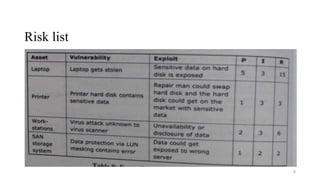
This document outlines a security concept and risk management process. It discusses identifying risks and assets, assessing impact and probability, and determining appropriate risk responses such as acceptance, avoidance, mitigation, and transfer. It also describes common security controls around availability, confidentiality and integrity. Attack vectors like malware, denial of service attacks, social engineering and phishing are examined. Finally, it discusses security patterns for identity and access management, segregation of duties, layered security and cryptography.