The document discusses processes involving ideal gases. It defines reversible and irreversible processes, and describes various types of processes including constant pressure (isobaric) processes. It provides equations to calculate heat, work, internal energy, enthalpy and entropy changes for ideal gases undergoing constant pressure processes in both closed and open/flow systems. Examples include piston-cylinder assemblies and heat exchangers like steam boilers and shell and tube heat exchangers. Practice problems at the end apply the concepts and equations to calculate various thermodynamic properties.
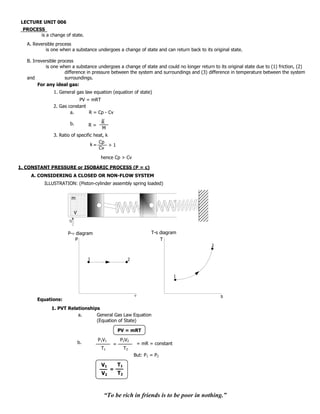
![2. Work Non-Flow, WNF 2
General Formula: WNF = P dV
1
2
= PV
1
= P (V2 - V1) where: P1 = P2 = P
WNF = (P2V2 - P1V1) = PV
= mRT2 - mRT1 = mR( T)
WNF = mR(T2 - T1) = mR( T)
3. Heat Energy, Q
Using NFEE;
Q= U + WNF
= mCv T + mR T
= m (Cv + R) T
Q = mCp T= H
4. Change in Total Internal Energy, U
U = mCv(T2 - T1) = mCv( T)
5. Change in Total Enthalpy, H
H = mCp(T2 - T1) = mCp( T)
6. Change in Total Entropy, S
From; dQ = TdS
dQ
dS =
2
T 2
dT
dS = mCp
1
1 T
S2 - S2 = mCp (ln T2 - ln T1)
T2 V2
S = mCp ln = mCp ln
T1 V1
B. CONSIDERING AN OPEN OR STEADY-FLOW SYSTEM
ILLUSTRATION: WSF
PE1 PE2
KE1 TS KE2
U1 (P = C) U2
Wf1 Wf2
Q
[ Ein = Eout]
PE1 + KE1 + U1 + Wf1 + Q = PE2 + KE2 + U2 + Wf2 + WSF
Q = (PE1 - PE2) + (KE2 - KE1) + (U2 - U1) + (Wf2 - Wf1) + WSF
“Success in any area requires constantly readjusting your behavior as a result of feedback.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/006isobaricprocess-110921083732-phpapp02/85/006-isobaric-process-2-320.jpg)
![Q= PE + KE + U+ Wf + WSF
Recall: H= U+ Wf
Q= PE + KE + H + WSF
When: PE ˜ 0 (z1 ˜ z2)
˜ ˜
KE ˜ 0 (v1 ˜ v2)
˜
Q= H + WSF
But: Q = H
WSF = 0
All ideal heat exchangers: (P=C)
1. Steam generator
a. economizer
b. steam boiler
c. superheater
2. Condenser
3. Evaporators
4. Air preheaters
5. Any shell and tube heat exchangers (water or oiler heaters)
Various heat exchanger configurations
Parallel and counterflow
Shell and tube
Cross-flow Direct-contact
ILLUSTRATION: Steam Boiler
PE1
KE1 SL
U1
Wf1
PE2
Flue gas KE2
D and SV
U2
Wf2
Water tube boiler
[Ein = Eout]
Hg1 + H1 = Hg2 + H2
mgCpgTg1 + mwCpwT1 = mgCpgTg2 + msCpsT2
mgCpg (Tg1 - Tg2) = msCpsT2 - mwCpwT1
mgCpg (Tg1 - Tg2) = ms(h2 - h1)
[Heat energy given off by the flue gas = Heat absorbed by the feed water]
“A good objective of leadership is to help those who are doing poorly to do well
and to help those who are doing well to do even better.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/006isobaricprocess-110921083732-phpapp02/85/006-isobaric-process-3-320.jpg)
![ILLUSTRATION: Shell and Tube type heat exchanger
1 mg
SL
mf
1
2
SL
mf
2 mg
[Heat energy given off by the gas = Heat absorbed by the fluid]
mgCpg(Tg1 - Tg2) = mfCpf(T2 - T1)
mgCpg(Tg1 - Tg2) = mf(h2 - h1)
PROBLEM SET:
1. A 2-kg mass of oxygen expands at a constant-pressure of 172 kPa in a piston-cylinder system from a temperature of 32oC
to a final temperature of 182oC. Determine (a) the heat required, (b) the work, (c) the change in enthalpy, (d) the
change in internal energy. [ ]
2. Methane undergoes a constant pressure process from 6 Mpa and 600 K to 400 K. Determine the heat transfer and work
done per unit mass. [ ]
3. A fresh water heat exchanger is used to cool the oil in a marine engine. Water temperature into the exchanger is 15oC and
the water temperature out is 30oC. Oil temperature in is 150oC and the oil flow is 80 L/min. The oil has a relative
density of 0.9 and specific heat capacity of 1.8 kJ/kg-K. If the outlet oil temperature is 100oC. Determine the flow
rate of water in liters per minute. [ ]
4. A refrigerant flows through a water-cooled condenser at a rate of 25 kg/min. The specific enthalpy of the refrigerant
entering the condenser is 400 kJ/kg, and leaving, is 220 kJ/kg. Determine the mass flow of cooling water through
the condenser for a temperature increase of the water at 10oC, assuming no external heat exchanges. [ ]
5. If 1 kg of air at 250 kPa pressure and 100oC where to be expanded at constant pressure in a closed process to twice the
original volume, determine:
a. the final state of air. [ ]
b. the amount of heat and work involved in the process. [ ]
6. An unknown ideal gas mixture is cooled at constant pressure from 300oC to 80oC. Assuming R=0.524 kJ/kg.K and k=1.39,
find (a) the change in entropy for 2.3 moles of this gas, (b) the final to initial volume ratio of this gas. [
]
7. An ideal gas with a molecular mass of 45 is heated at constant pressure from 135oC to 420oC. If the enthalpy change is
320 kJ/kg, determine (a) the change in internal energy, (b) the change in entropy. [ ]
8. An unknown gas mixture Cp = 0.7136 kJ/kg.K and k=1.35 initially occupies a volume of 435 L at atmospheric pressure and
30oC. Constant pressure heating causes the temperature of the gas to increase to 100oC. Determine (a) U, (b)
H (c) WNF (d) V. [ ]
9. Air is cooled at a constant pressure of 1 atm from an initial specific volume of 1.34 m3/kg to a final density of 1.205 kg/m3.
for the process and 2.5 kg of air, find (a) the change in internal energy (b) the change in enthalpy and (c) the
change in entropy. [ ]
10. 8 kg of a gas, R = 280 J/kg.K and Cv = 0.78 kJ/kg.K undergo a reversible nonflow constant pressure process from V1 = 1.2
m3, P1 = 700 kPaa to a state where t2 = 480oC. Find (a) the change in internal energy, change in enthalpy, Q, WNF
(b) if the process had been reversible steady flow type with change in PE and KE are zero, find WSF. [
]
“People perform better when leadership roles are defined.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/006isobaricprocess-110921083732-phpapp02/85/006-isobaric-process-4-320.jpg)
