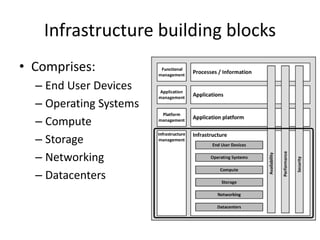
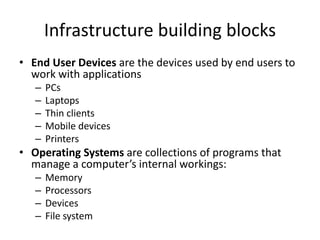
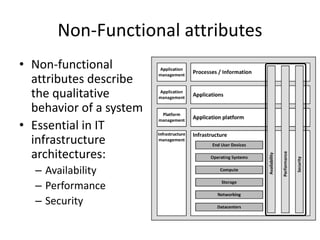
This document provides an introduction to IT infrastructure architecture, defining key concepts and building blocks. It discusses how infrastructures have become more complex with new applications and the need for agility. The definition of infrastructure is examined, noting it depends on perspective. Infrastructure comprises processes/information, applications, application platforms, and underlying hardware/network blocks. Non-functional requirements like availability, performance and security are crucial to infrastructure and often conflicting to balance. Architecture is needed to manage infrastructure design, use and changes.