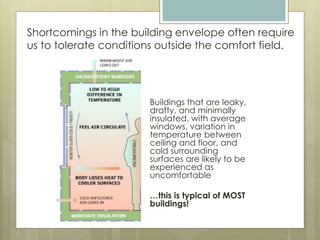
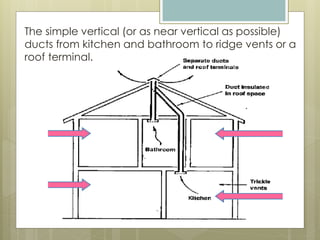
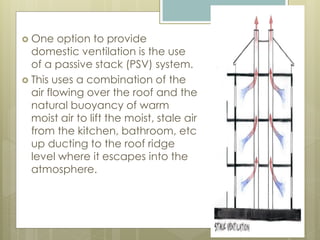
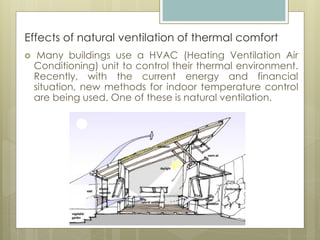
This document discusses thermal comfort and factors that affect it. Thermal comfort is defined as a psychological state of satisfaction with one's thermal environment. It is affected by environmental factors like air temperature, humidity, air speed, and radiant heat as well as personal factors like activity level and clothing. Proper ventilation and control of temperature, humidity, and air speed are needed to maintain thermal comfort. The building envelope and mechanical systems work together to provide thermal comfort by minimizing heat transfer and maintaining a balance between heat production and heat loss in the body.