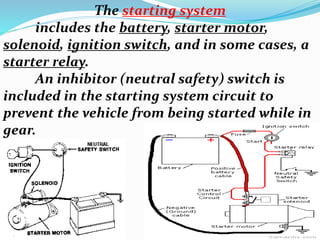
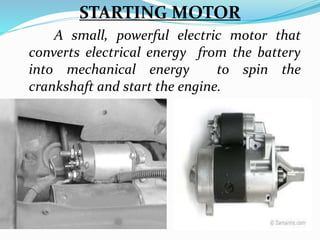
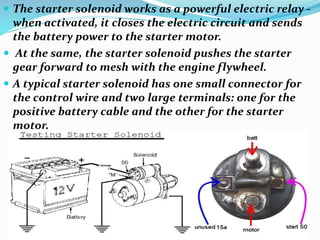
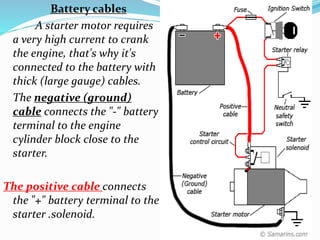
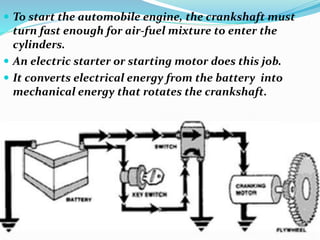
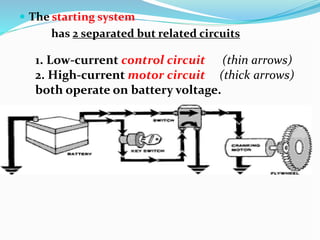
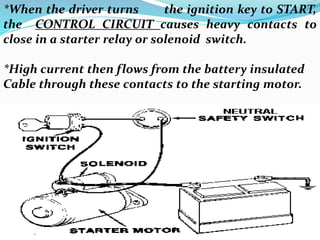
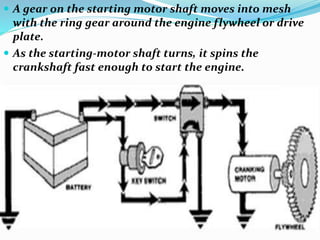
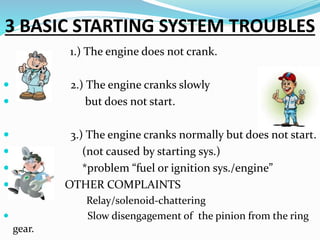
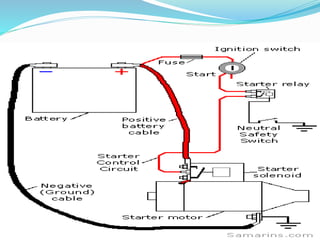
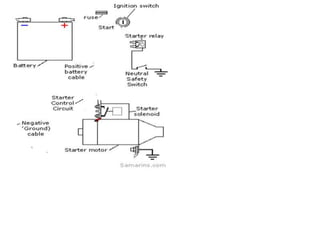
The starting system includes the battery, starter motor, solenoid, ignition switch, and neutral safety switch. The battery stores electrical energy to power the starter motor, a small electric motor that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to spin the crankshaft. The solenoid connects the battery to the starter motor when activated. The ignition switch controls power to the starting system, while the neutral safety switch prevents starting in gear. Together, these components allow the engine to be started electrically.