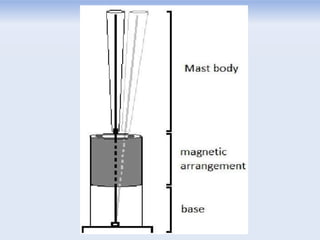
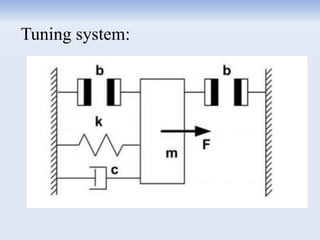
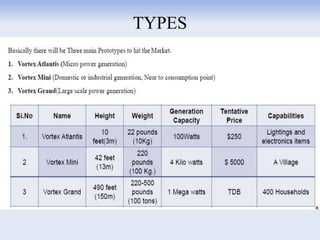
The document discusses the vortex bladeless wind turbine, a device that generates electricity from wind energy without using rotating blades, relying on the phenomenon of vortex shedding. It outlines the construction, working mechanism, advantages such as cost-effectiveness and low noise, as well as disadvantages like lower efficiency compared to traditional turbines. The turbine has potential applications in various sectors including industries, schools, and residential areas.