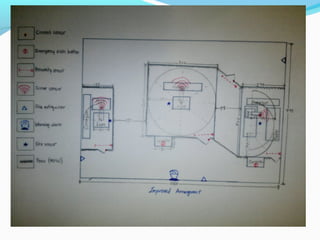
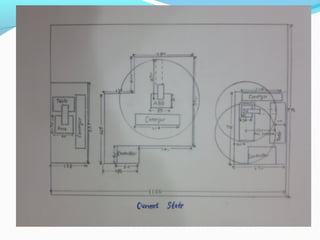
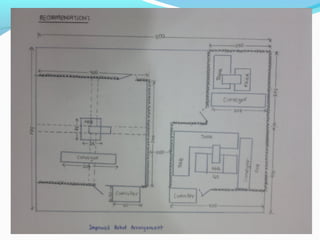
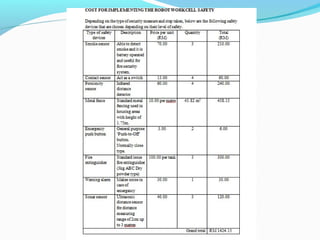
The document discusses designing a proper robot safety work cell for robots in a university robotics laboratory. It identifies that the current safety measures are insufficient, lacking things like emergency stop buttons and adequate barriers between robot workspaces. The objectives are to familiarize students with robot safety and workcells. It outlines various safety factors to implement, including barriers, alarms, safety sensors, maintenance procedures, and operator training. It also describes the functions of different safety devices and keeps costs low by utilizing resources efficiently. Recommendations include floor covering, grounding cables, decreasing arm speeds, and a two-position part manipulator.