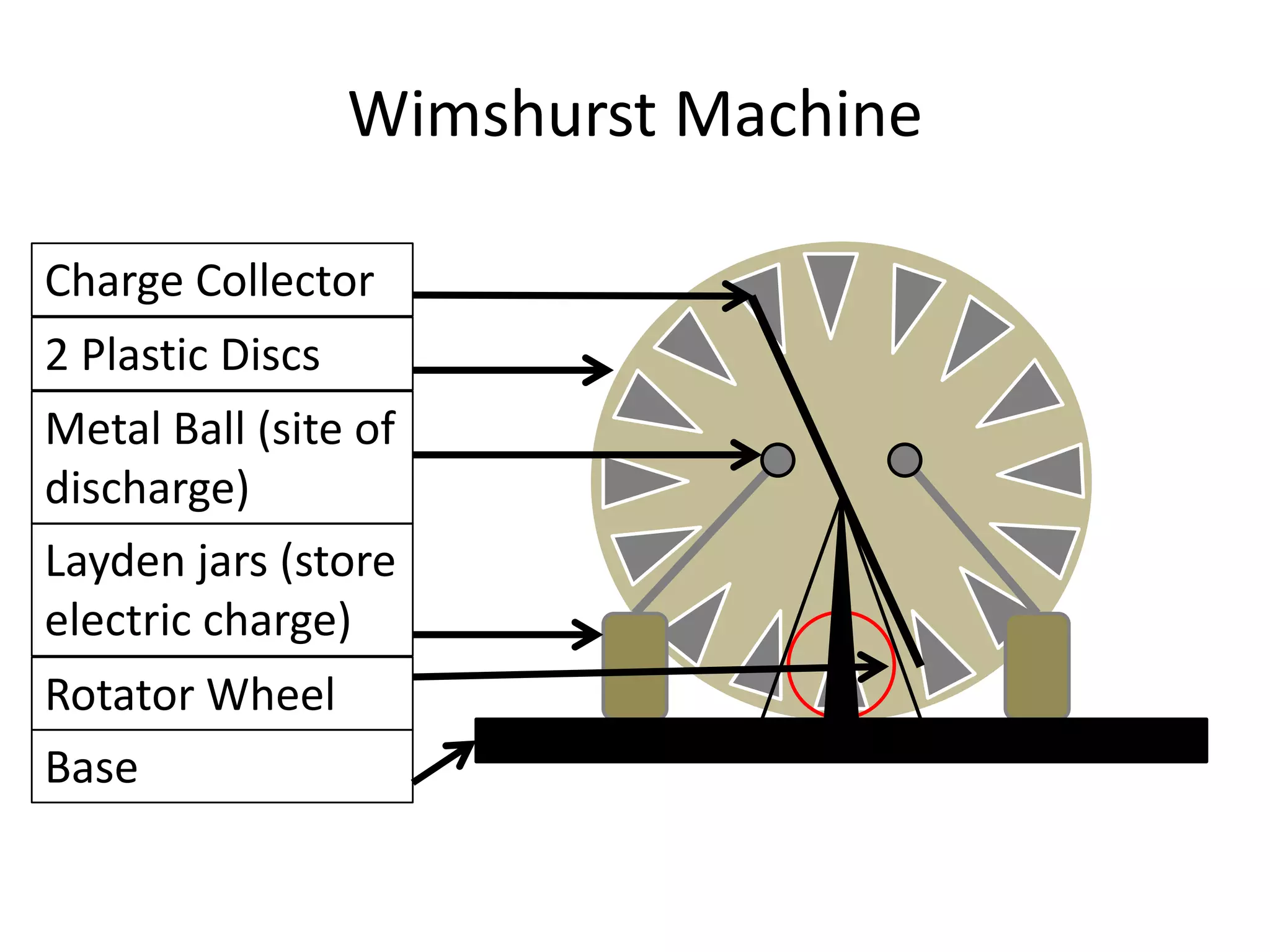
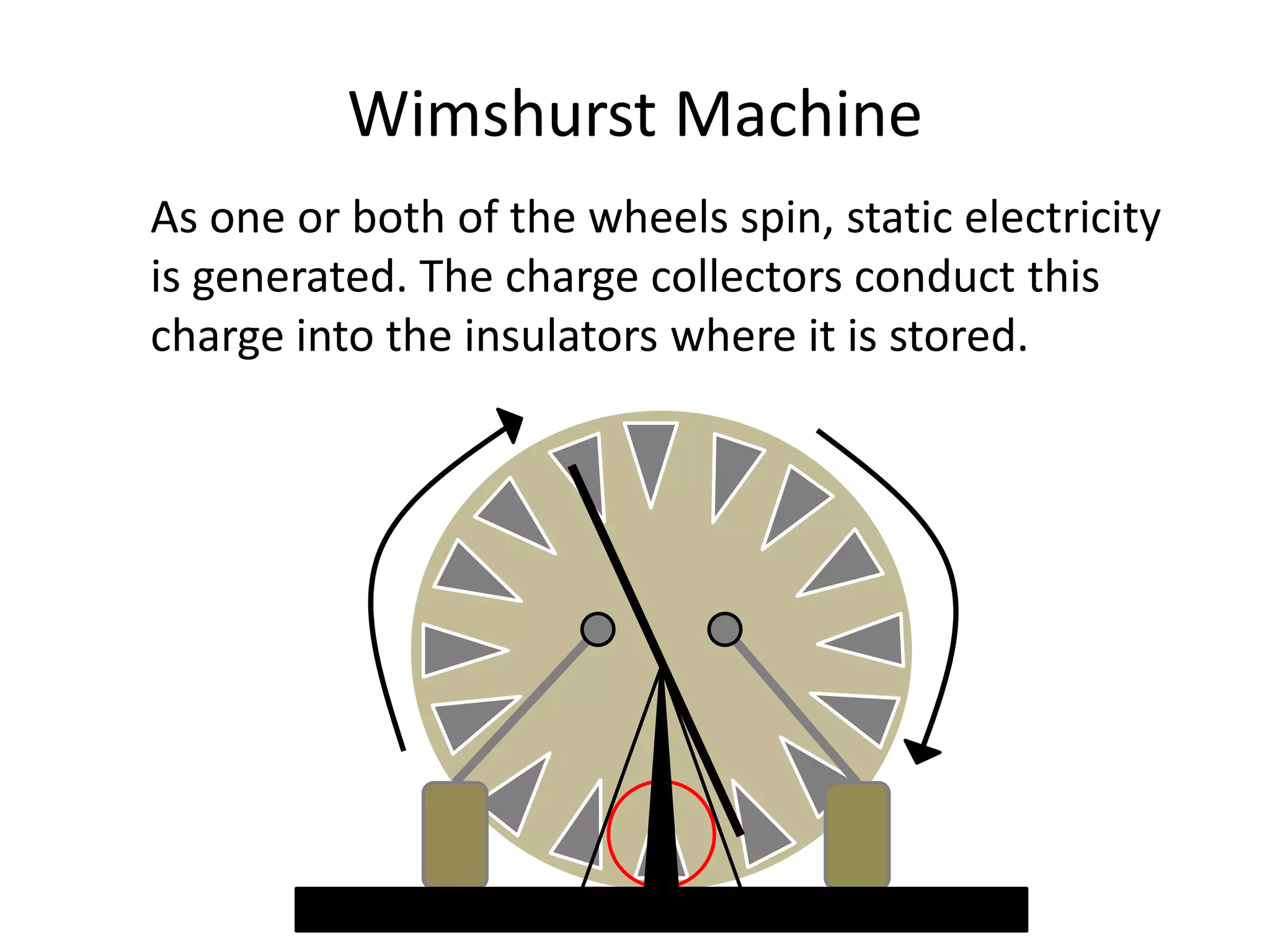
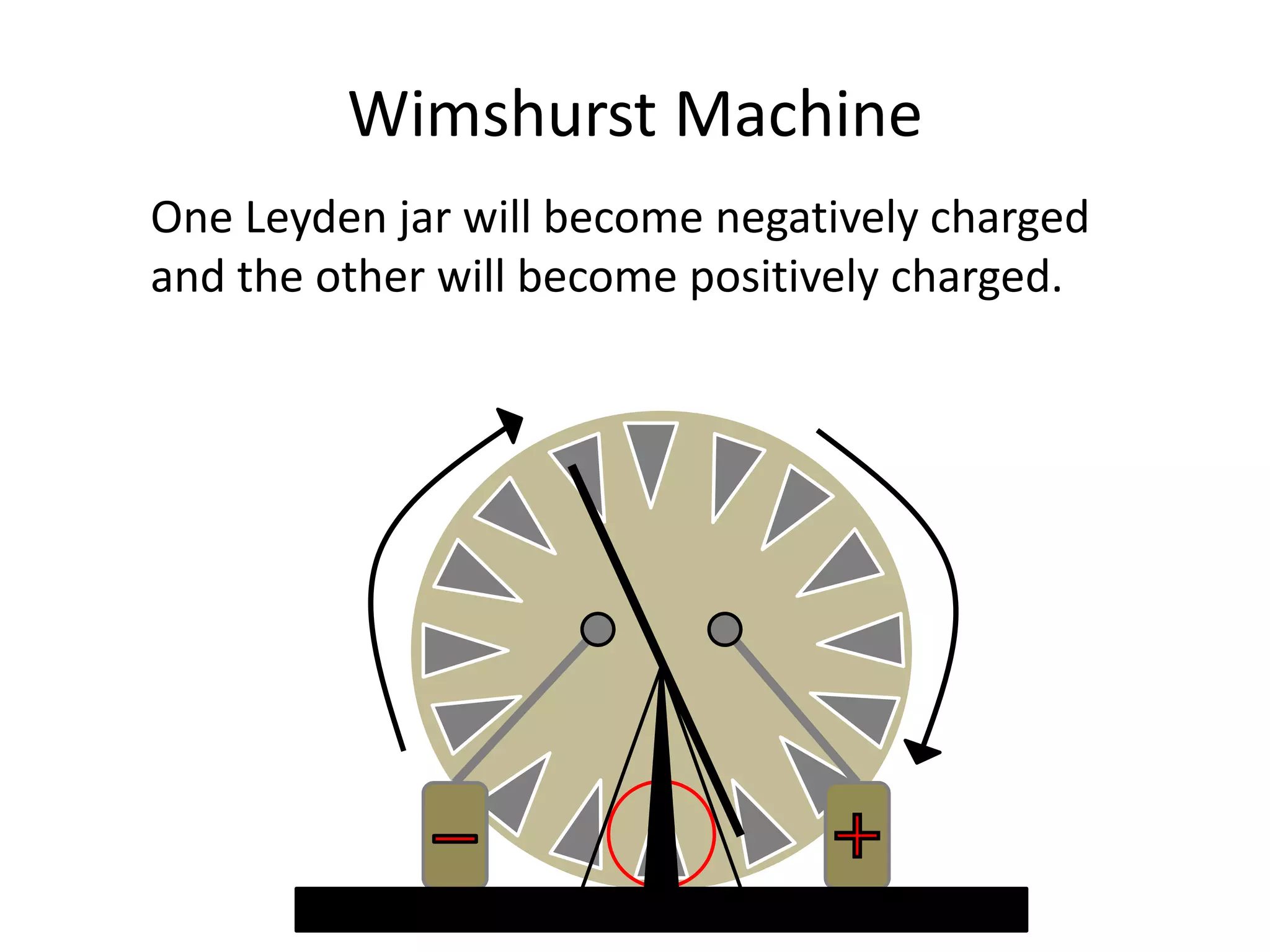
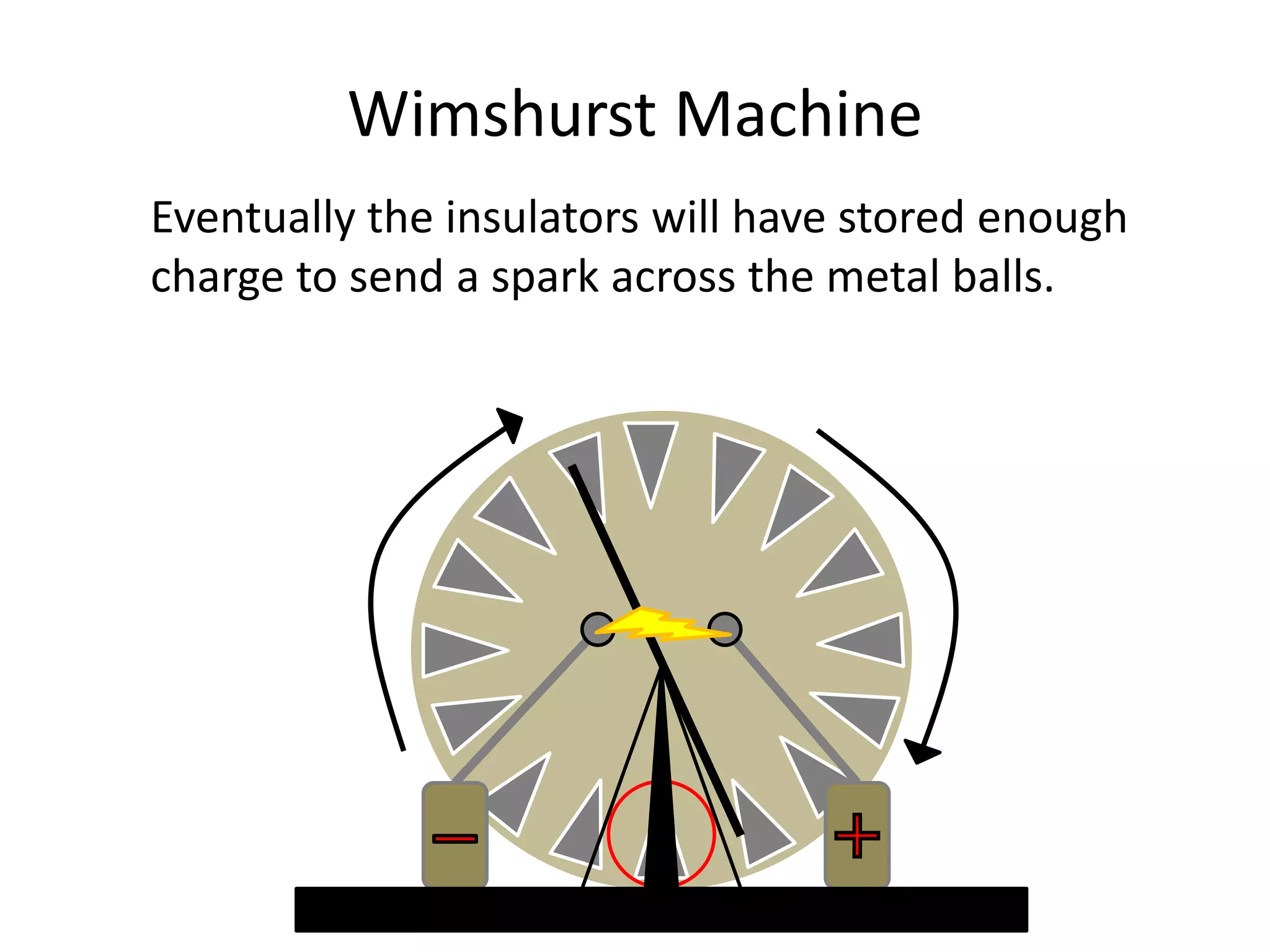
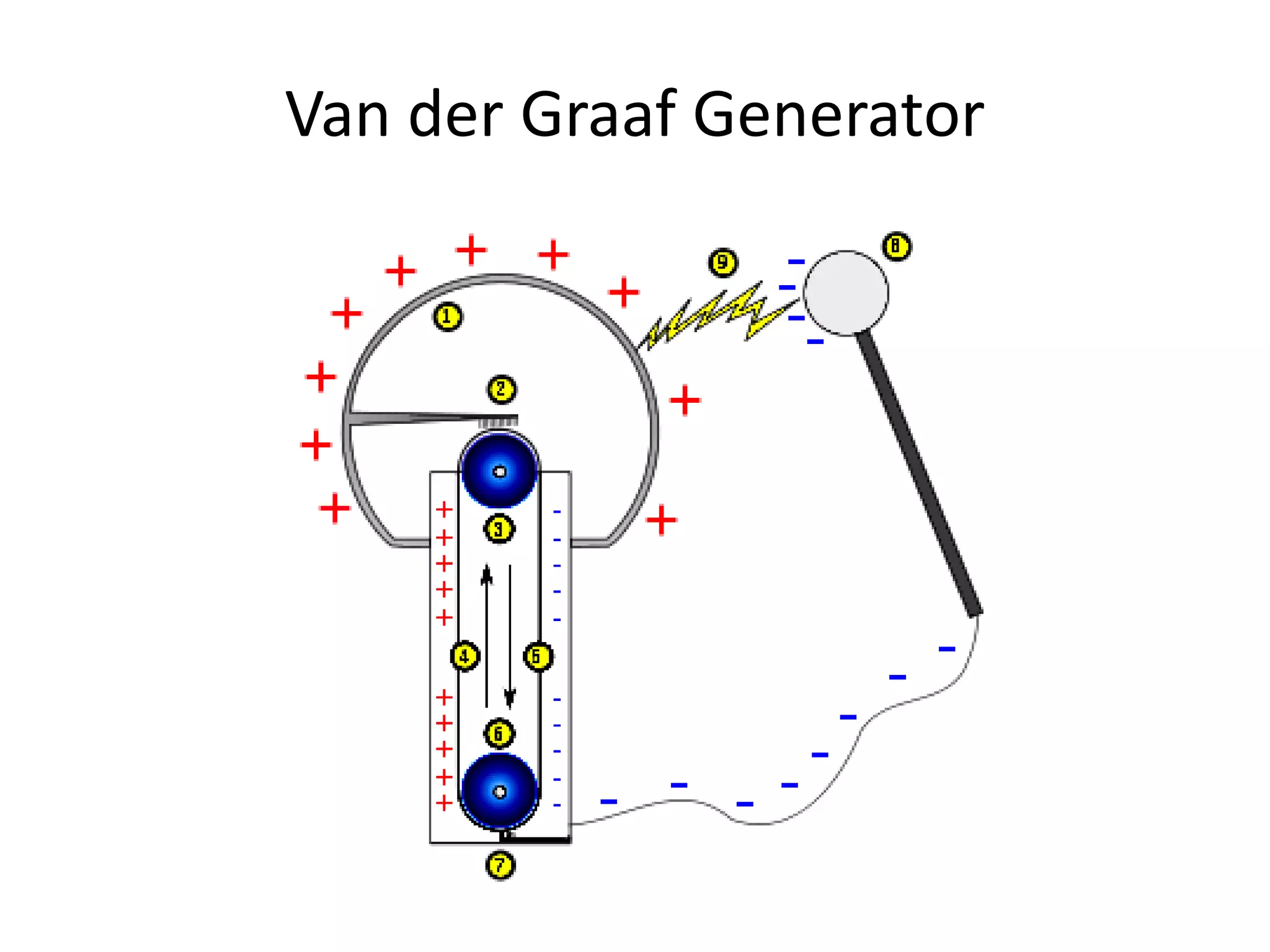
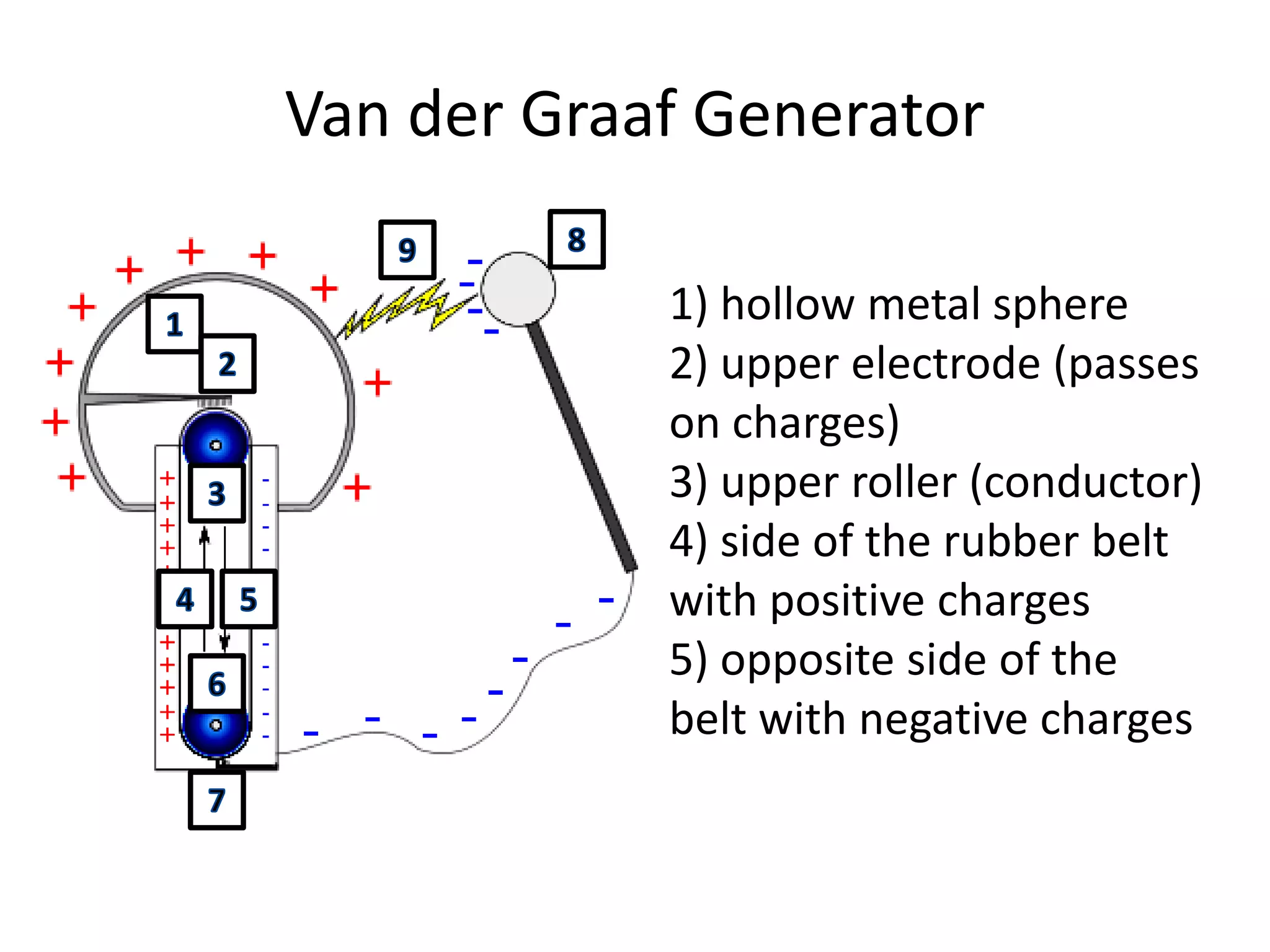
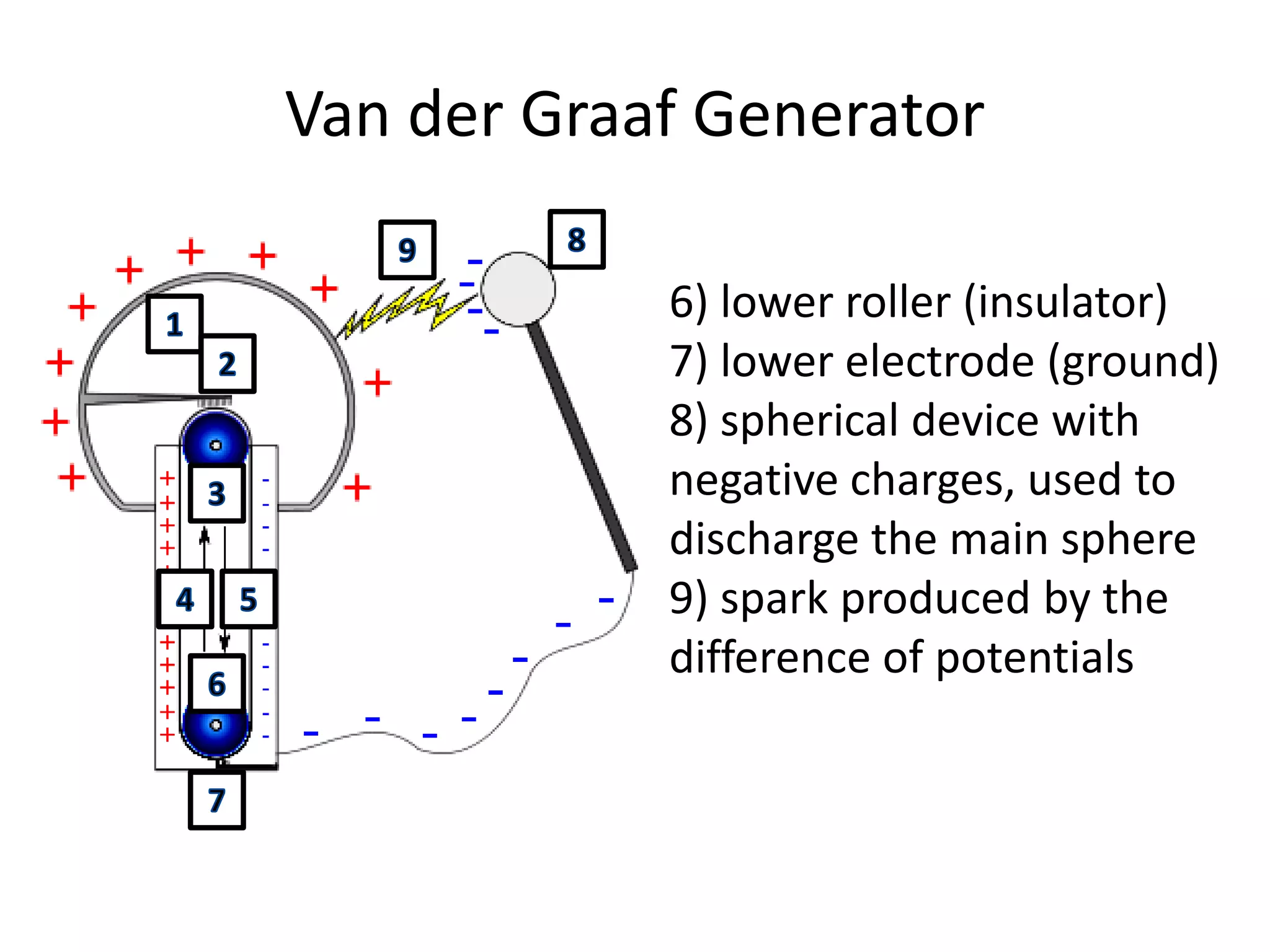
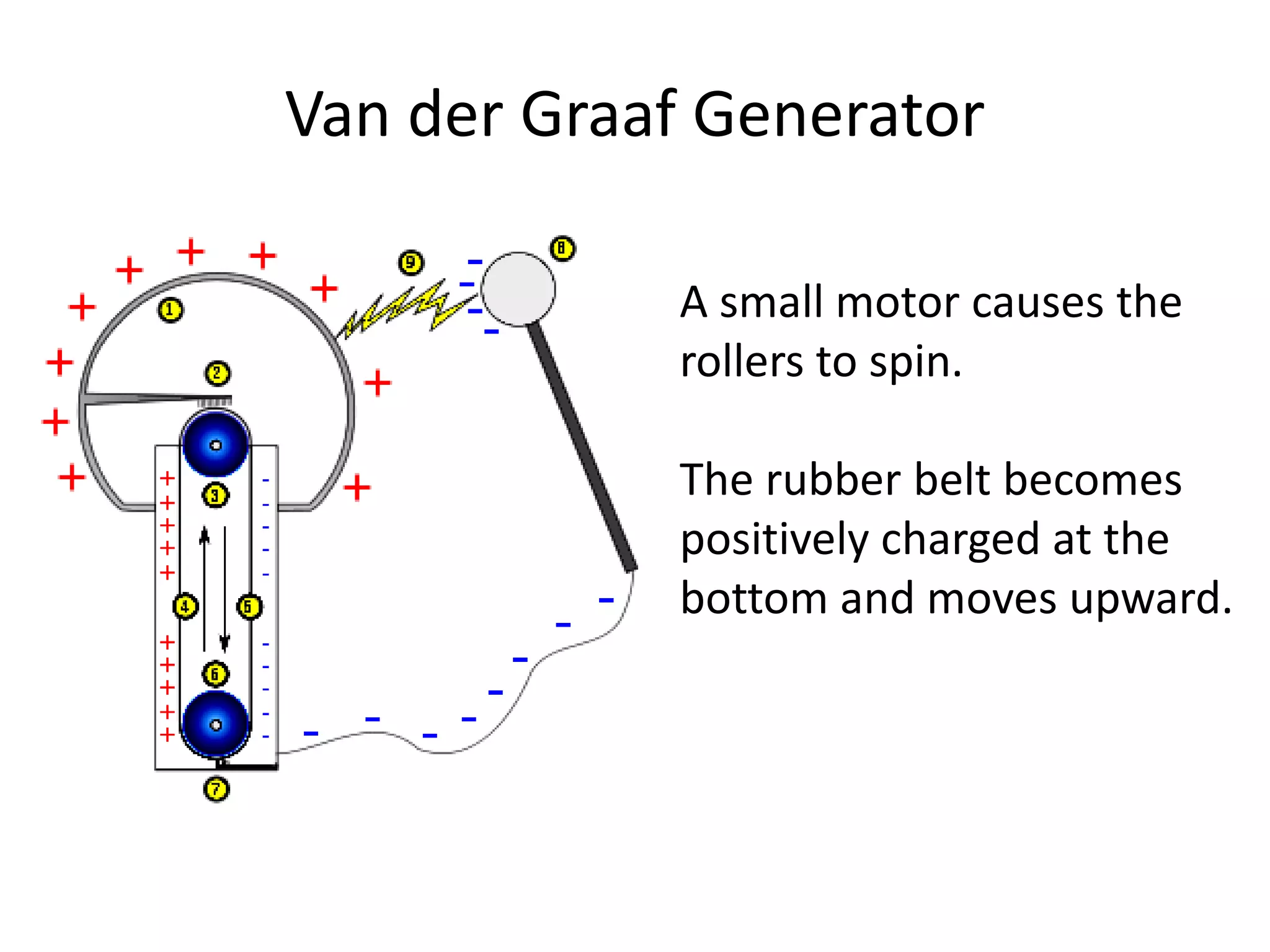
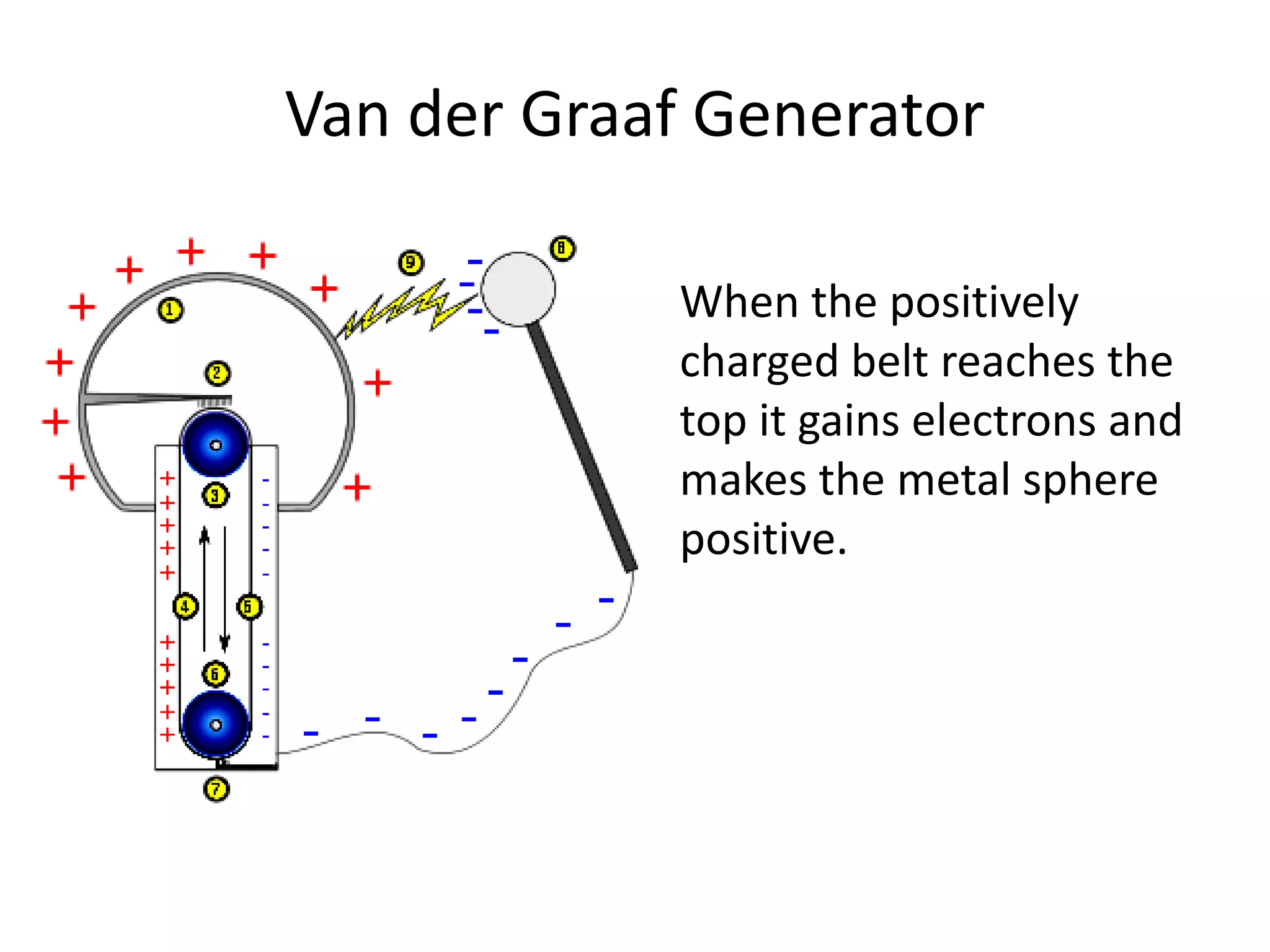
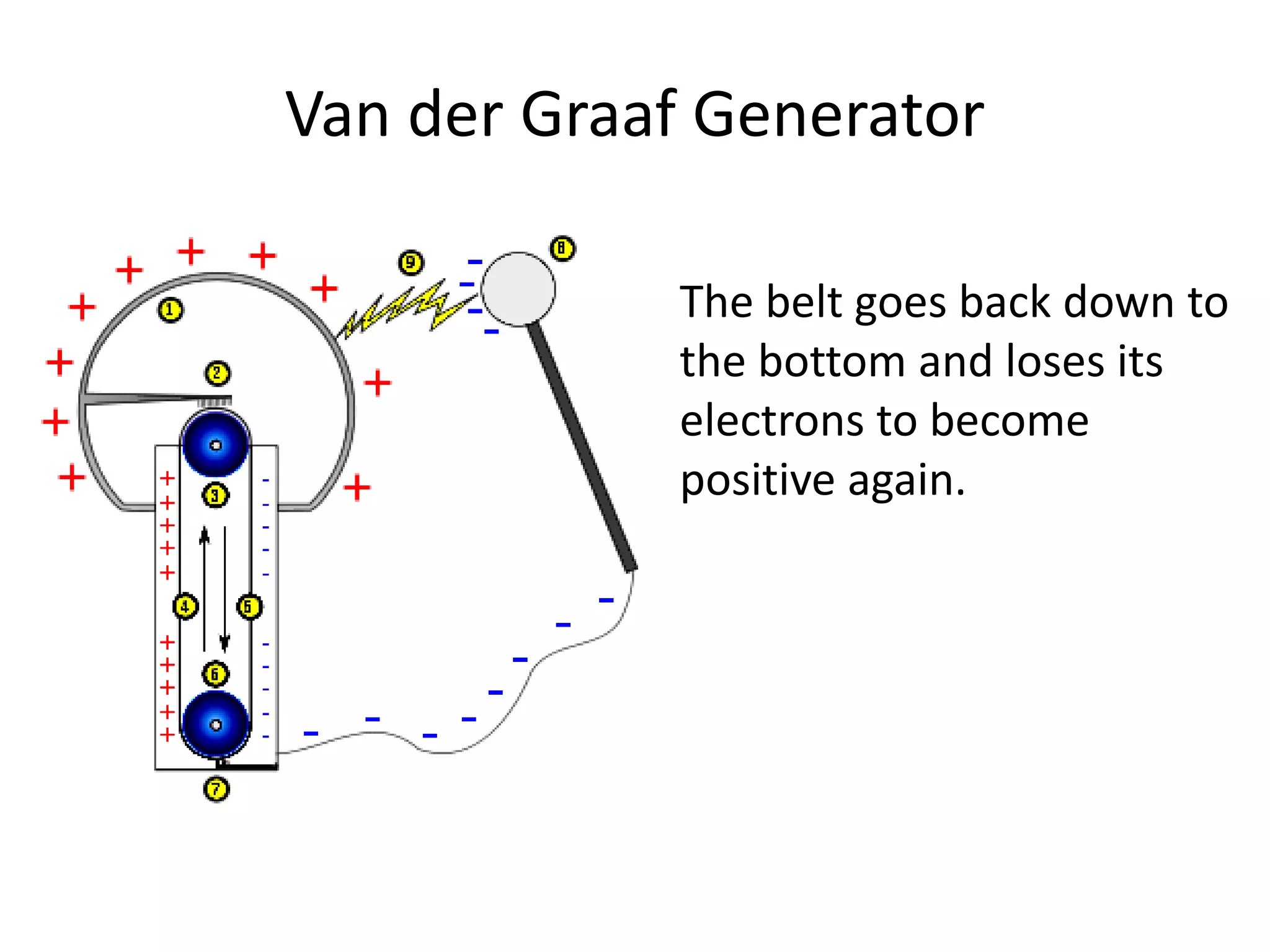
The document describes two types of electrostatic generators: the Wimshurst machine and the Van de Graaf generator. The Wimshurst machine uses two plastic discs to generate static electricity through friction, storing the charges in Leyden jars. The Van de Graaf generator uses a motor-powered rubber belt to induce charges on a hollow metal sphere, creating high voltage static electricity. Both devices produce sparks through the separation of positive and negative charges.