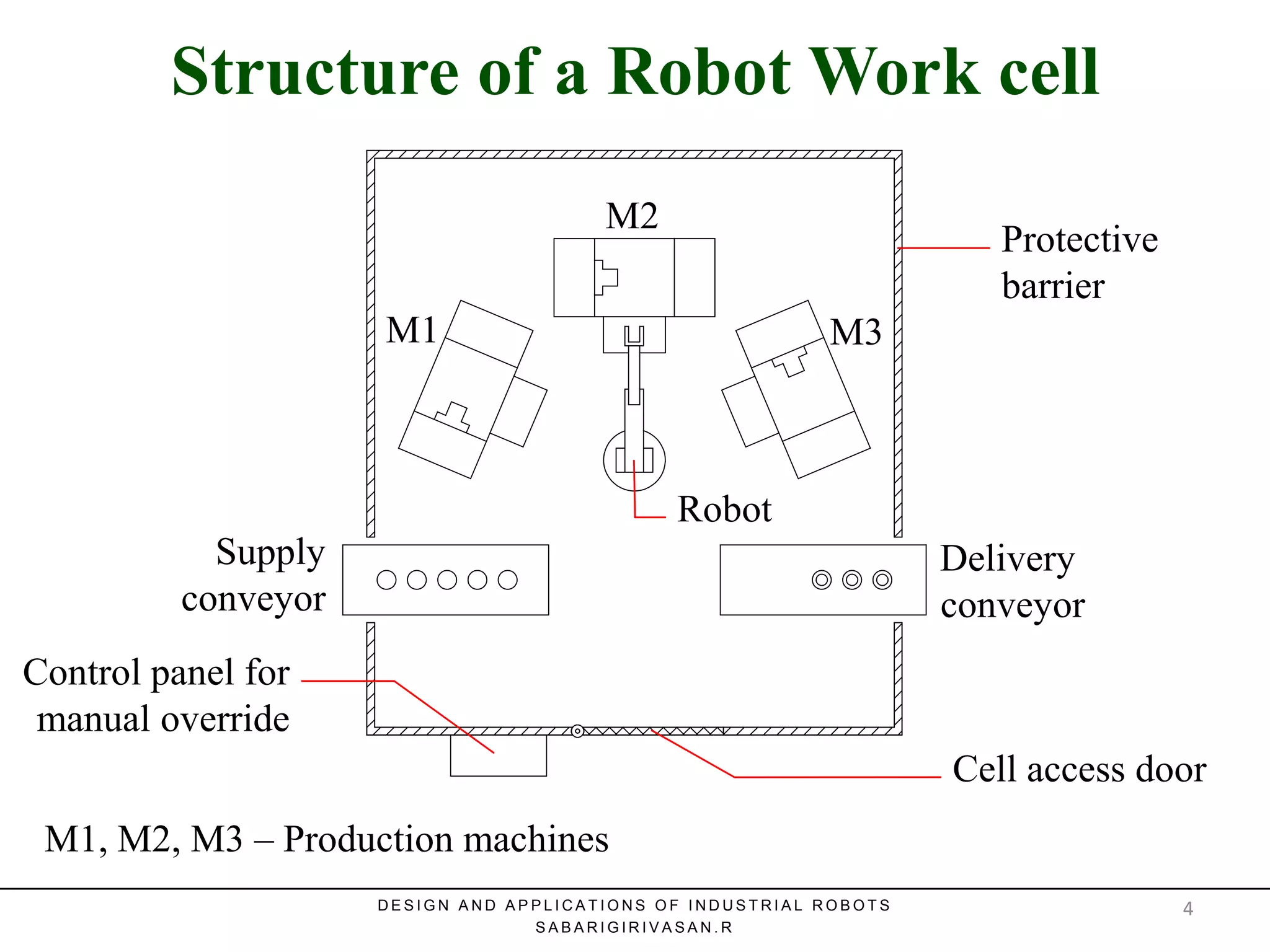
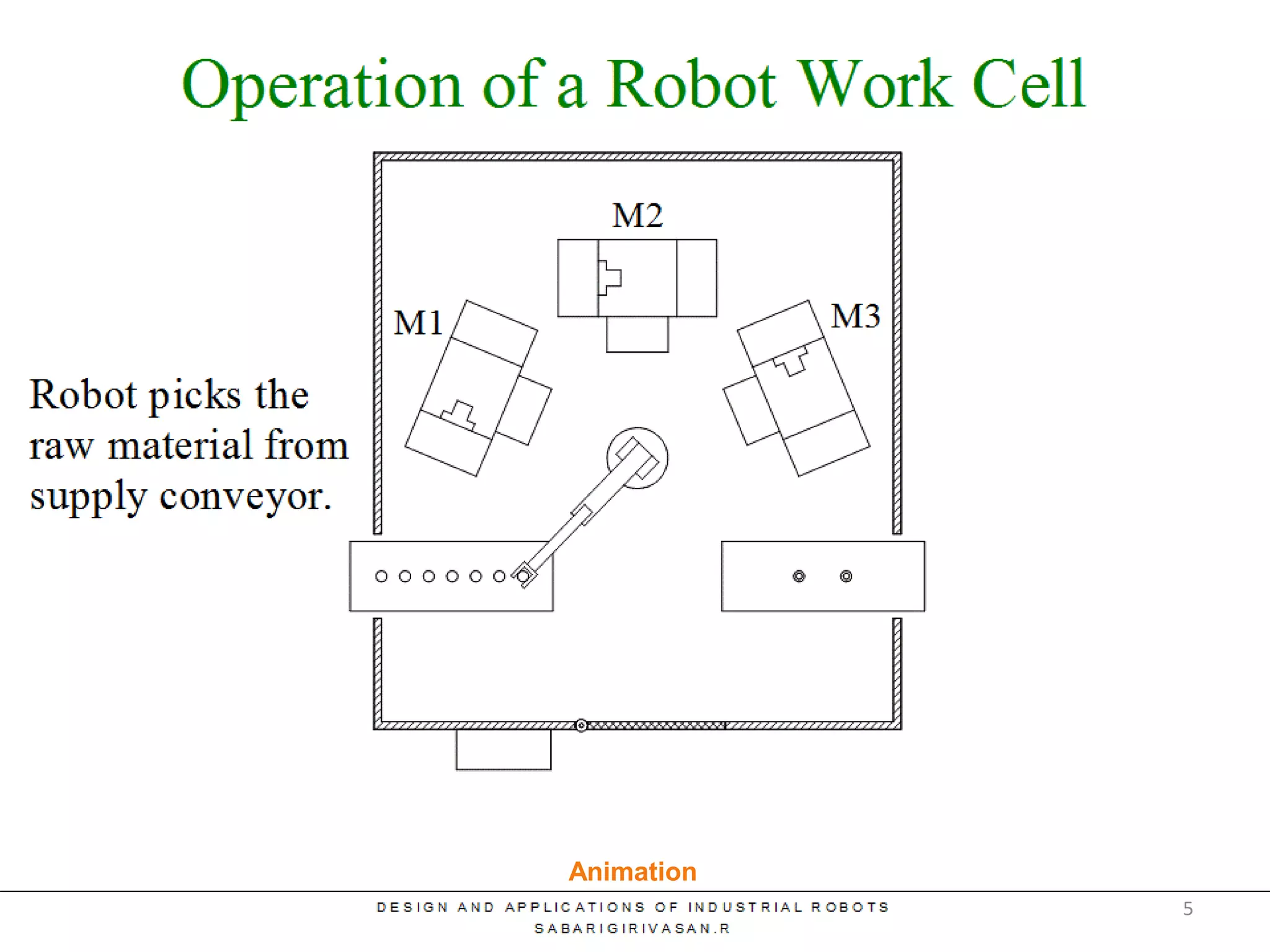
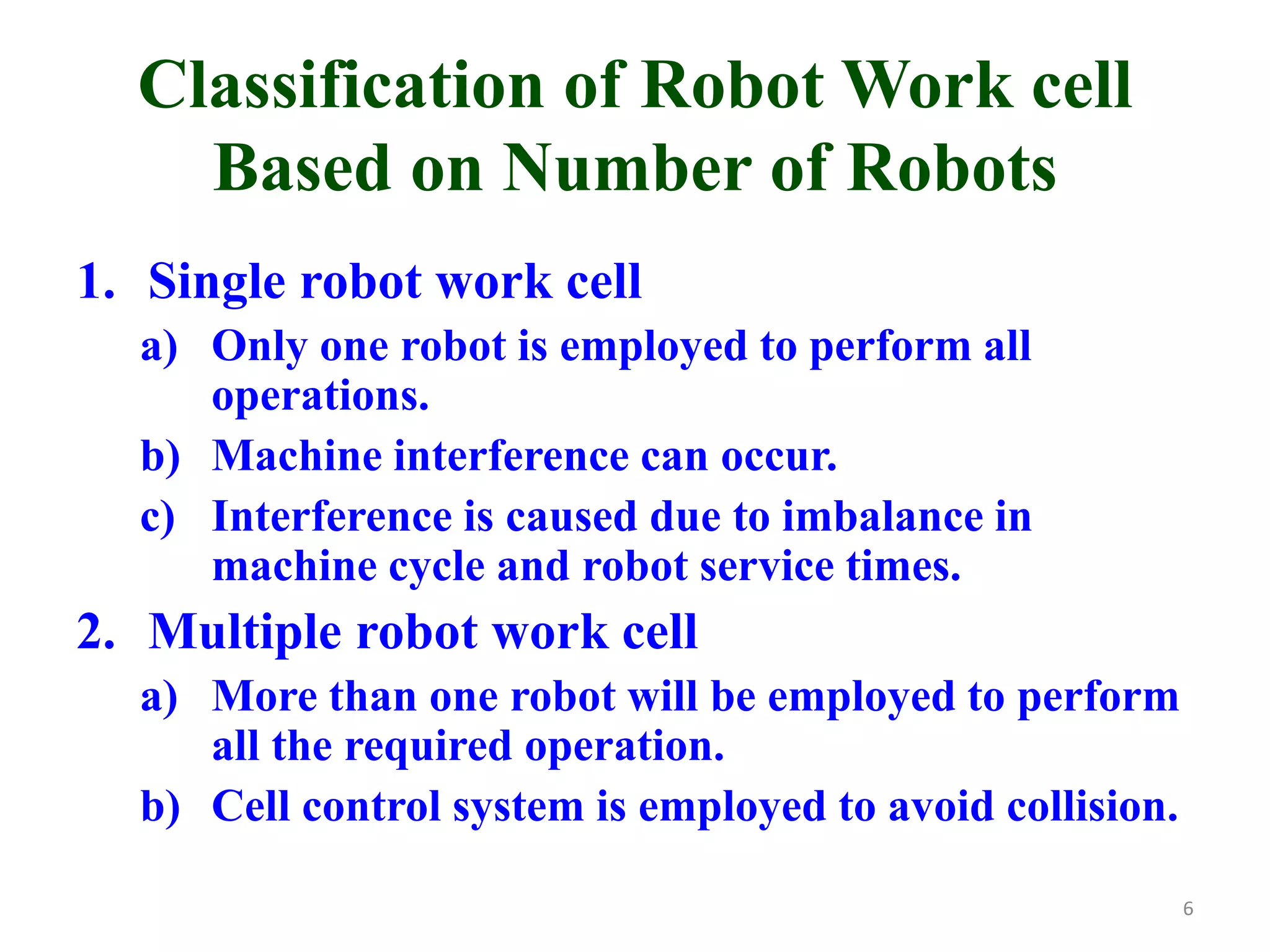
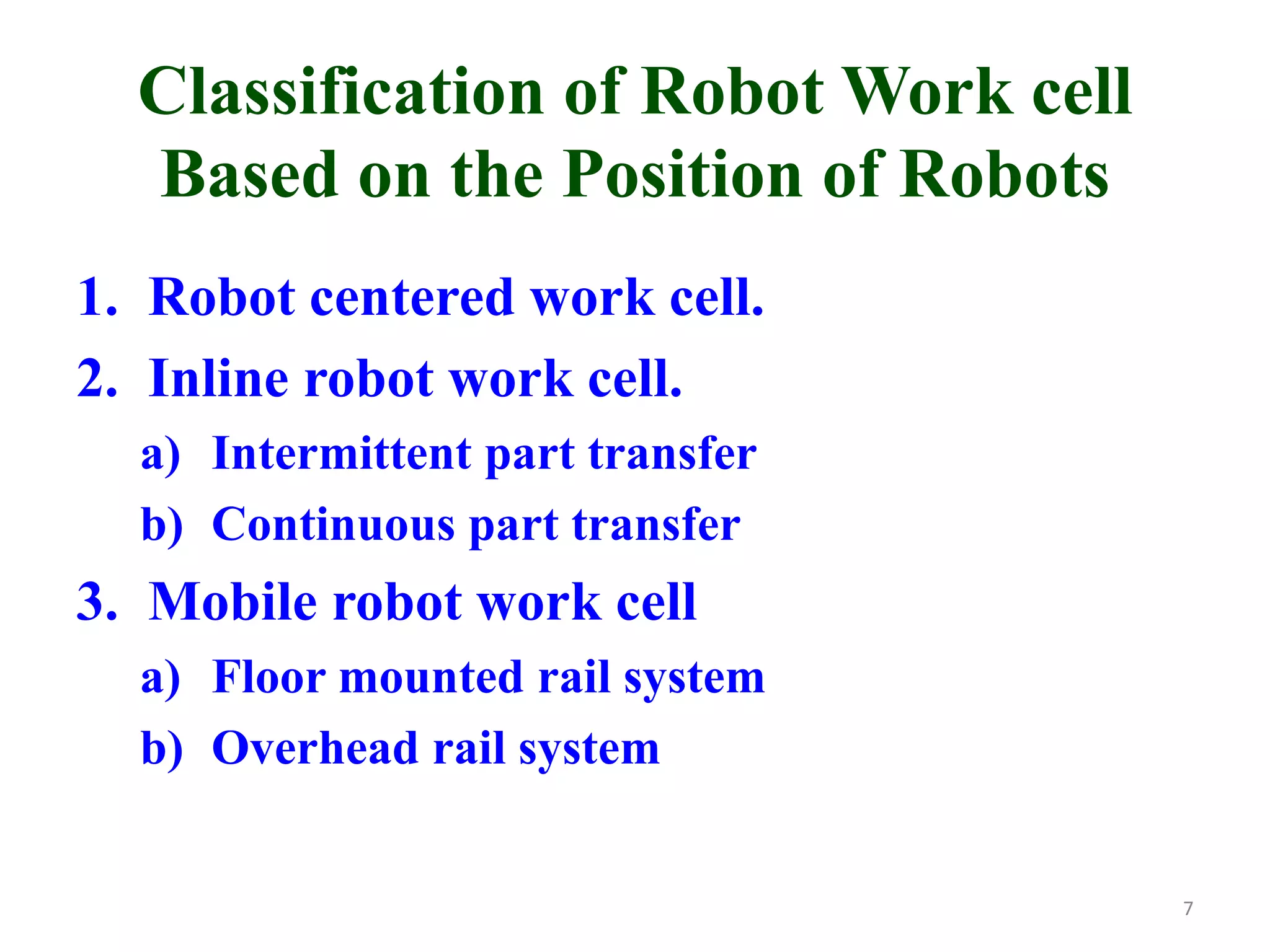
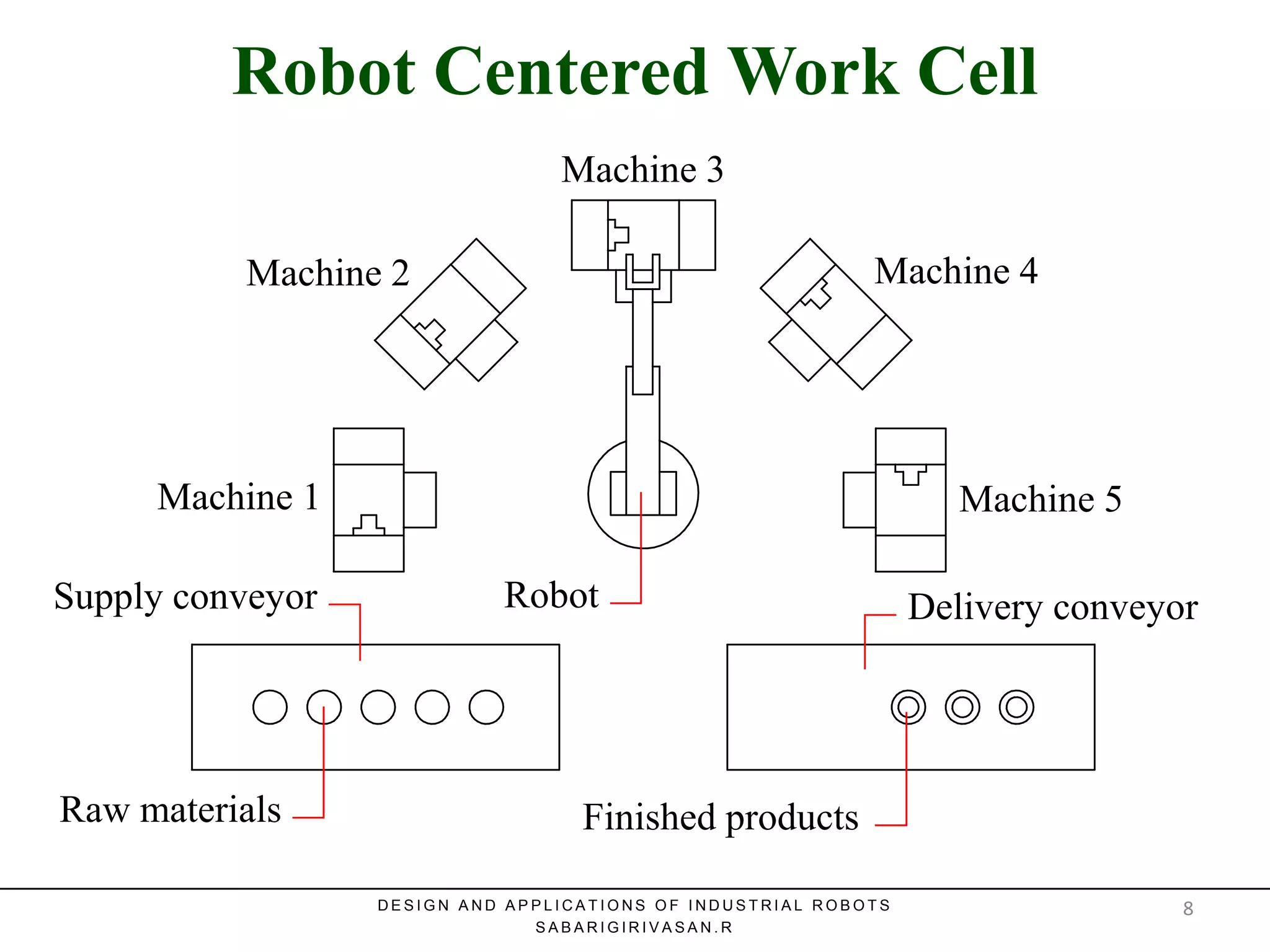
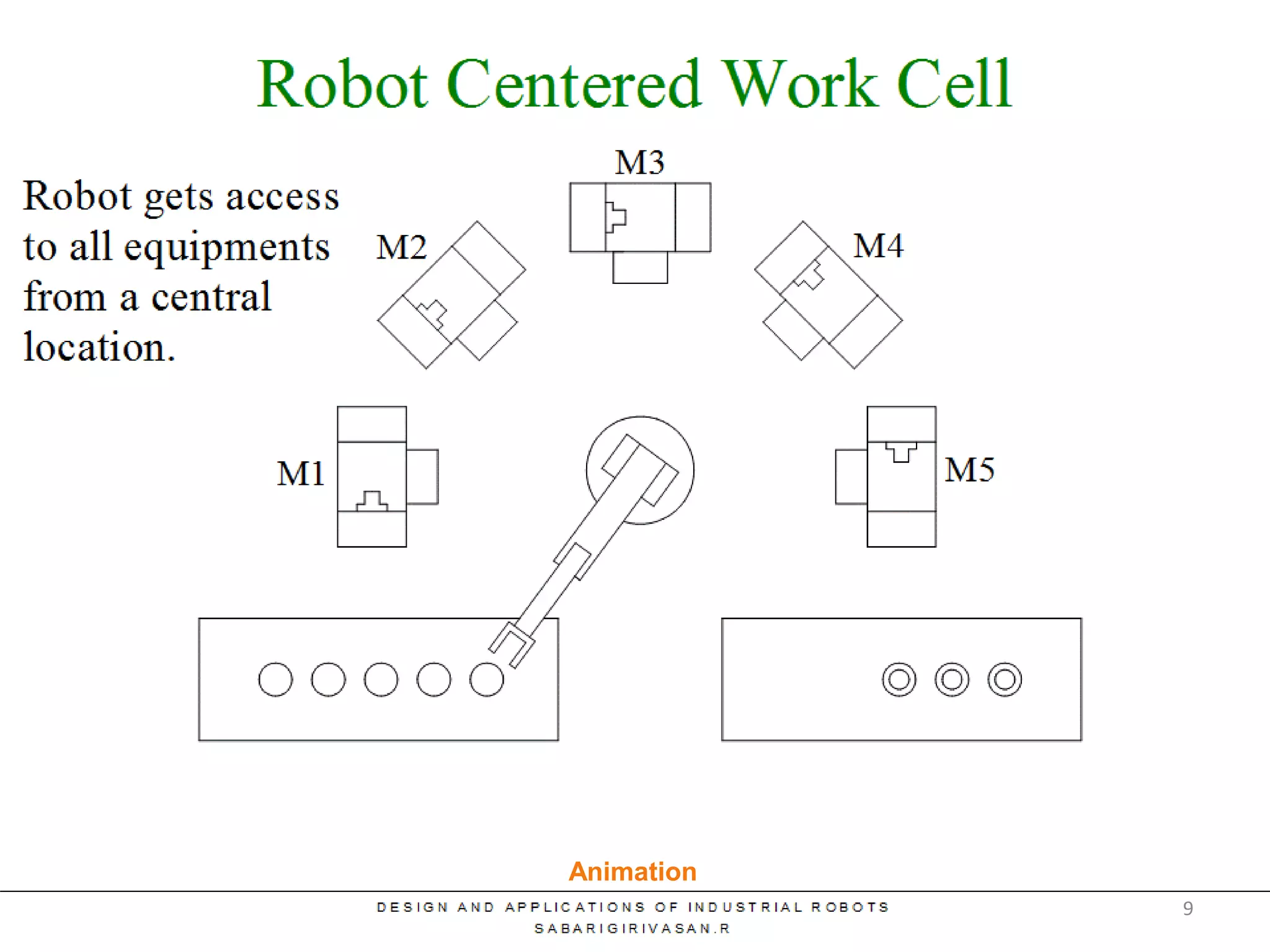
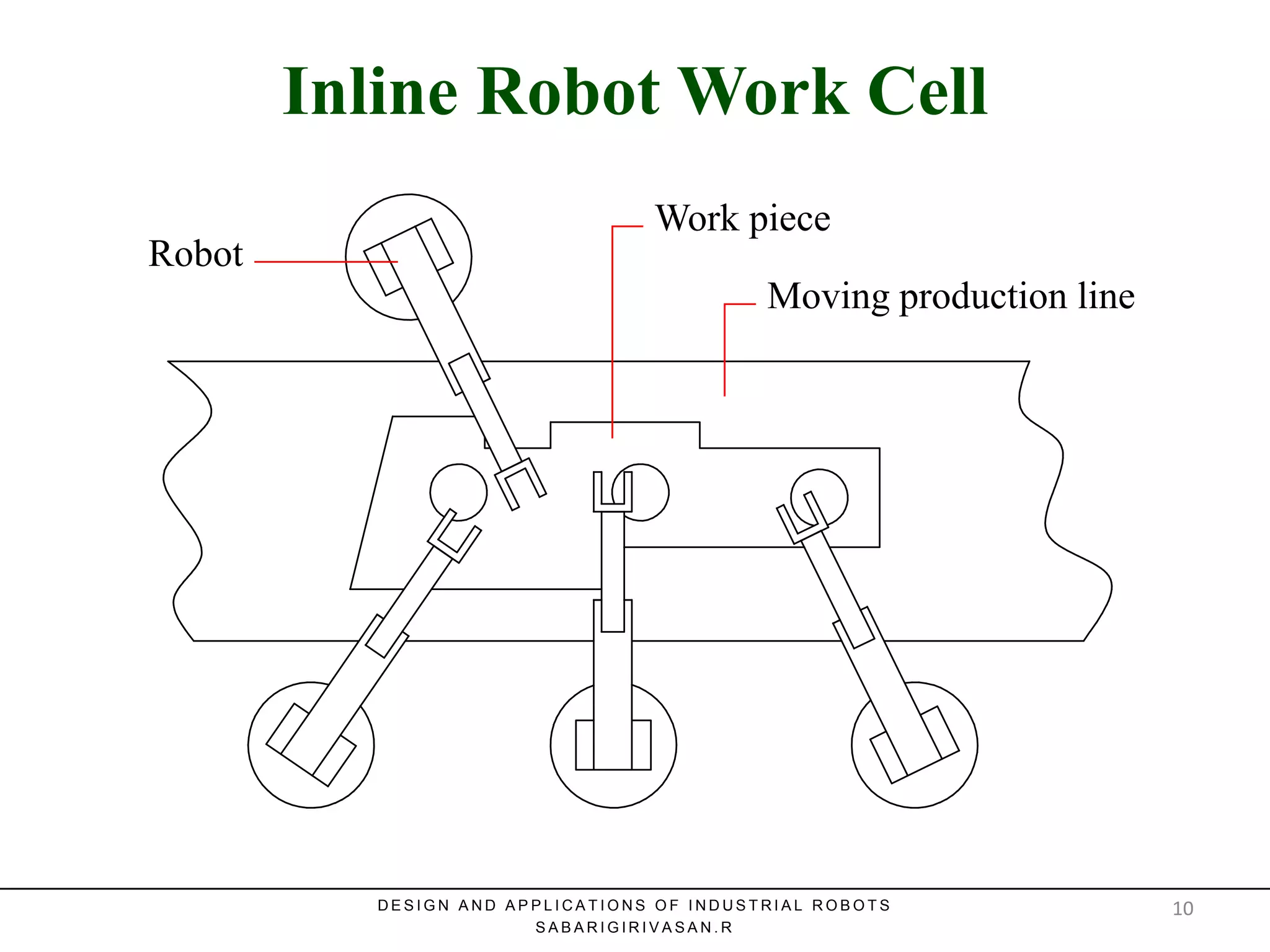
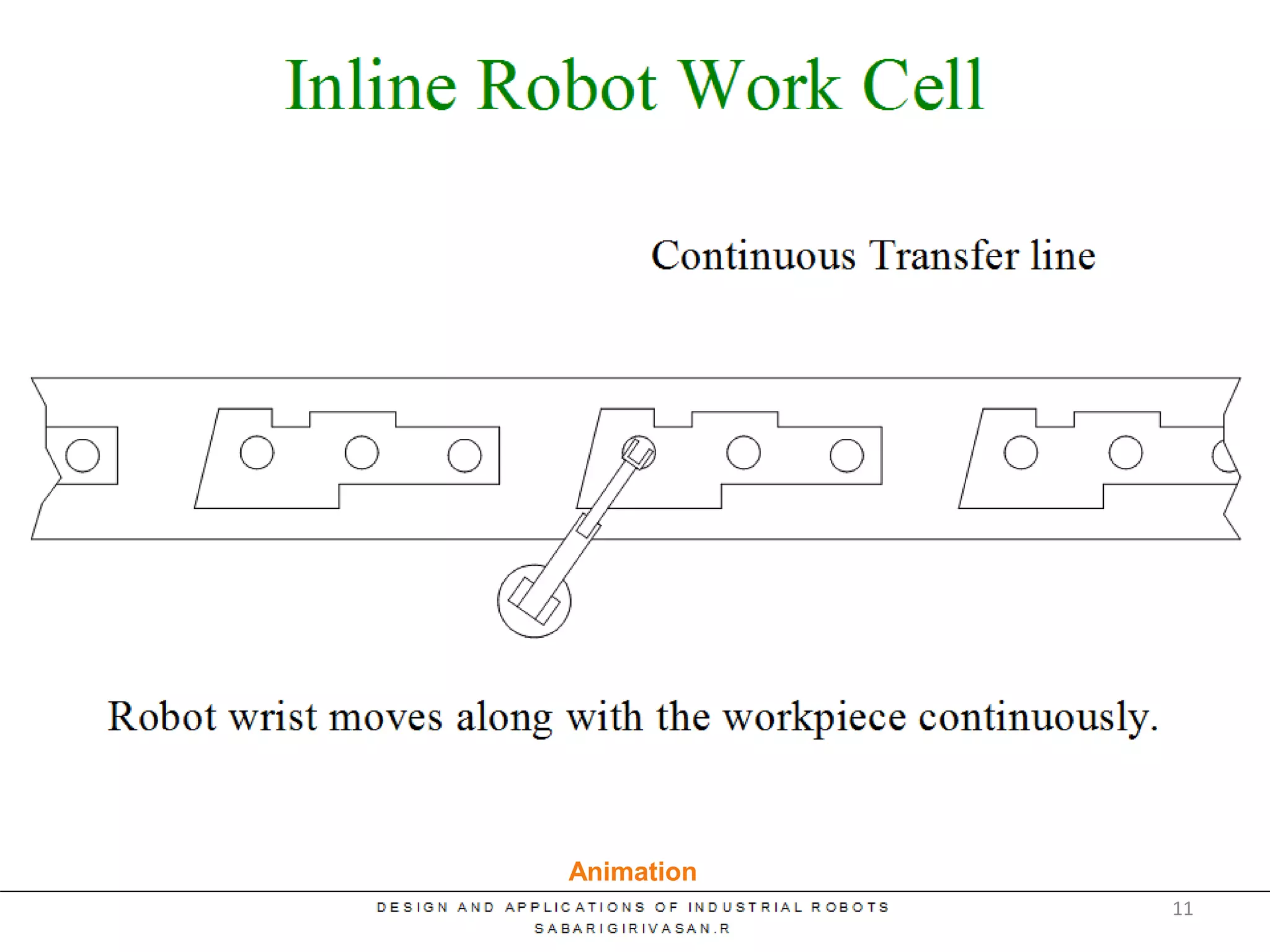
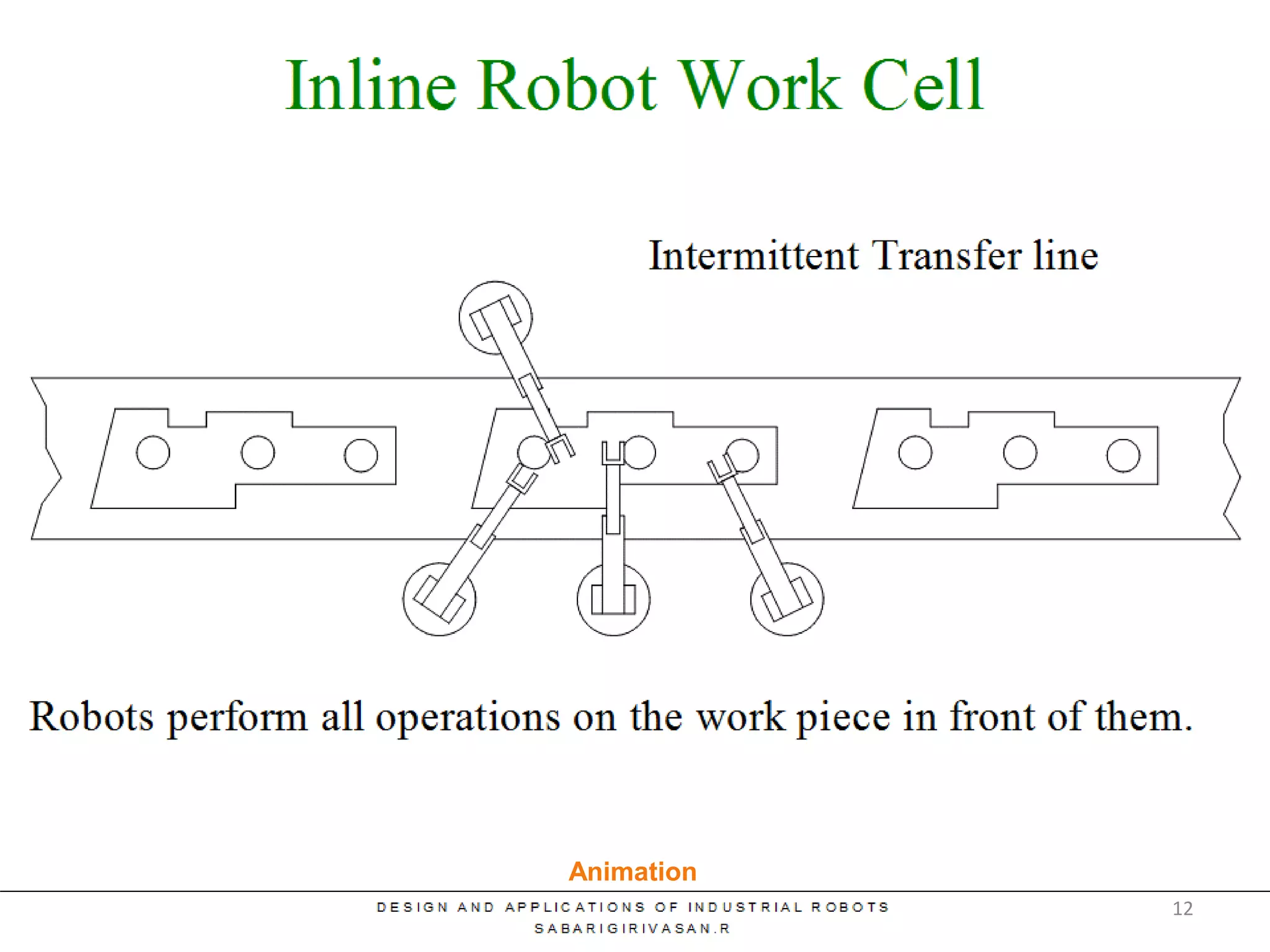
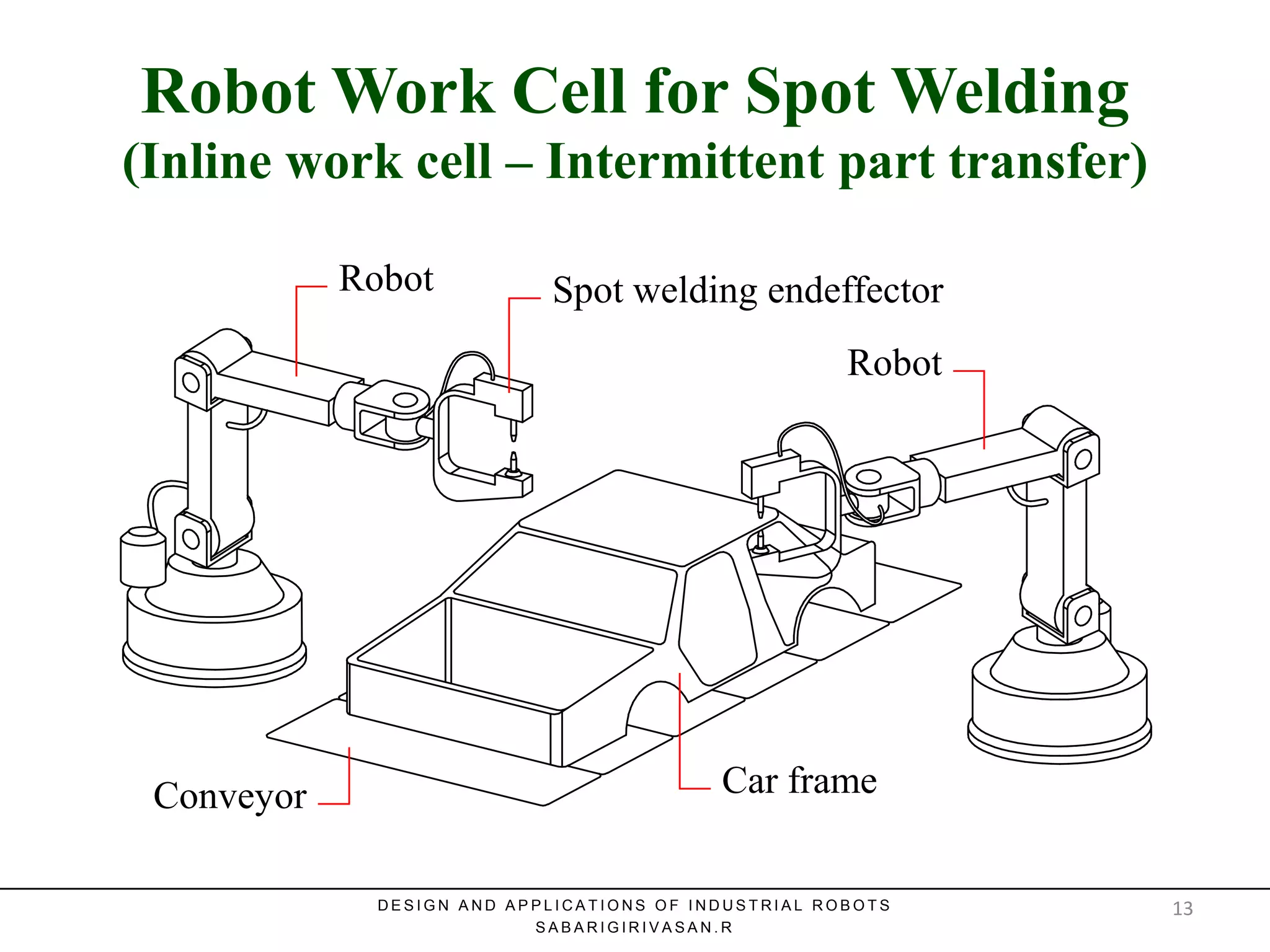
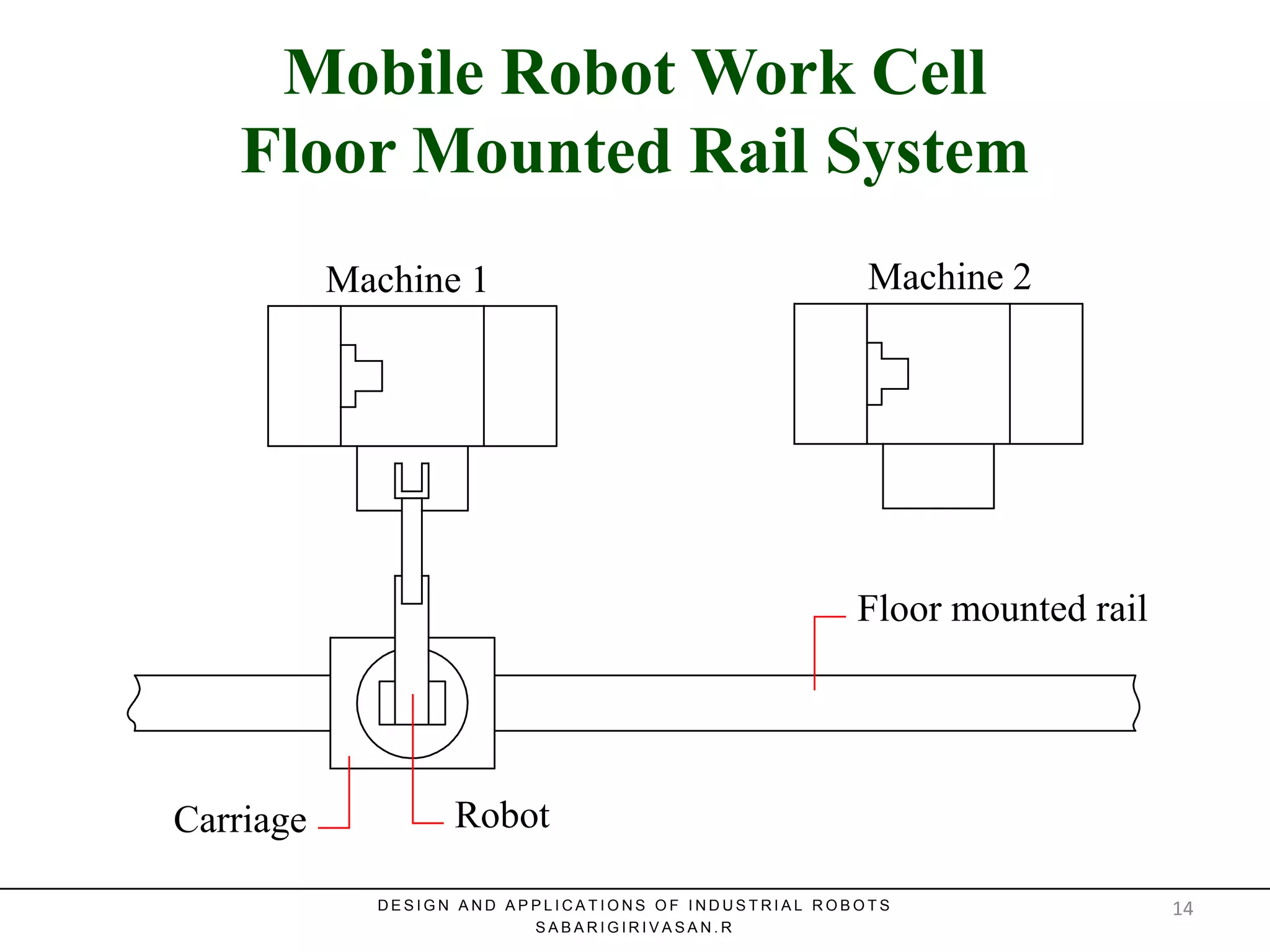
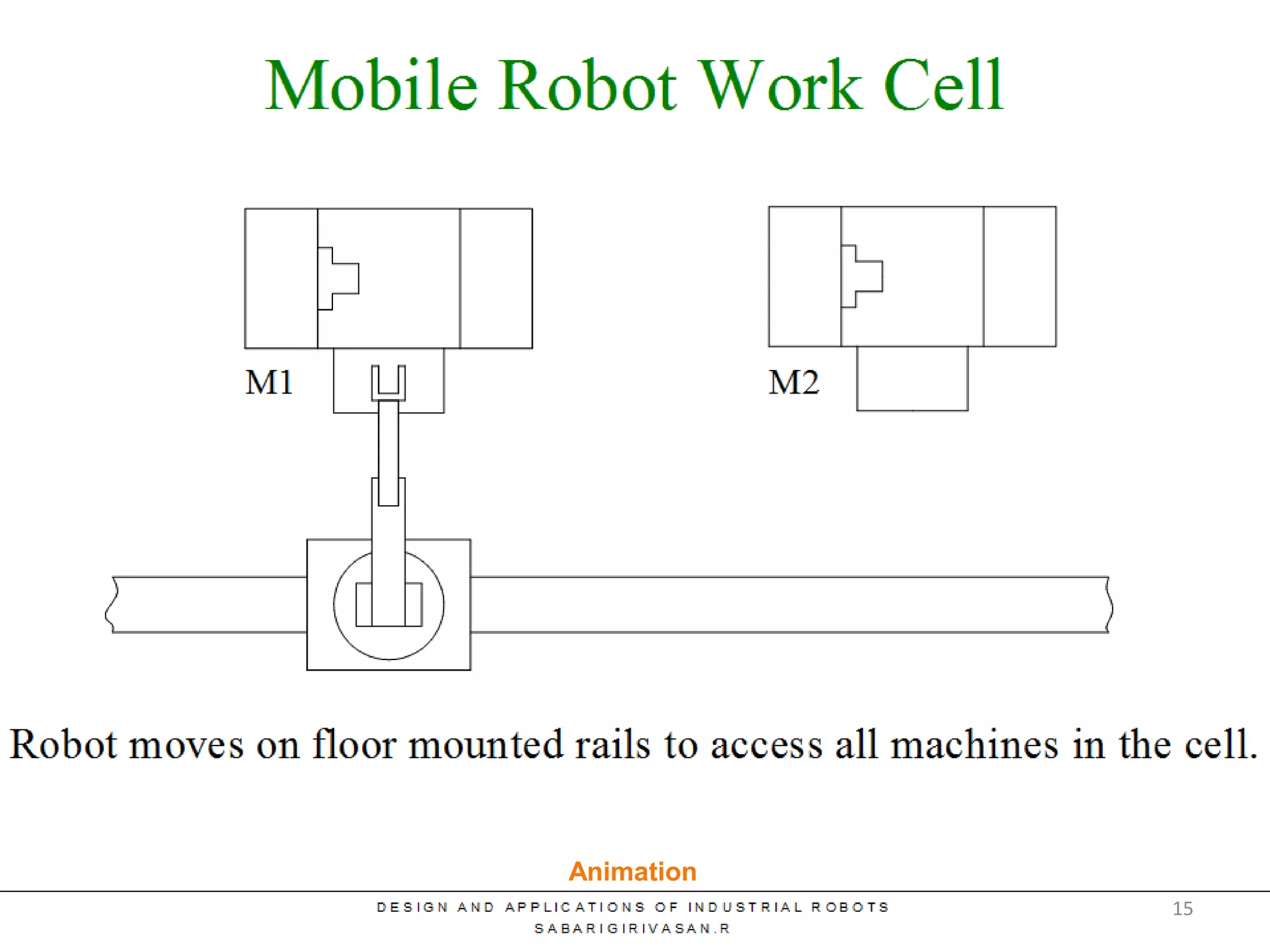
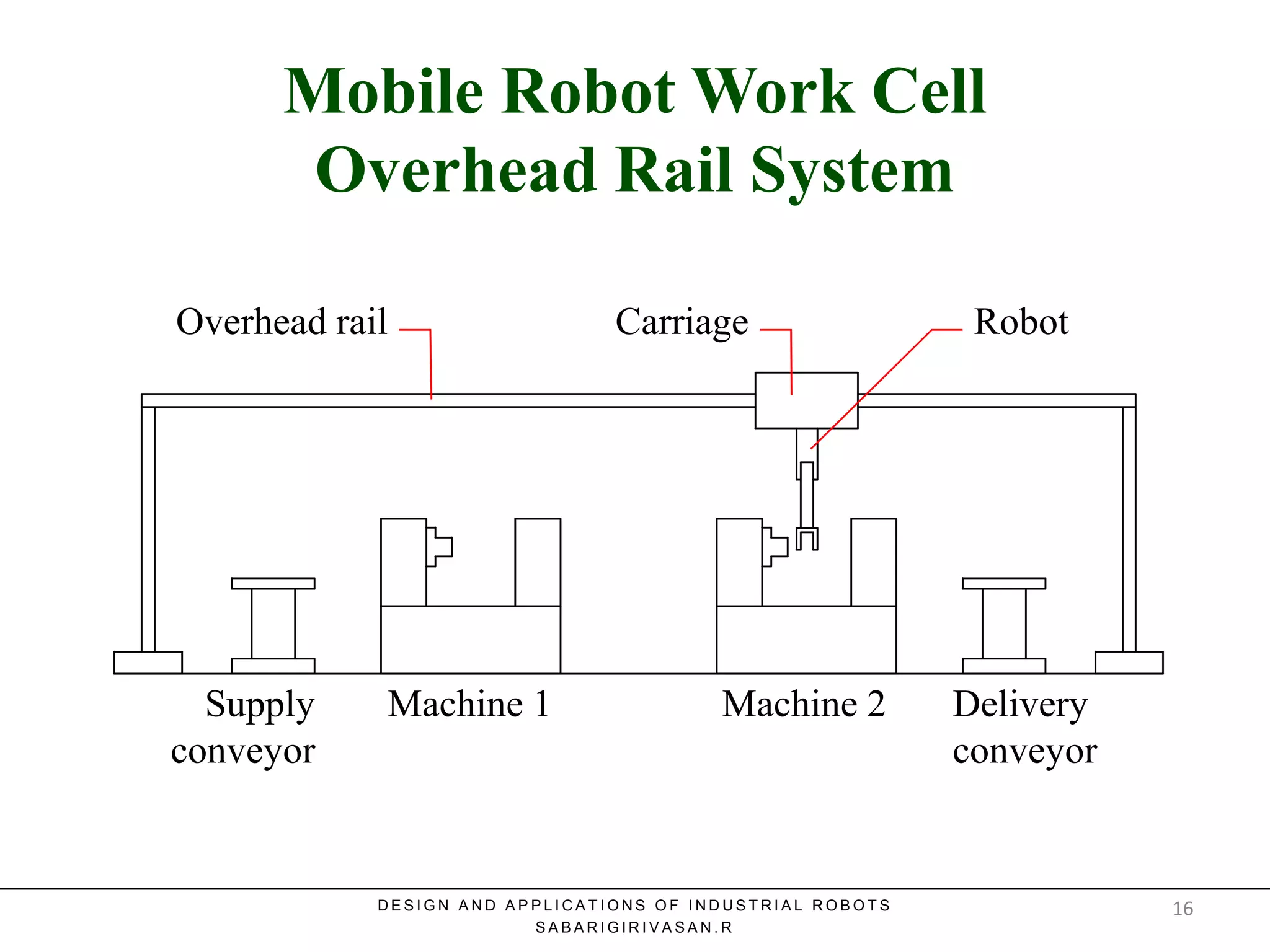
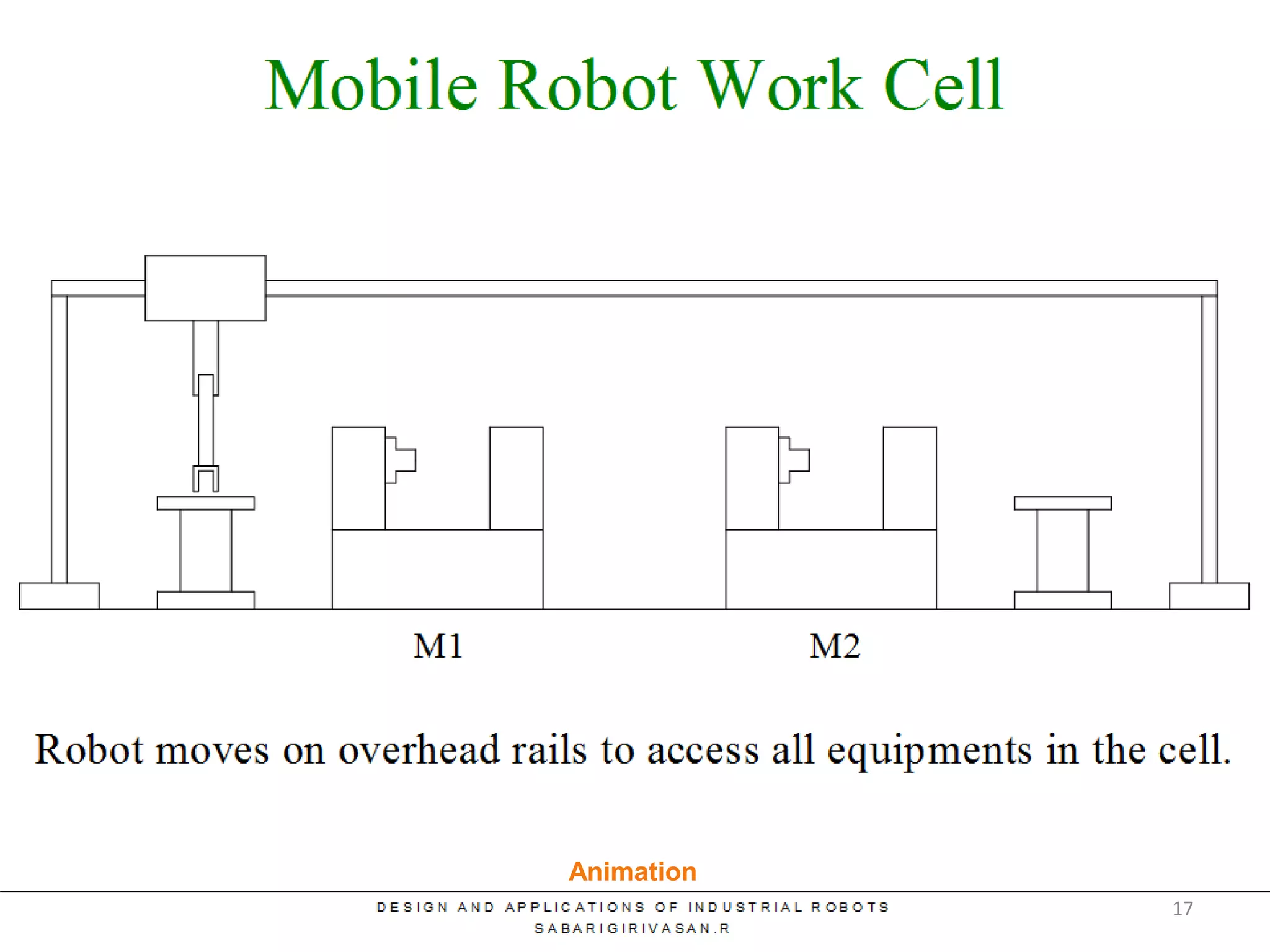
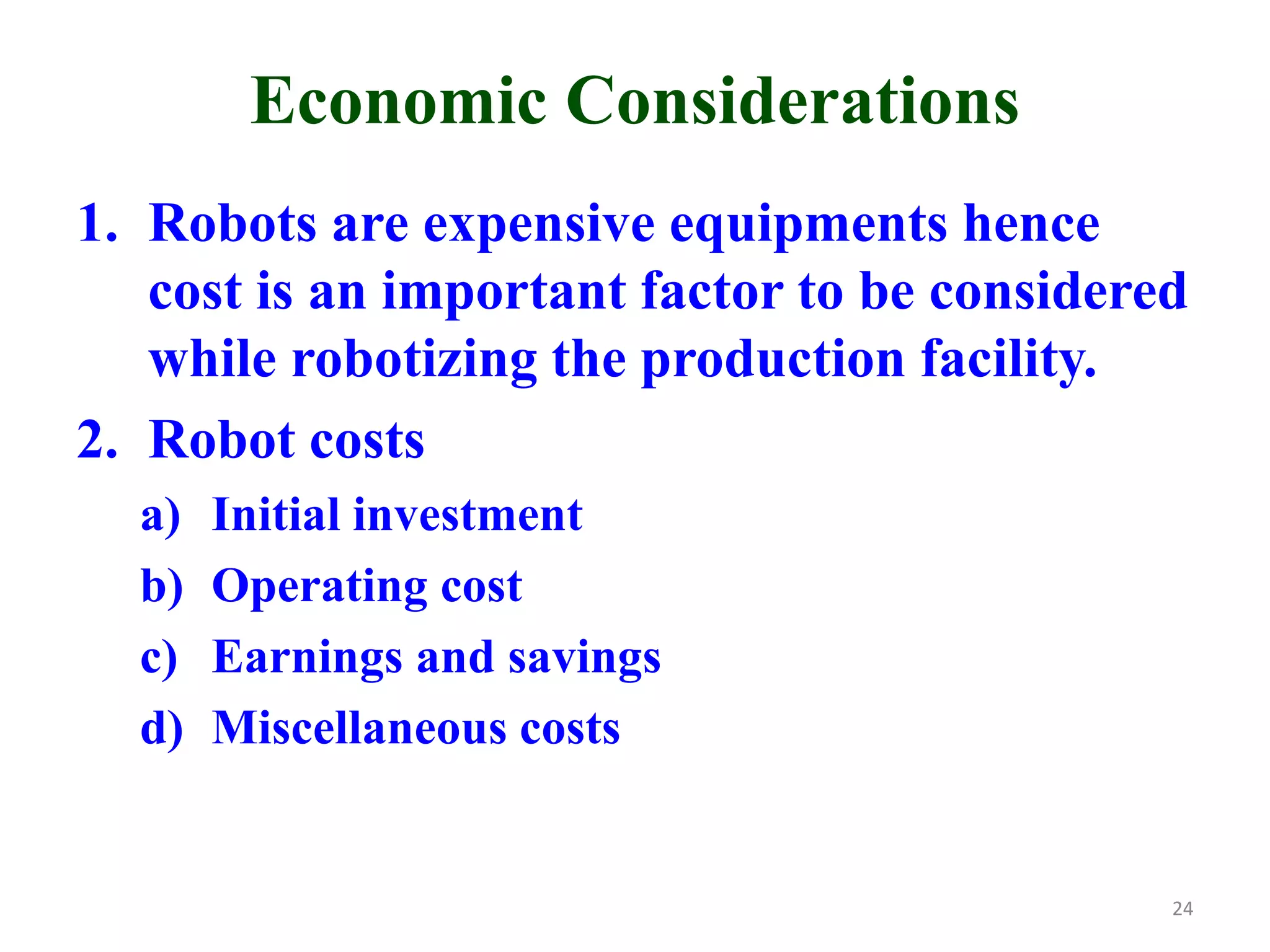
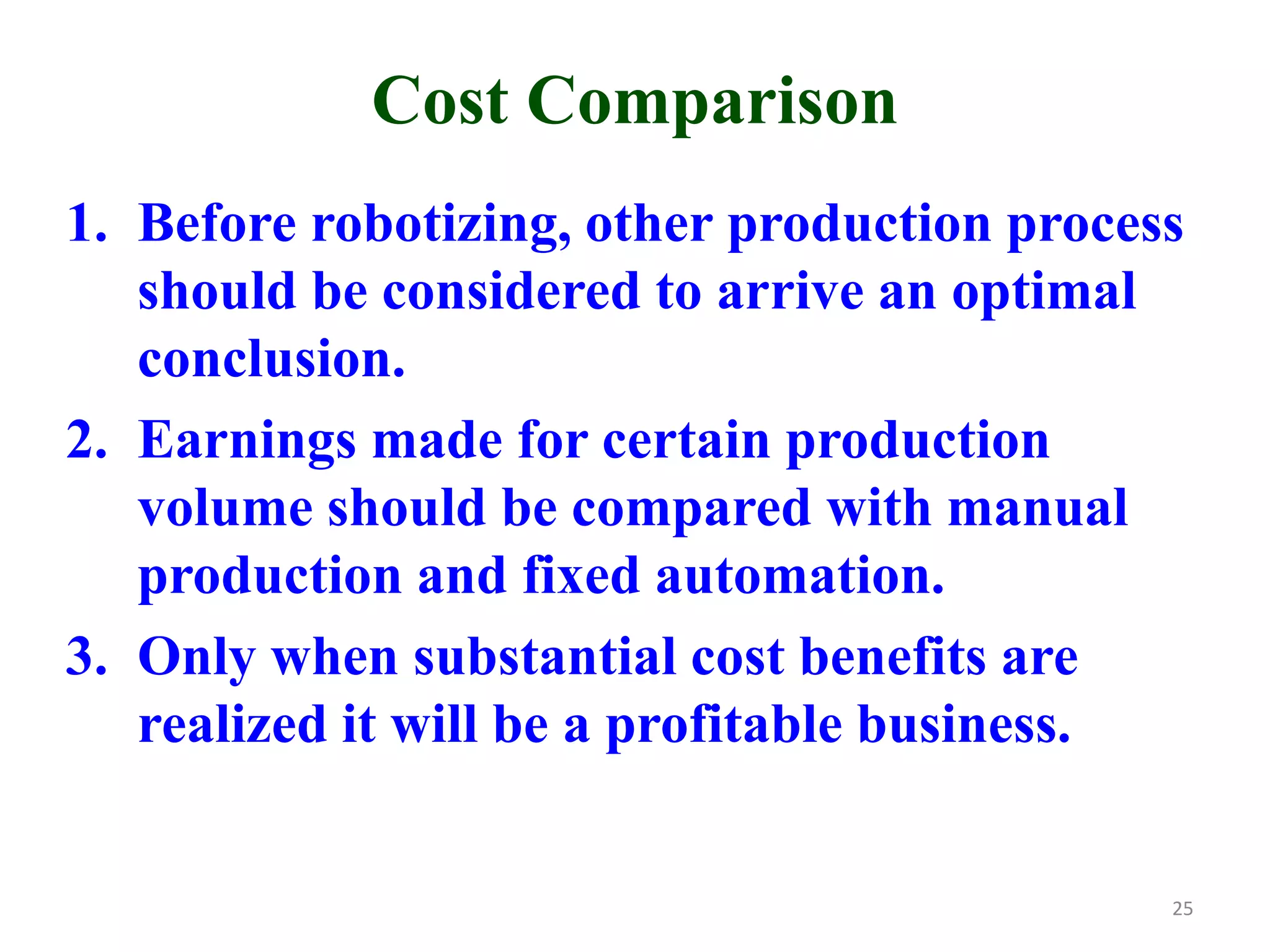
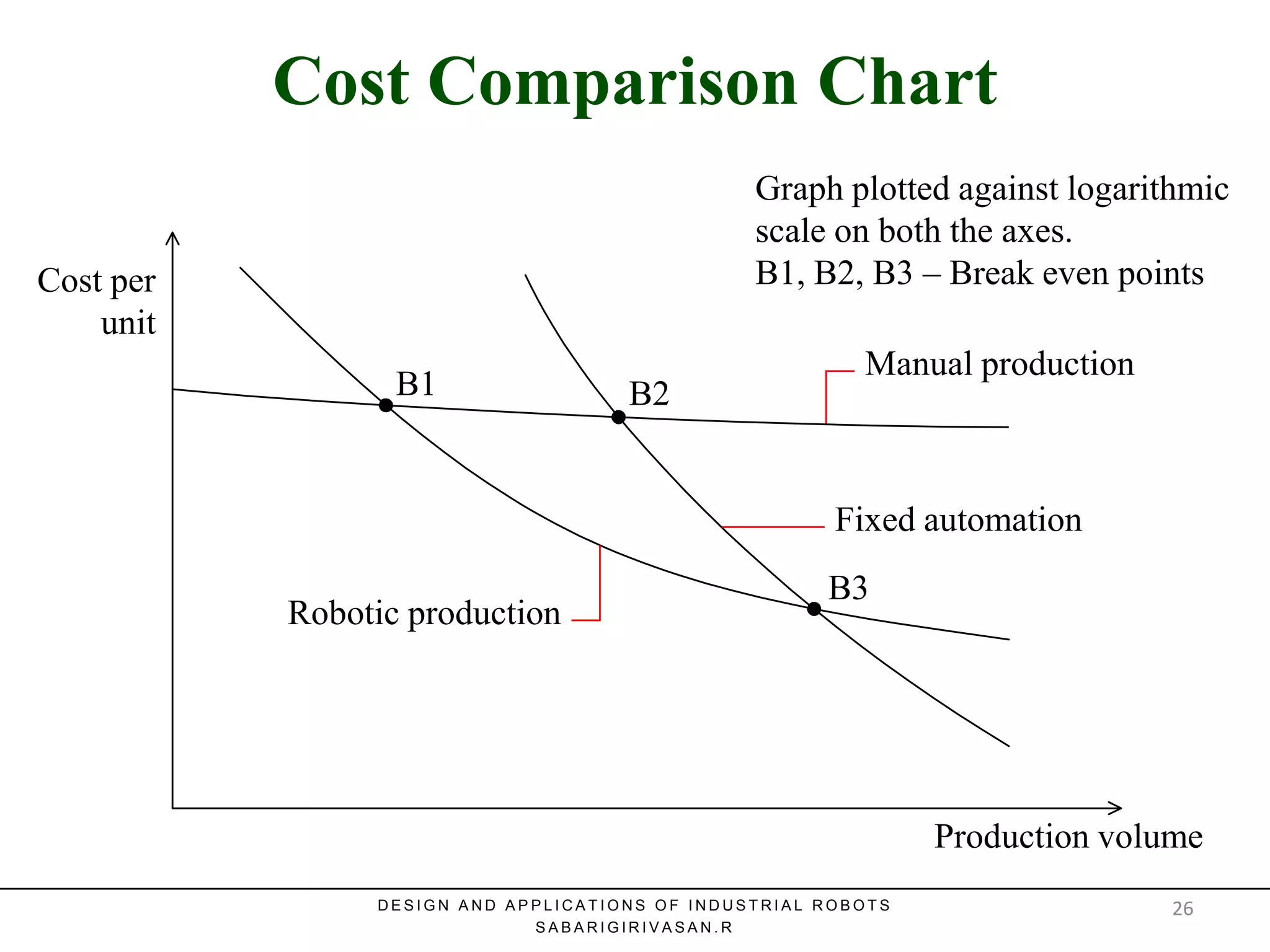
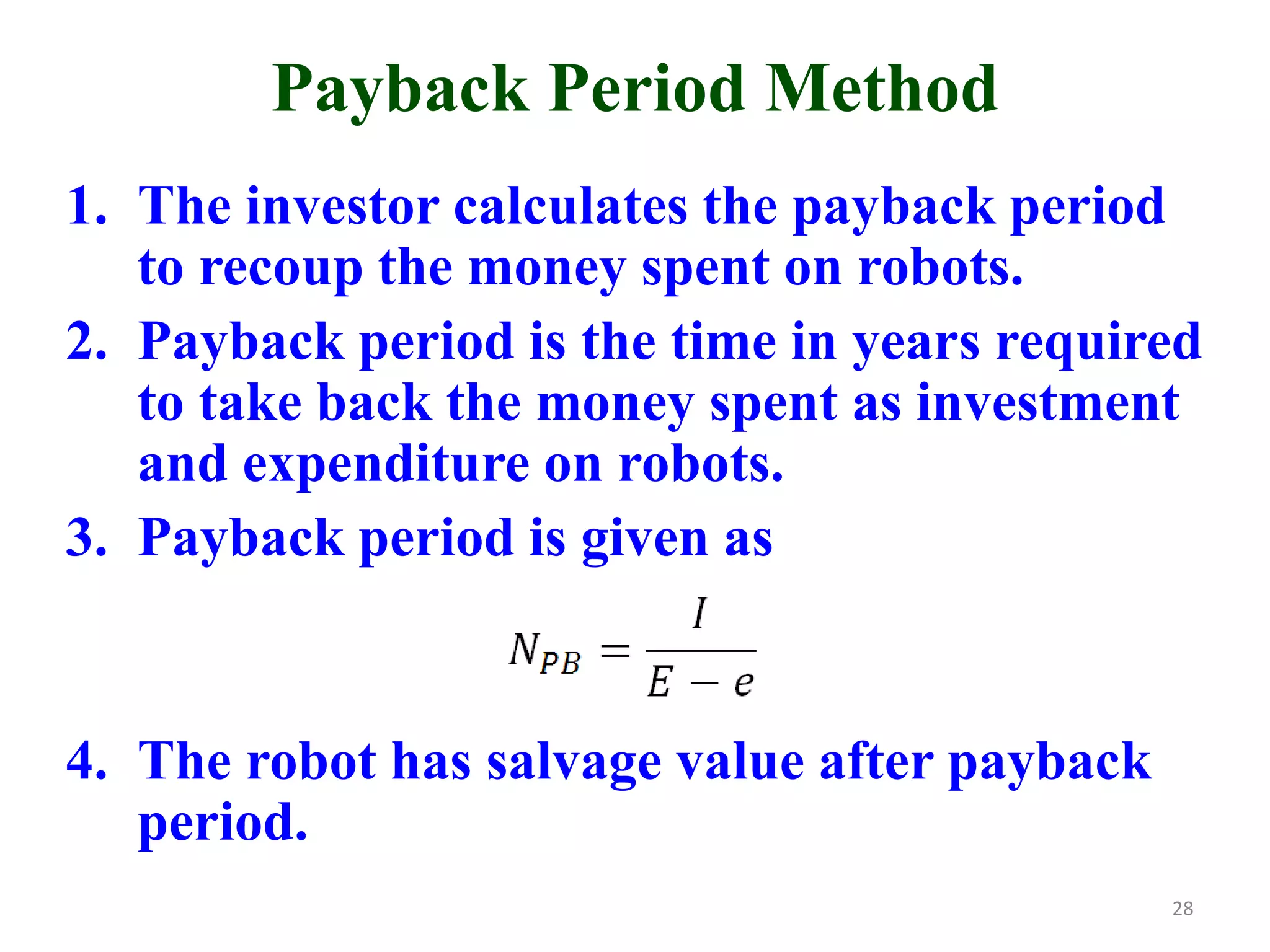
This document discusses robotic manufacturing systems and robot work cells. It describes the basic components of a robot work cell including robots, production machinery, conveyors, and safety barriers. It also categorizes robot work cells based on the number of robots and robot positioning. Economic considerations for robotization like cost analysis, payback period, and return on investment methods are presented. Robot selection criteria such as accuracy, speed, payload, and cost are also discussed.