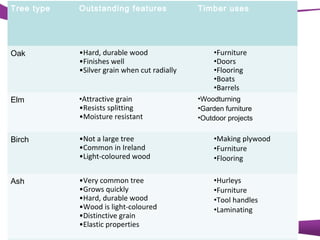
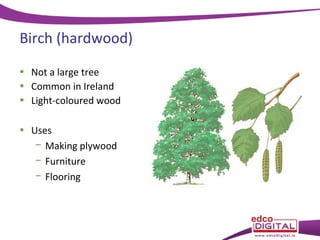
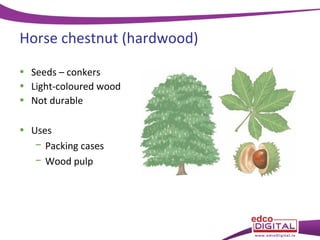
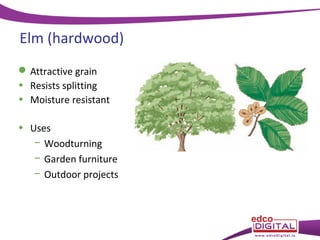
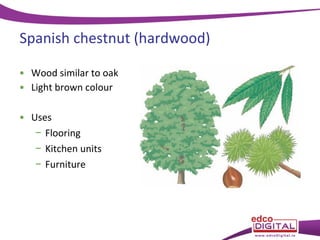
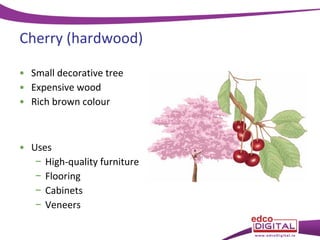
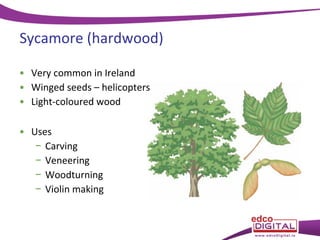
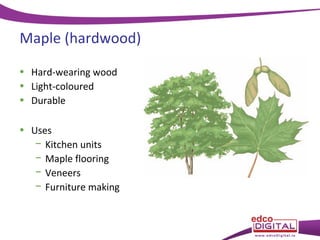
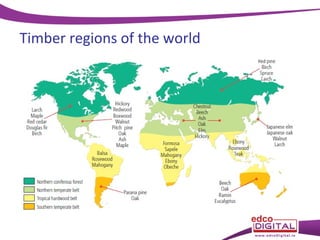
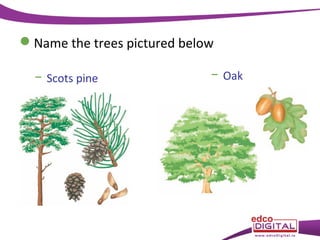
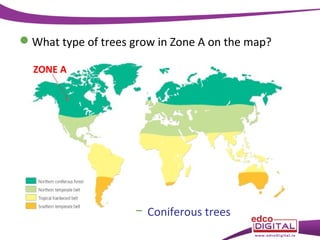
This document discusses different types of trees. It describes two main groups: coniferous and deciduous trees. Coniferous trees are softwoods that have needle-like leaves and remain green year-round, while deciduous trees are hardwoods that lose their broad leaves in autumn. Several deciduous trees are then outlined, including oak, ash, birch, and beech, along with their features and common uses for their wood. Coniferous trees such as Scots pine, Douglas fir, and Sitka spruce are also described. The document concludes with a brief overview of timber regions around the world.