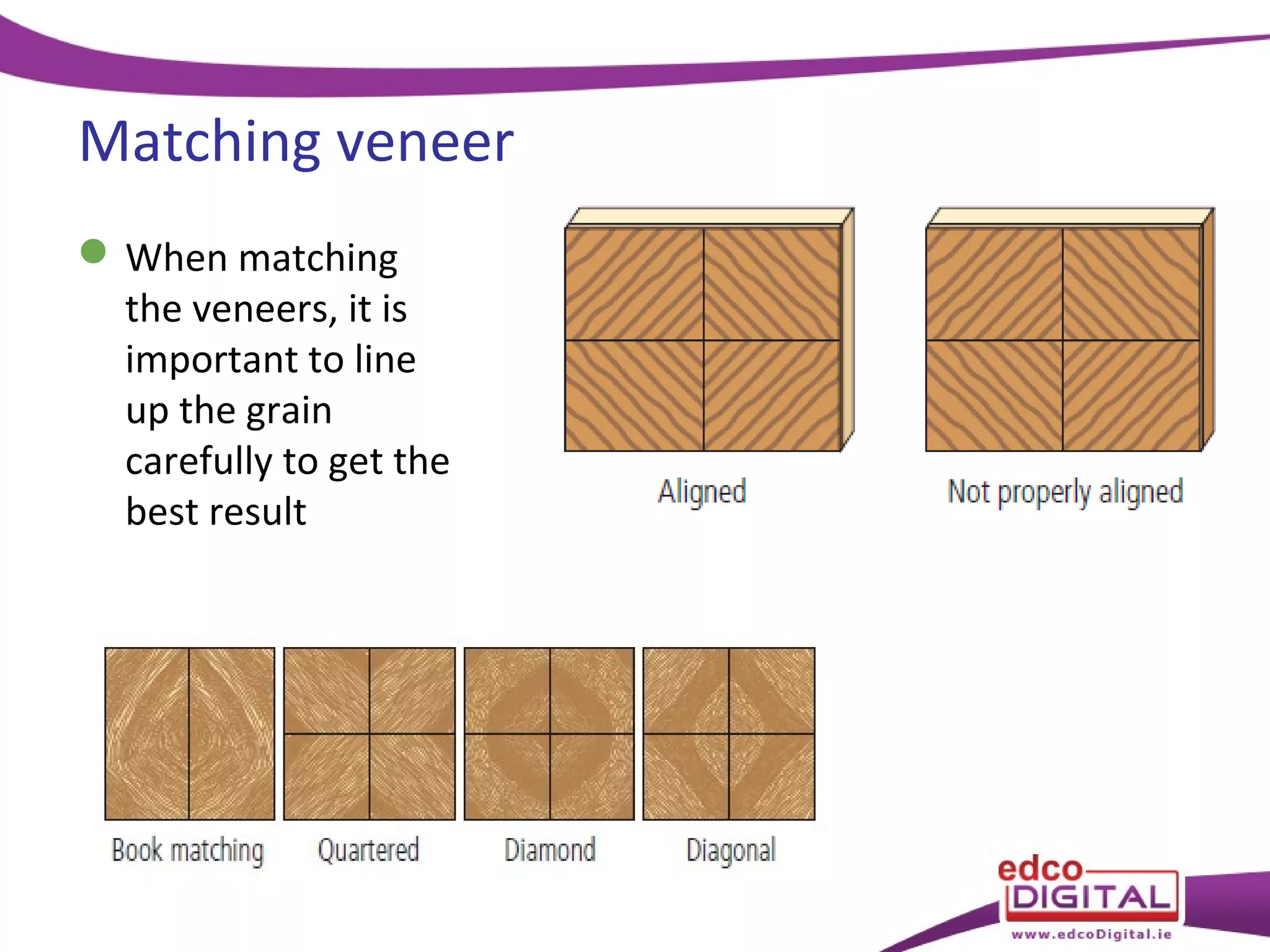
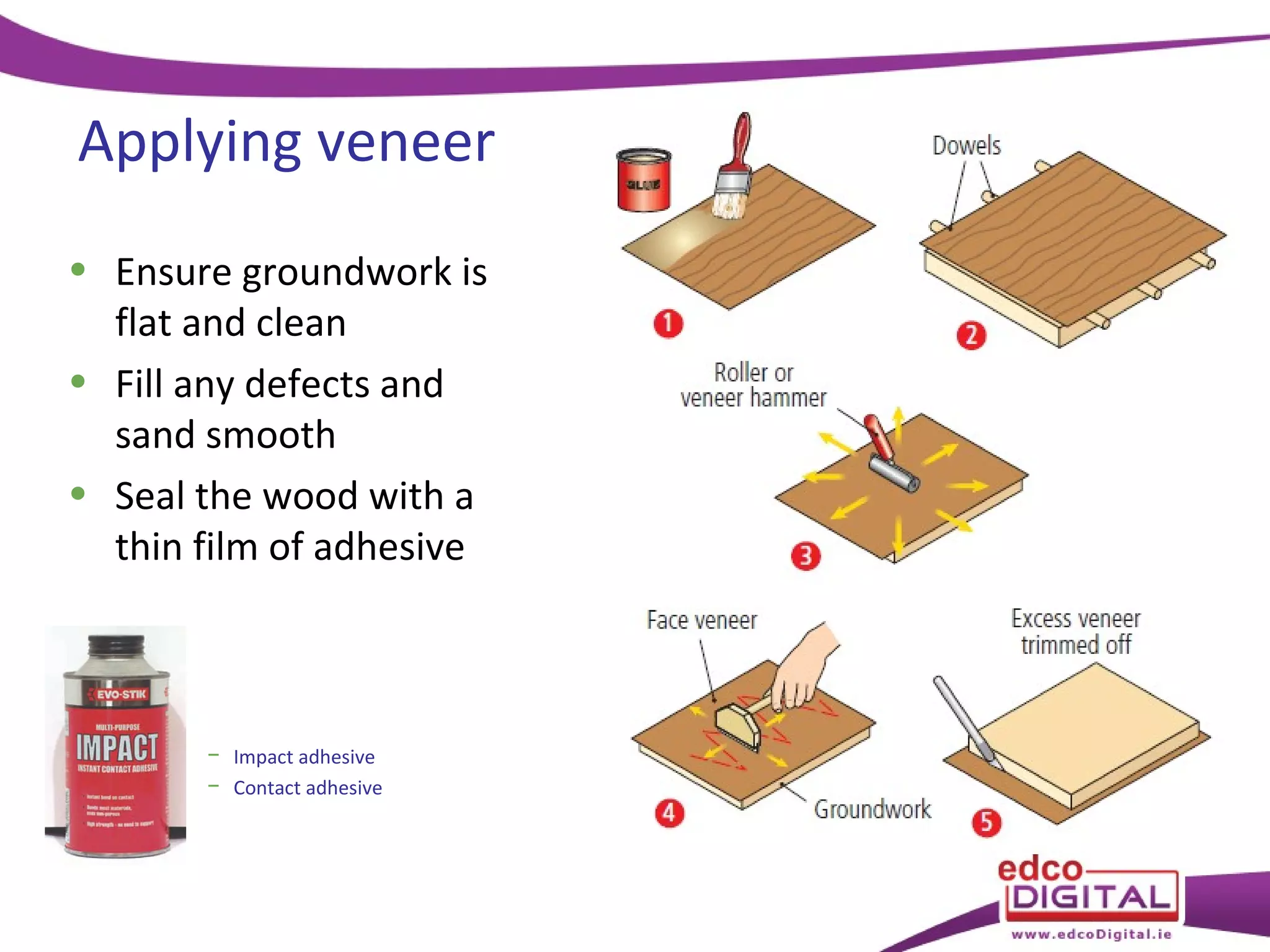
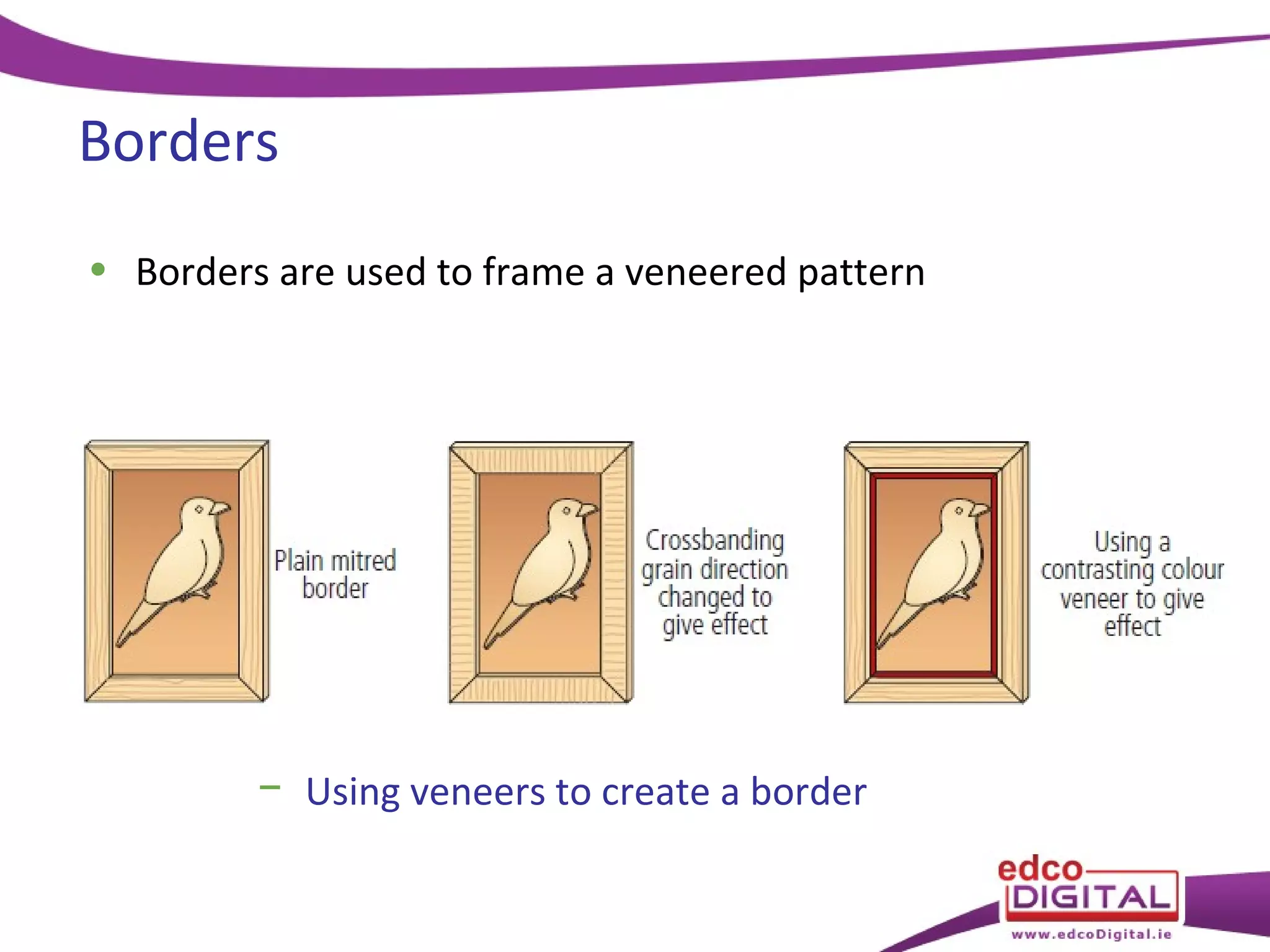
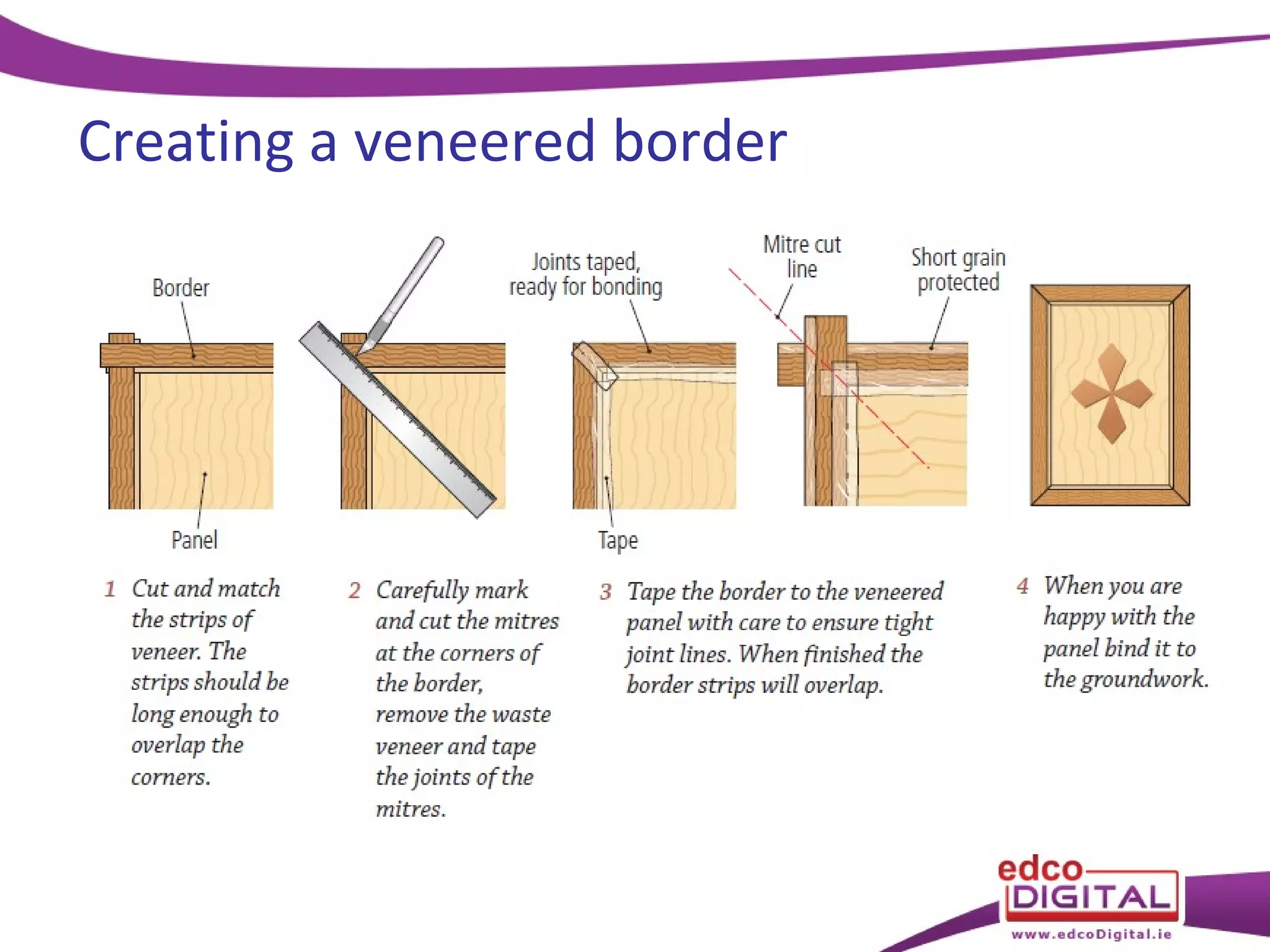
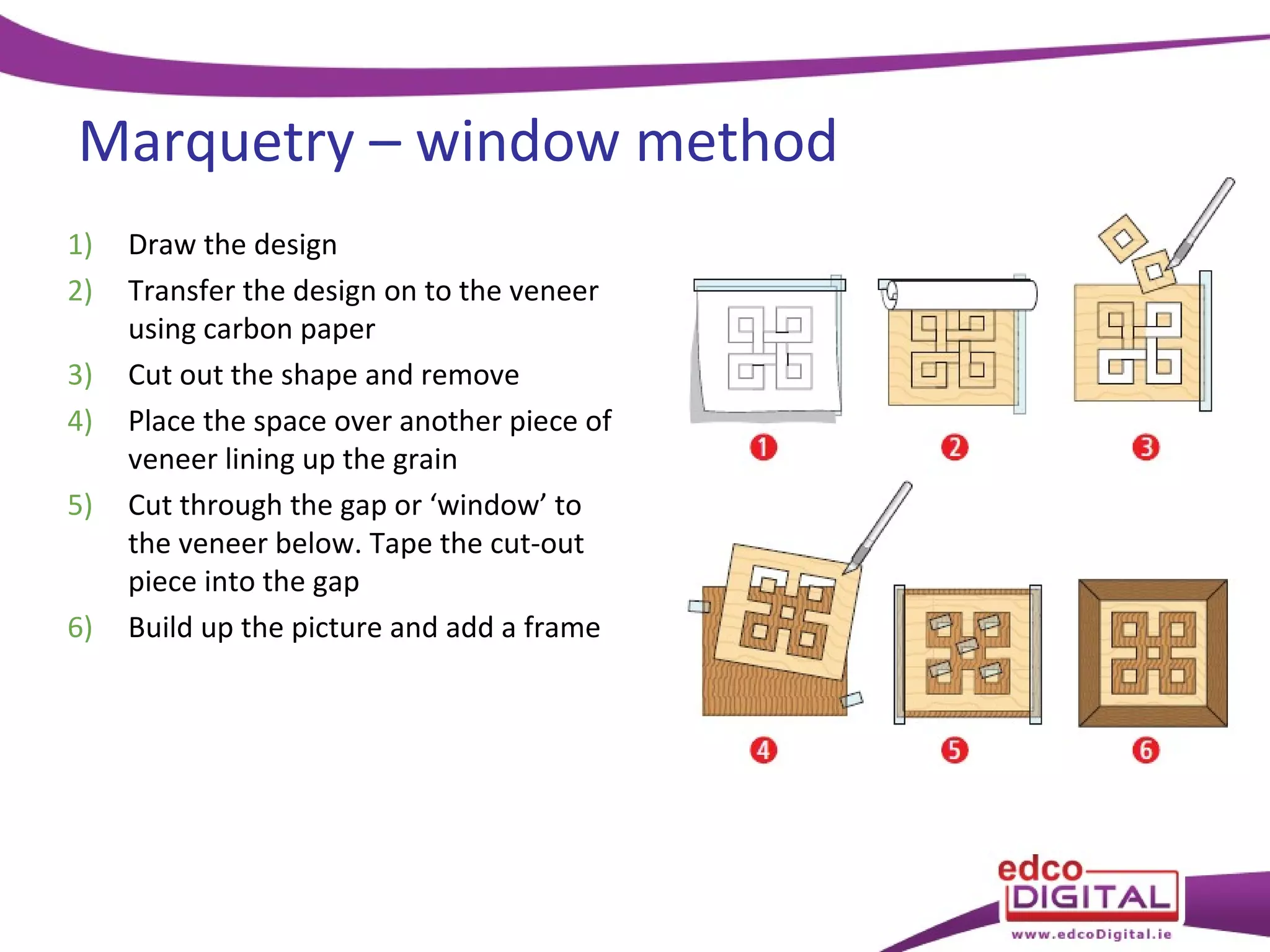
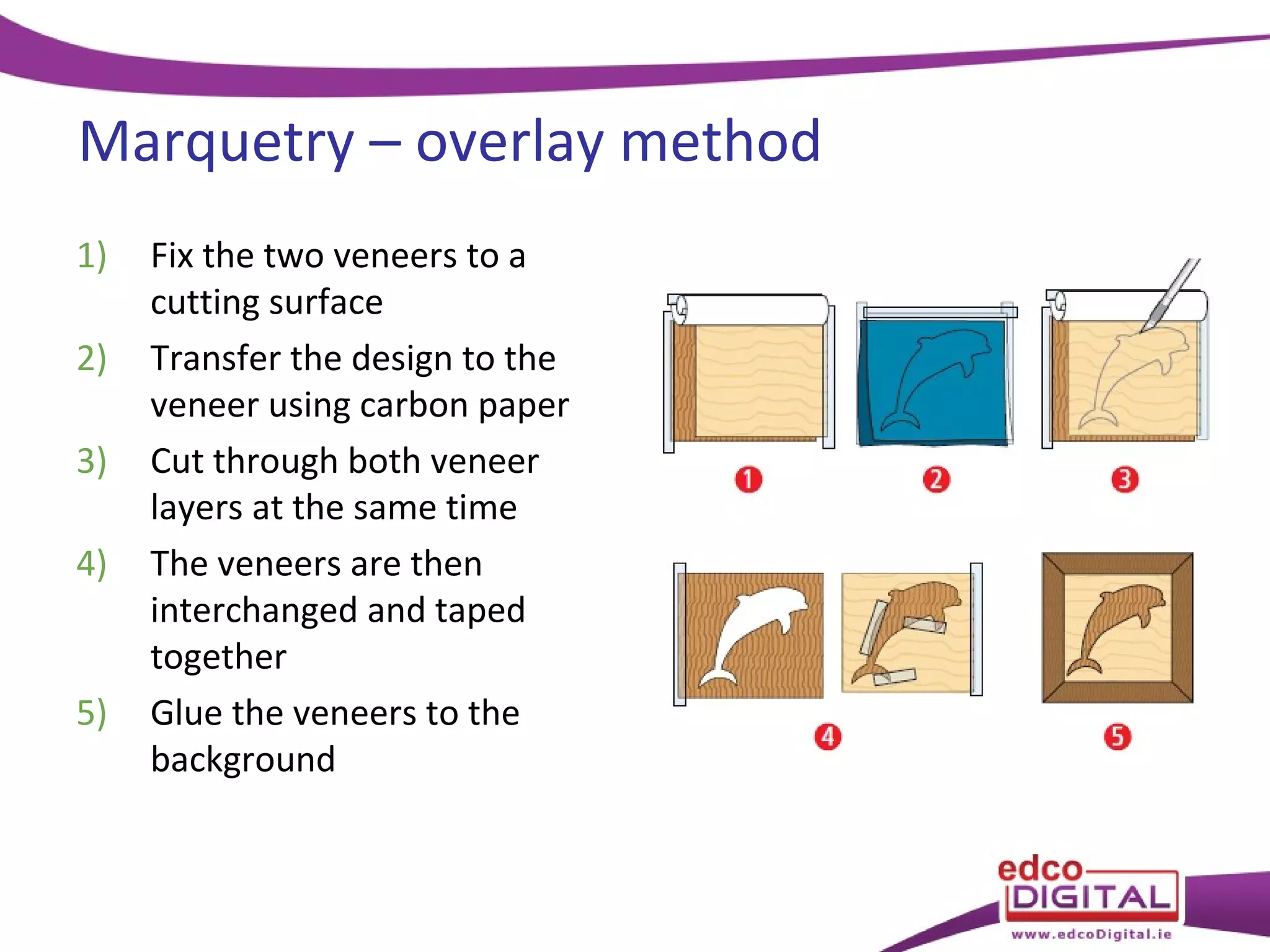
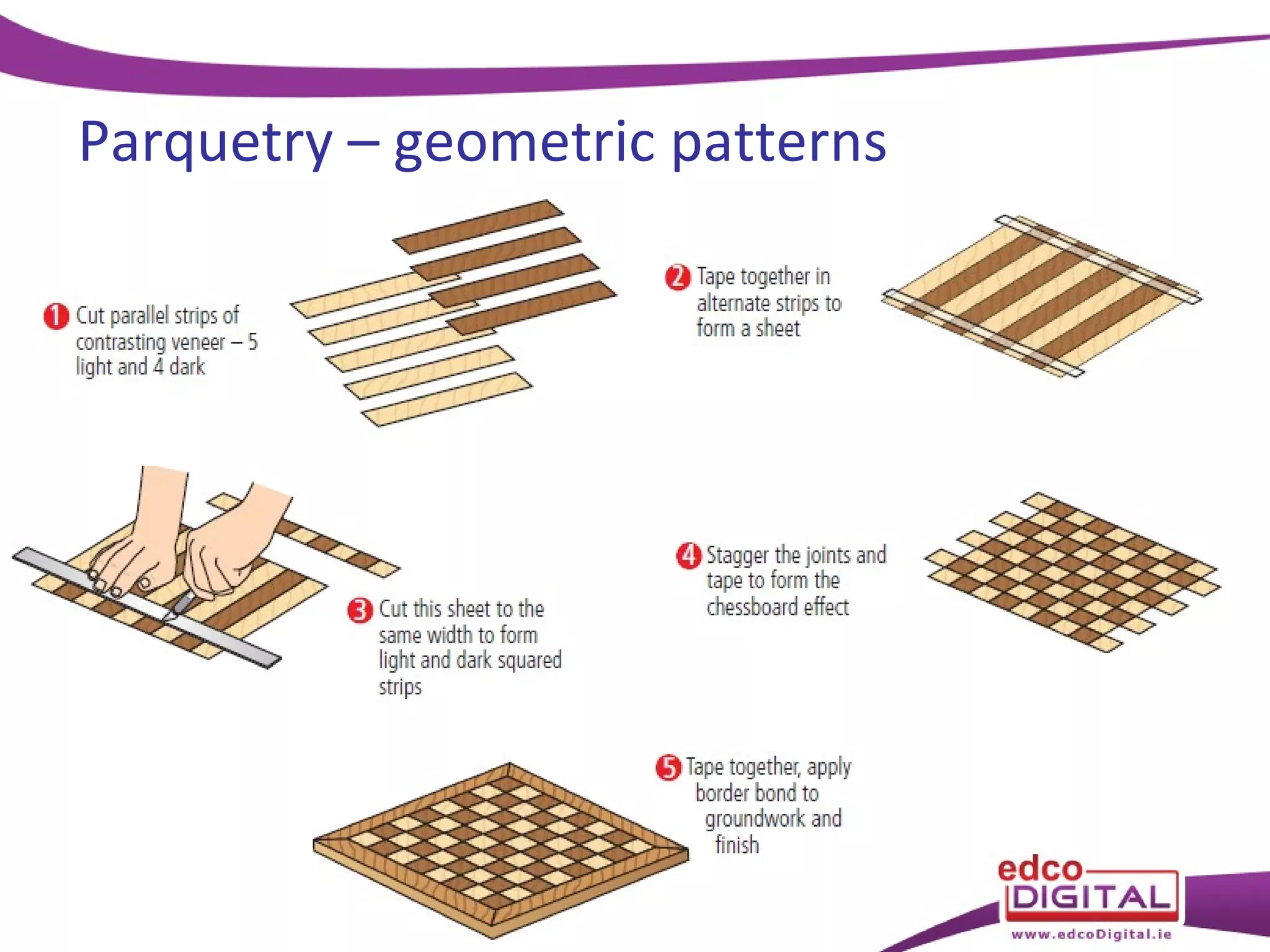
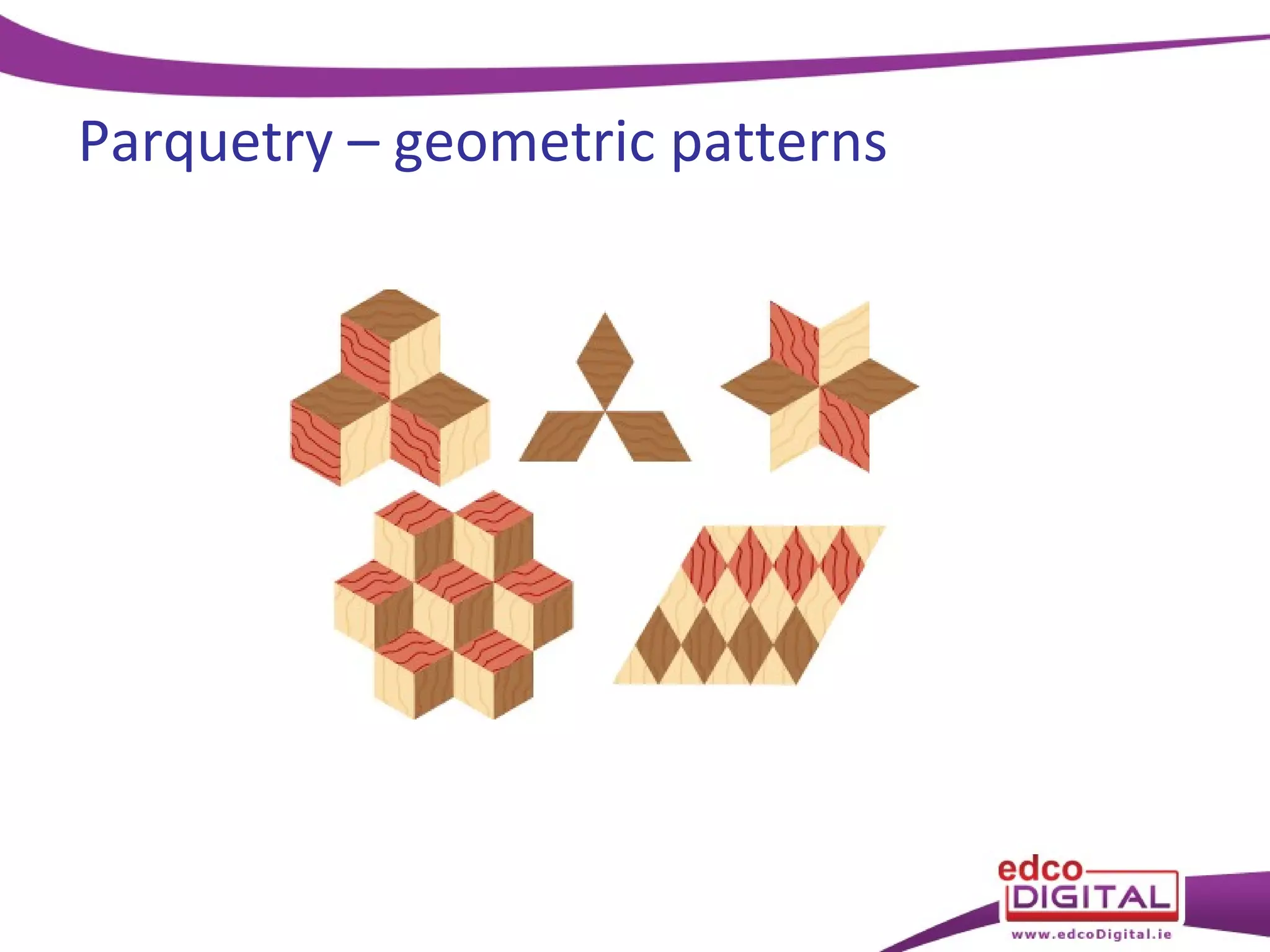
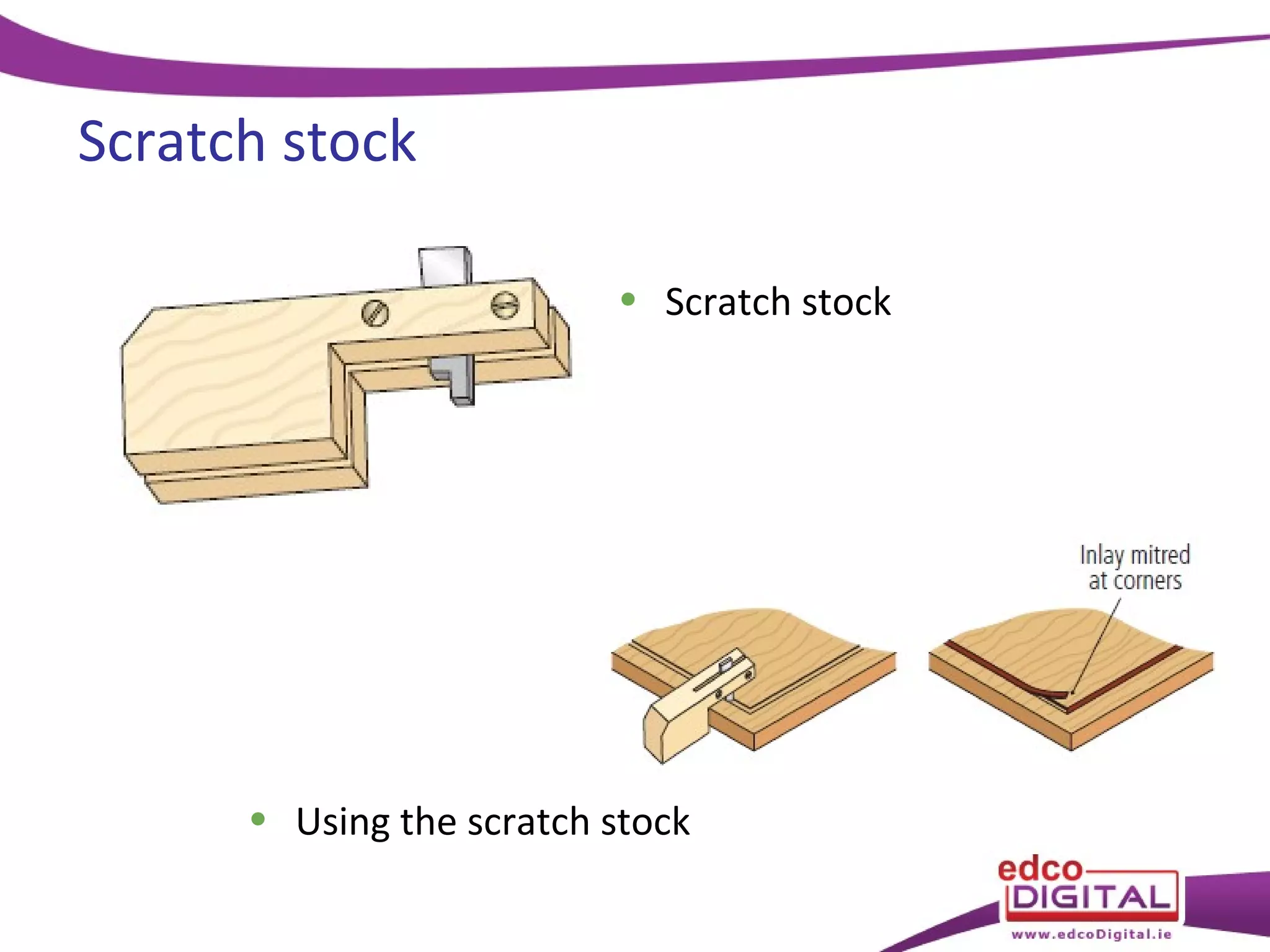
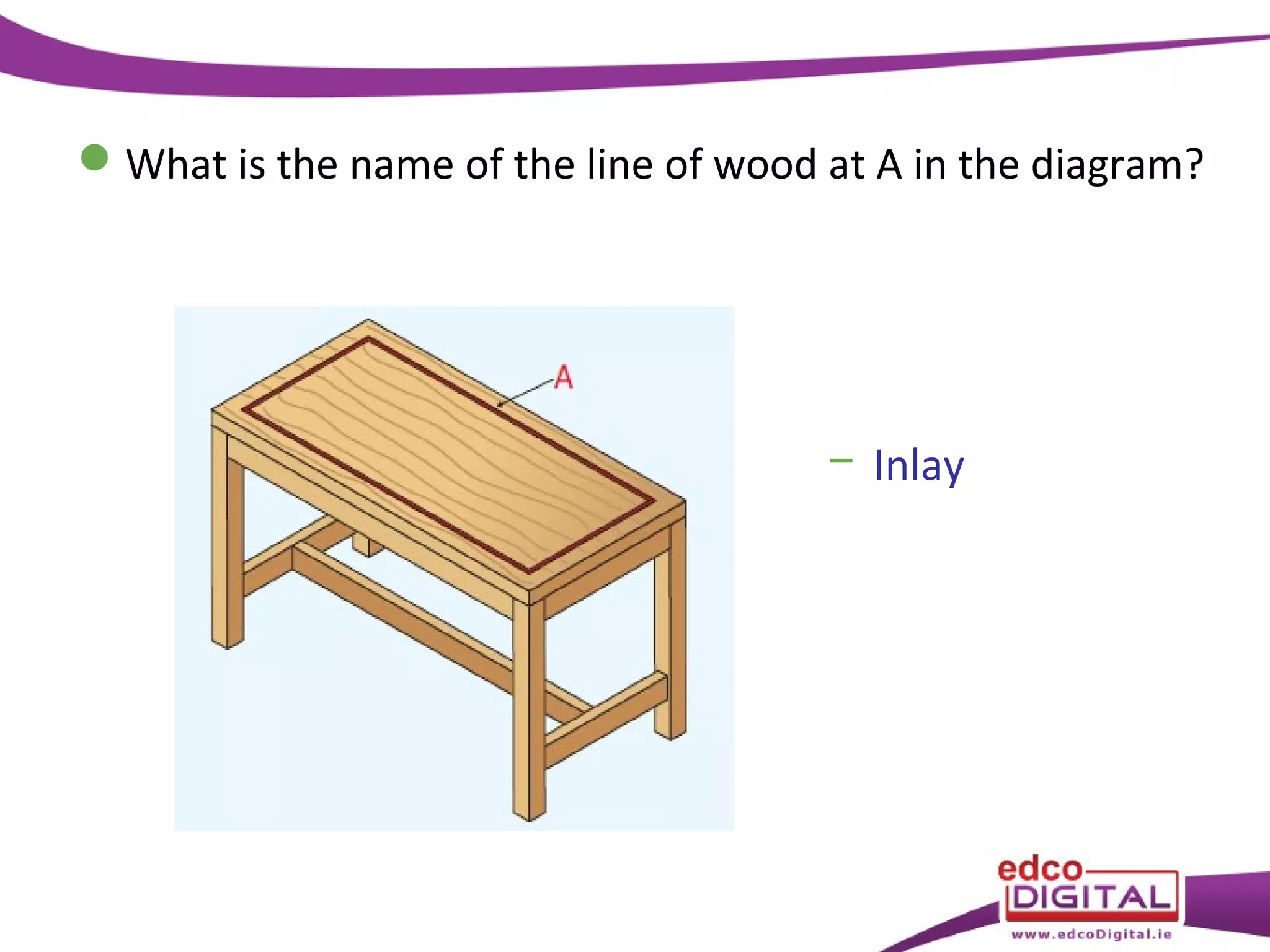
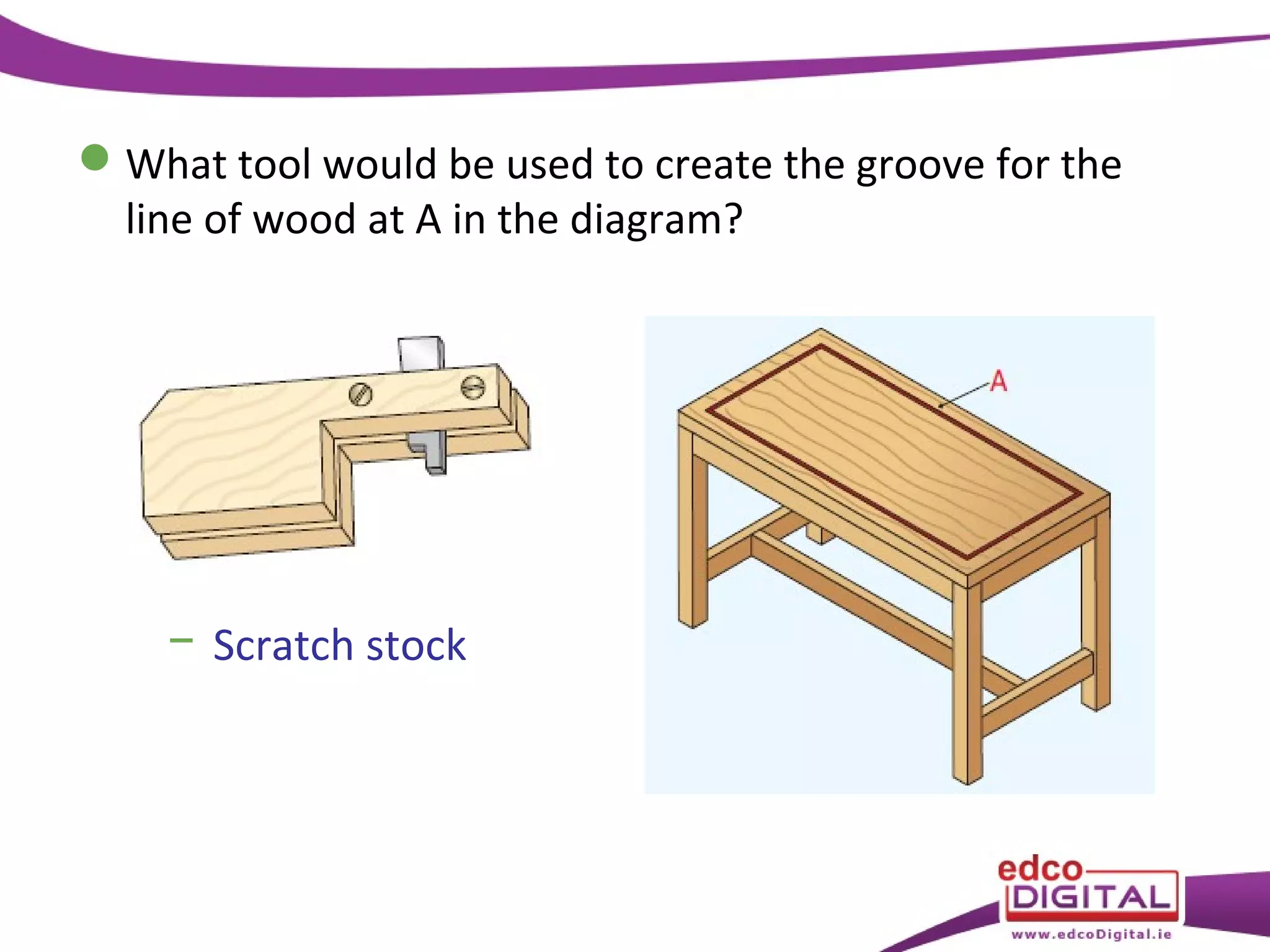
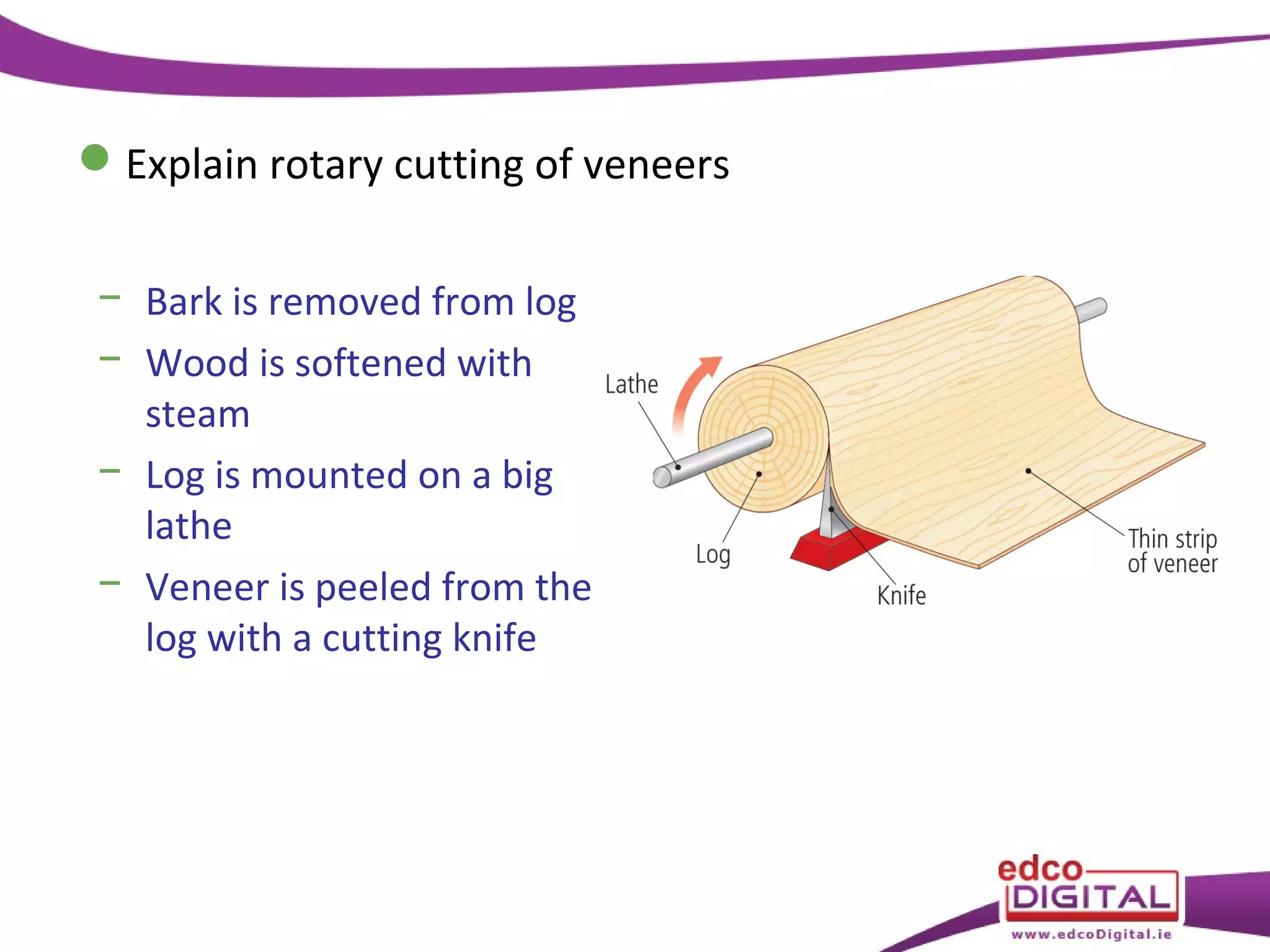
This chapter discusses veneering and inlay techniques in woodworking. It covers topics such as using veneers to efficiently use expensive woods or cover large surfaces. Proper preparation of the groundwork and careful cutting, matching, and application of veneers is emphasized. Different patterns like borders, marquetry, parquetry and the use of inlay are also described. The chapter concludes with a short quiz to test the reader's understanding.