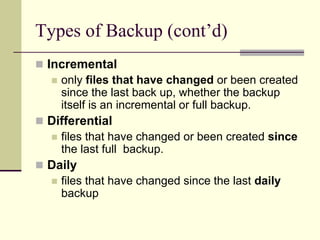
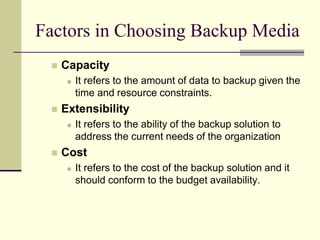
This document discusses data backup, recovery, and disaster planning. It defines backup as creating duplicate copies of important data and explains different backup types (full, incremental, differential). Backup media include tapes, disks, and optical storage. Creating a backup schedule, testing restores, and storing backups securely and offsite are recommended. Disaster recovery involves restoring systems after damage and includes strategies like automated recovery, backing up open files, and maintaining hot, warm or cold backup sites.