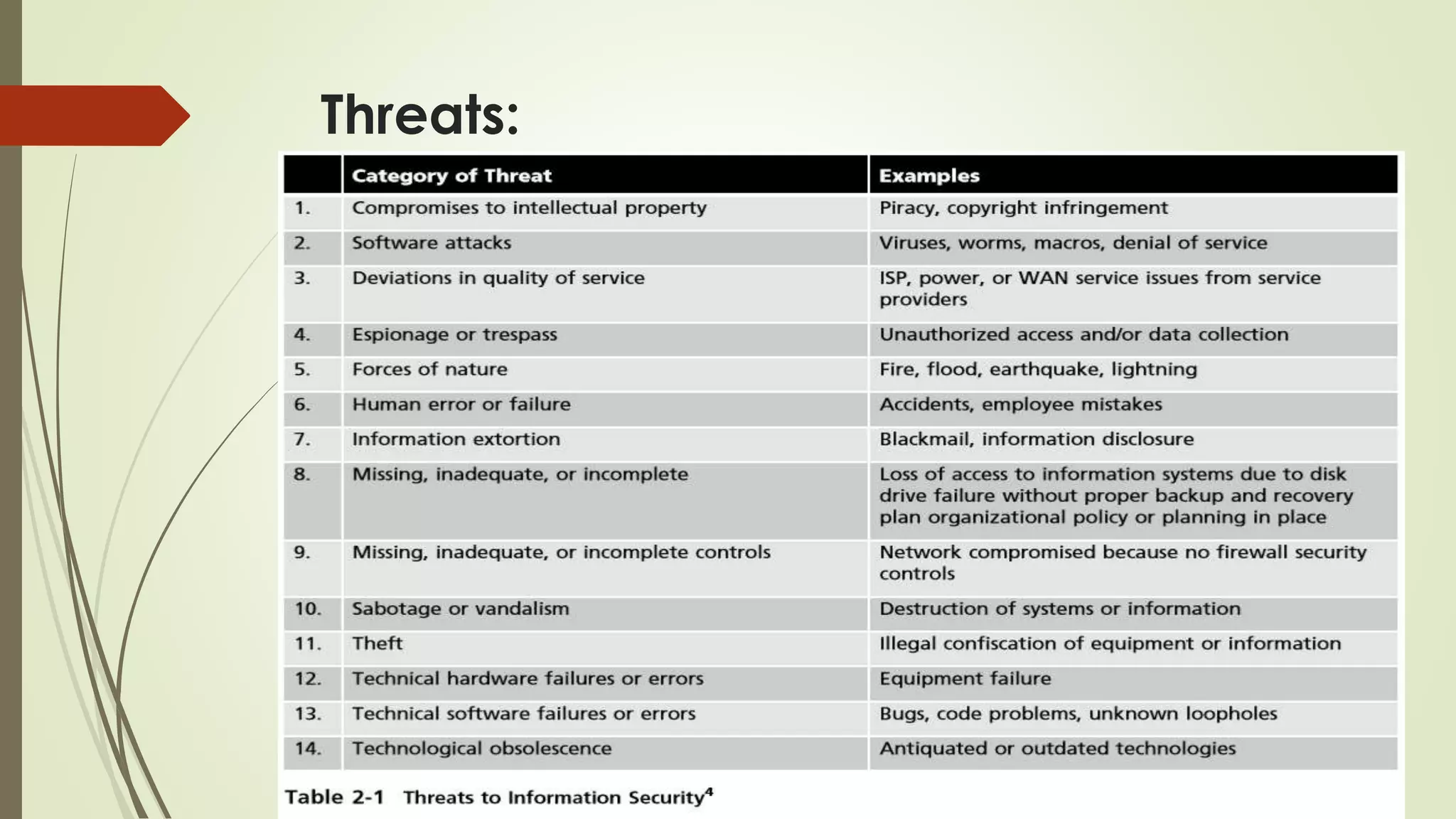
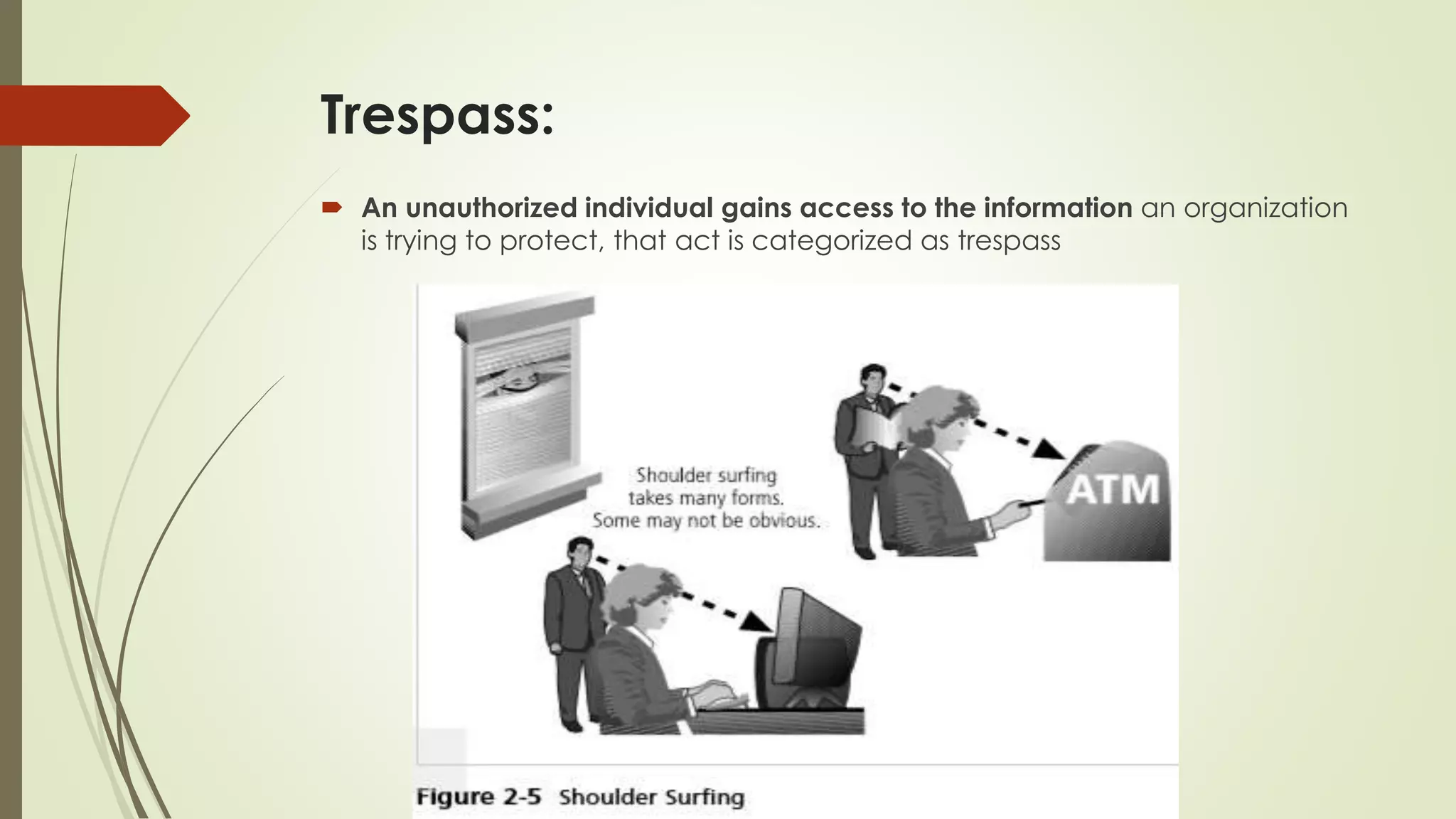
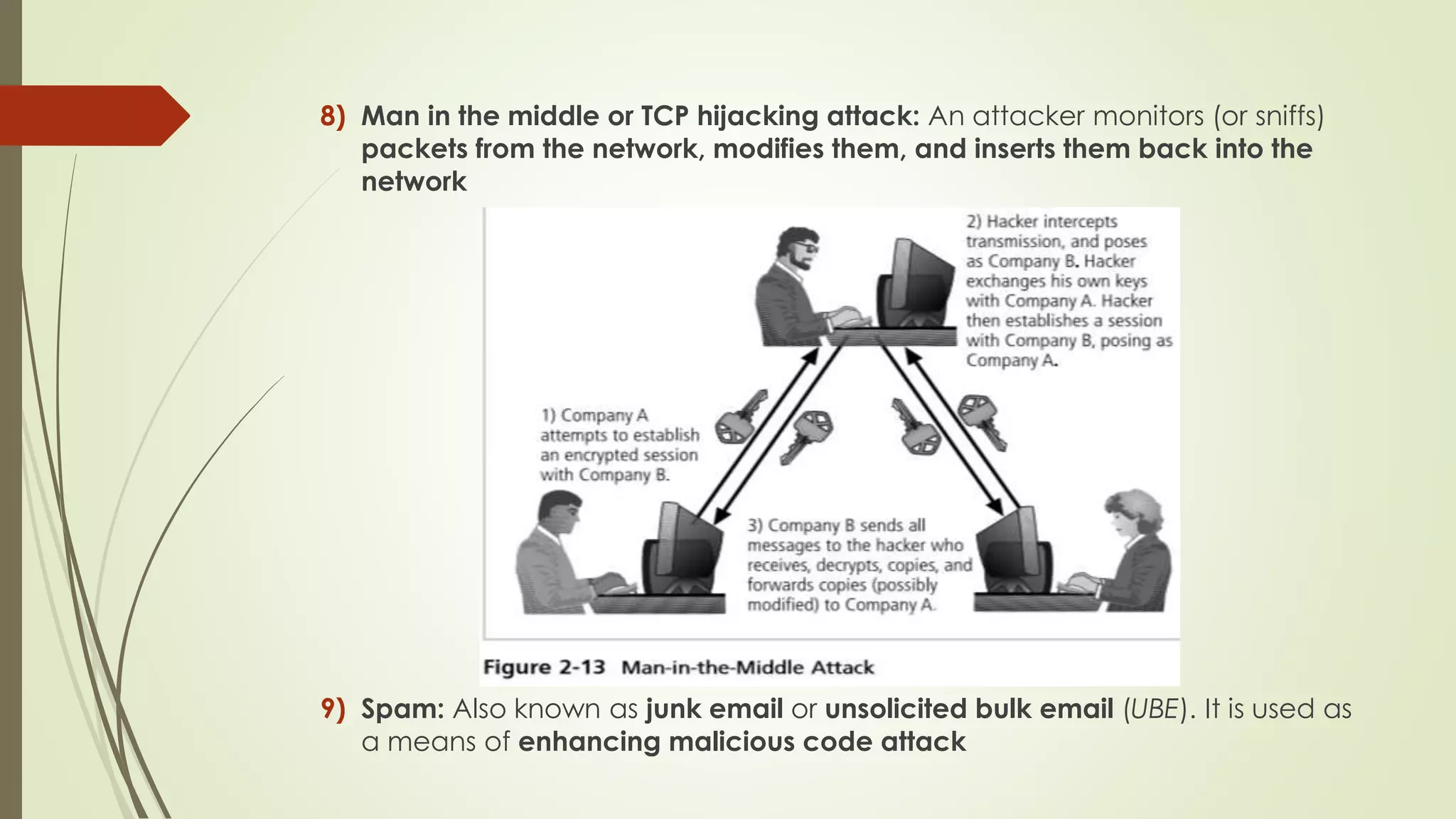
This document discusses why information security is needed for organizations. It provides four key functions of information security: 1) protecting the organization's ability to function, 2) enabling safe application operation, 3) protecting data, and 4) safeguarding technology assets. It then discusses various threats to information security, including intellectual property breaches, software attacks like viruses and worms, service disruptions, unauthorized access, natural disasters, human error, extortion, sabotage, theft, and technical failures. It concludes with discussing secure software development and common security problems.