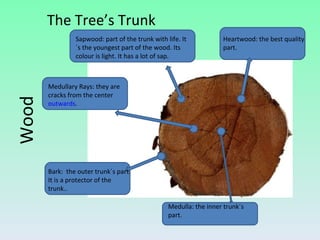
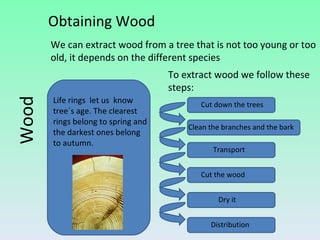
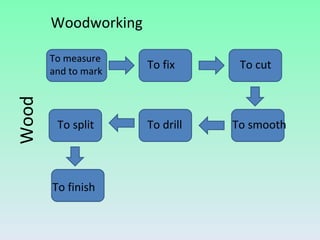
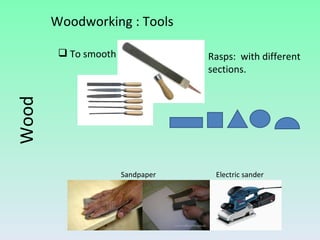
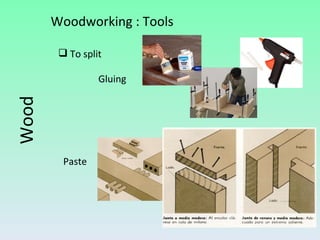
The document summarizes information about wood, including its properties, uses, and processing. It discusses how wood is obtained from trees and processed. Key steps include felling trees, removing branches and bark, cutting the wood, and drying it. Wood has properties like being hygroscopic, a poor conductor of heat and electricity, and varying in hardness between species. Derivatives like plywood, chipboard, and fiberboard are also mentioned. Common woodworking tools are outlined for cutting, fixing, measuring, smoothing, drilling, splitting, and finishing wood.