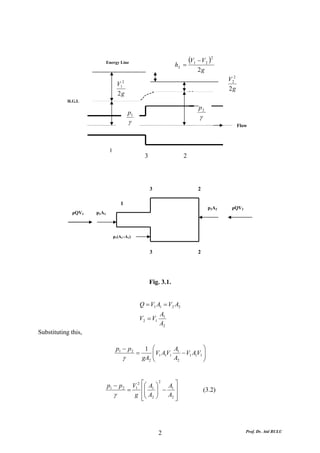
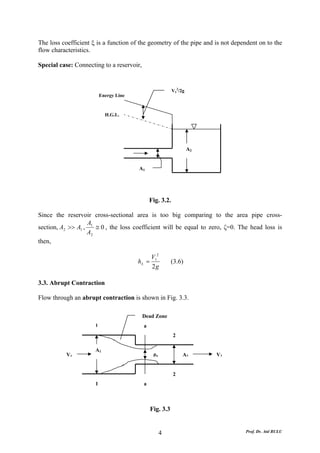
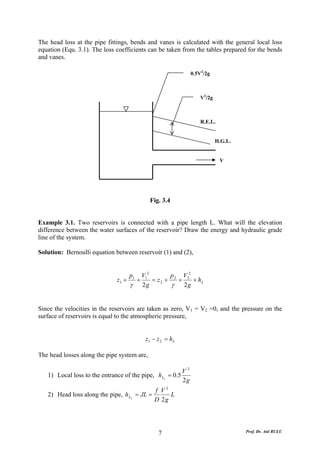
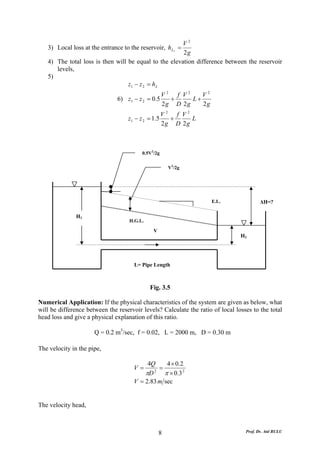
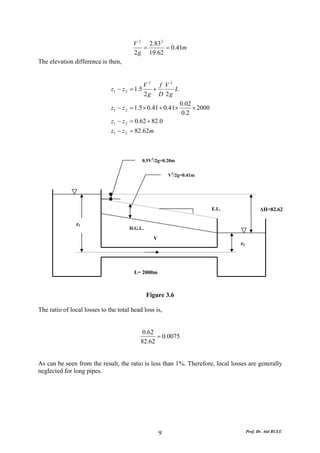
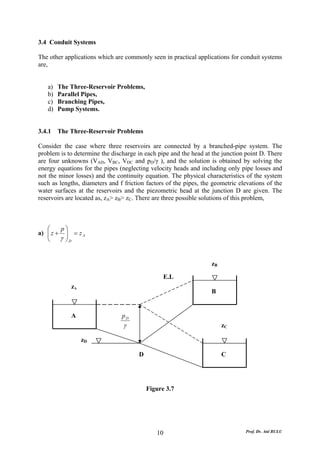
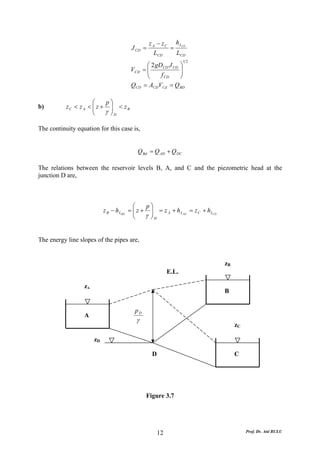
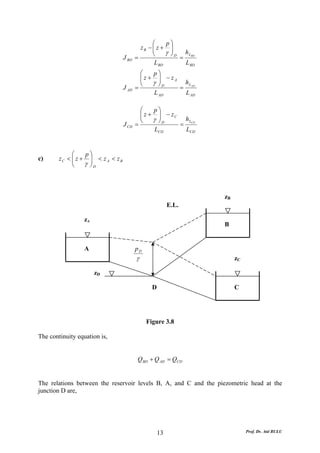
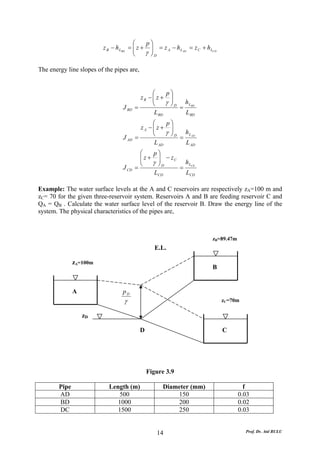
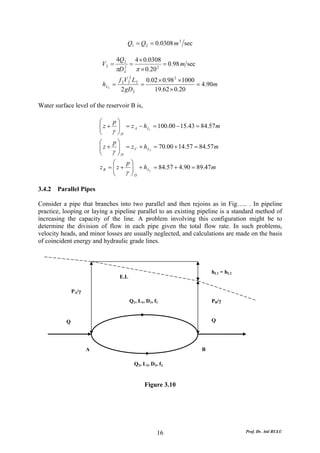
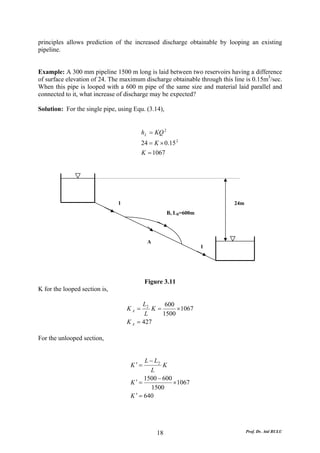
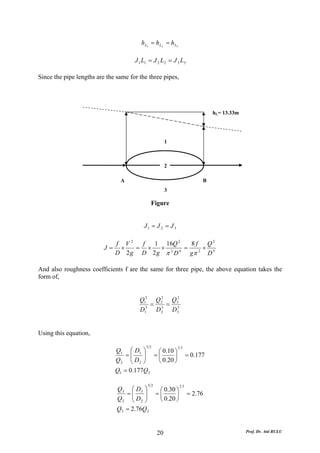
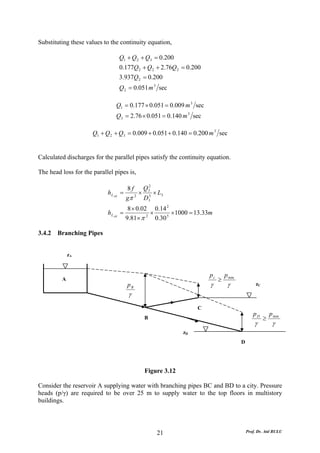
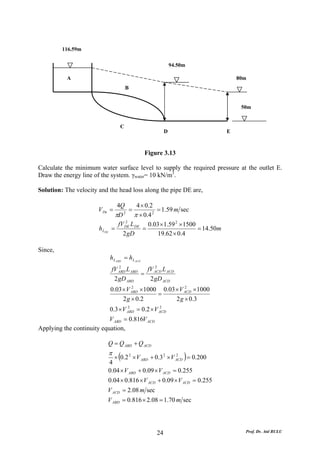
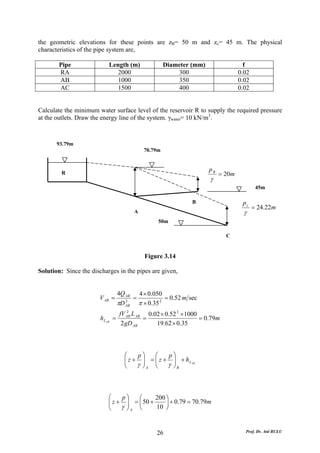
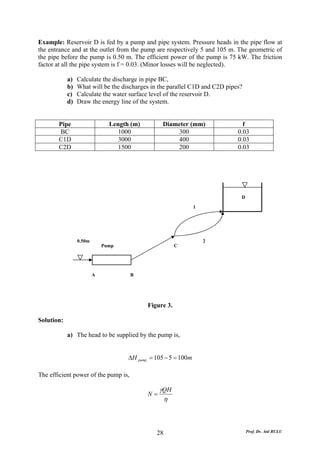
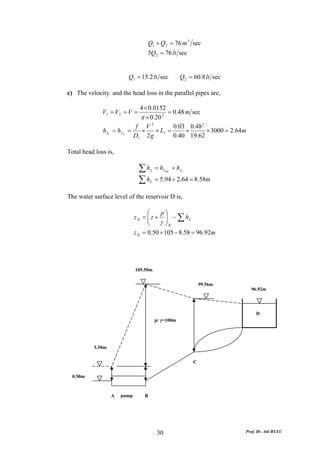
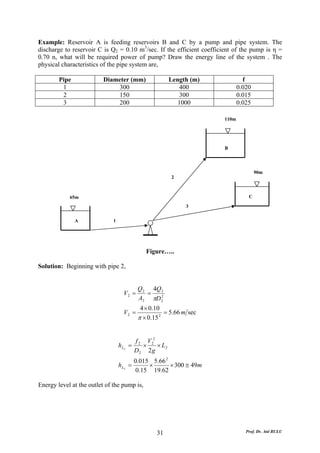
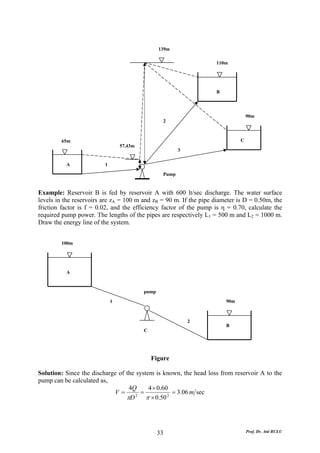
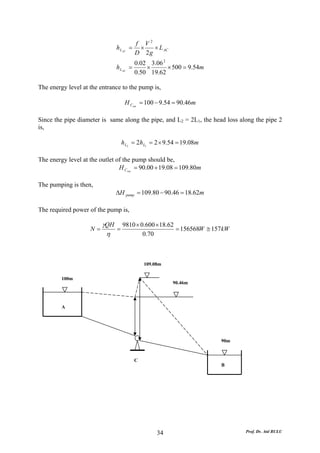
This document discusses local energy (head) losses that occur in pipes due to changes in pipe geometry or flow direction. It introduces minor losses that are proportional to the velocity head and defined by a loss coefficient. Specific minor losses are examined for abrupt enlargements and contractions using the continuity, momentum, and Bernoulli equations. Loss coefficients are determined experimentally and provided in tables based on the area ratio. The total head loss in a pipe system is calculated considering losses at the pipe entrance/exit and along the length. Local losses are generally negligible for long pipes.