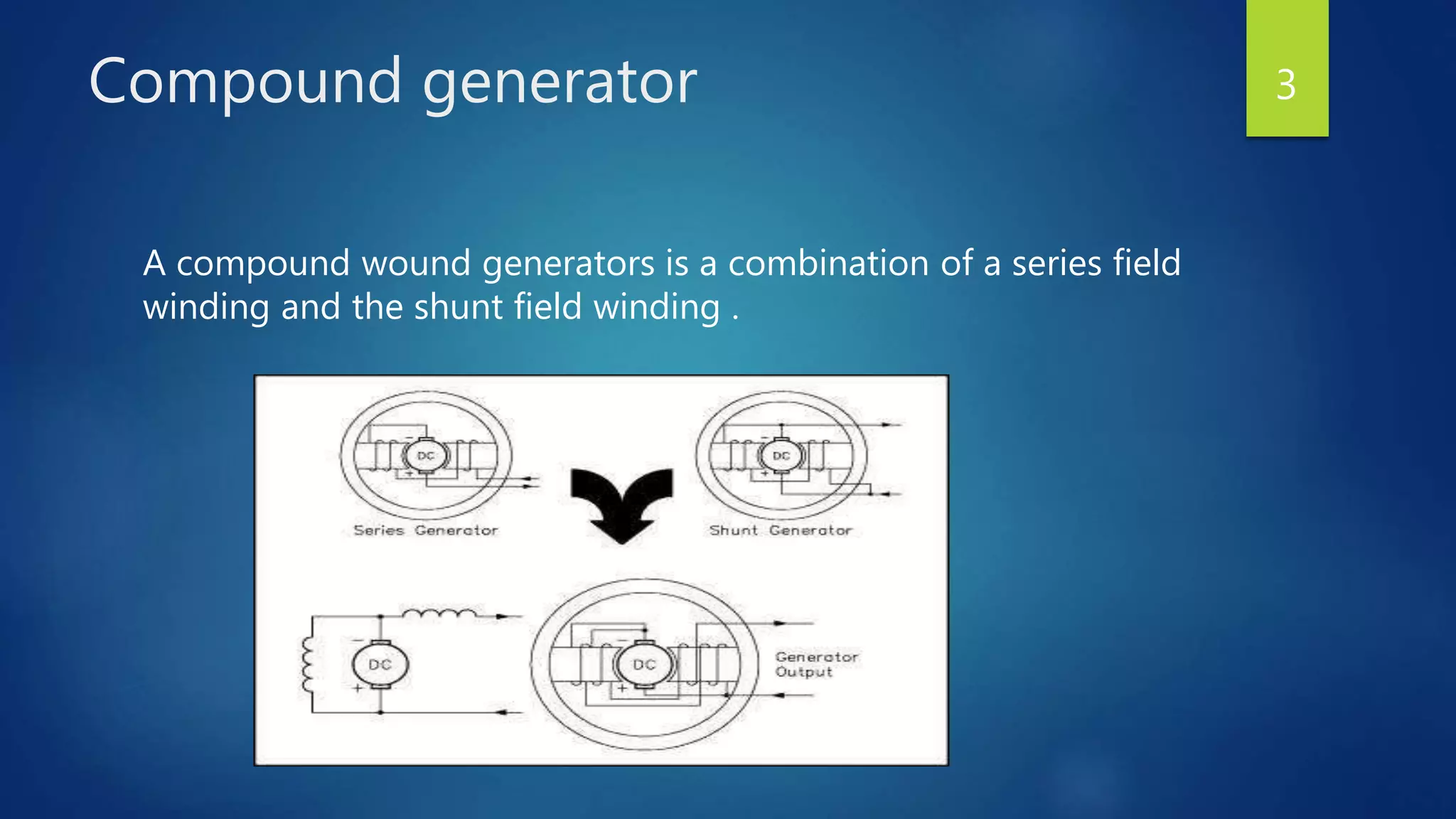
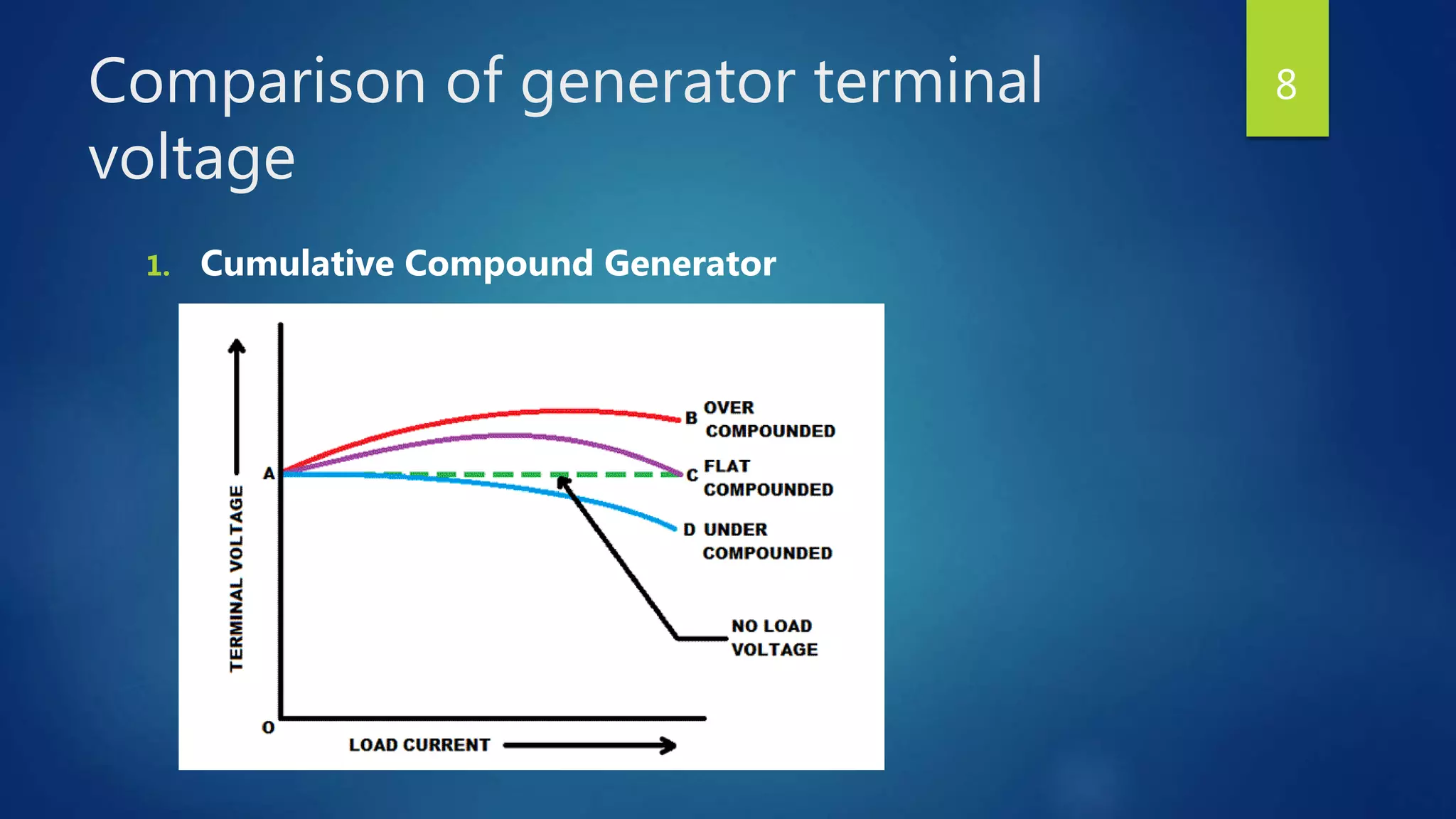
The document discusses compound generators, detailing their types: cumulative and differential. It explains the function of a diverter in adjusting compounding for desired voltage regulation and compares the terminal voltage characteristics of over, flat, and under compound generators. The differences in induced voltage due to opposing magnetic flux in differential generators are also highlighted.