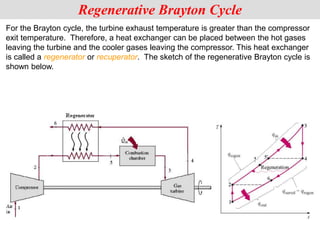
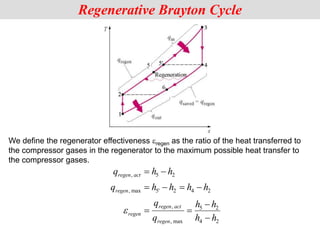
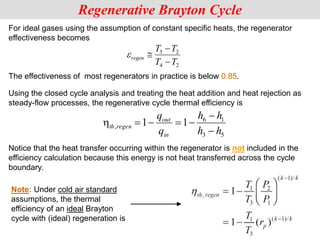
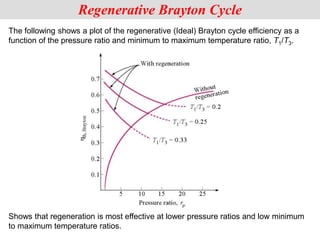
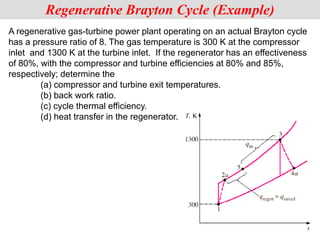
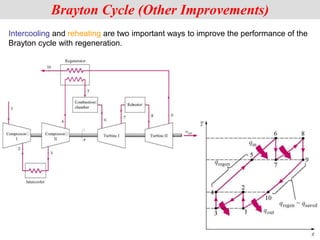
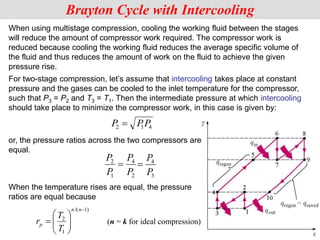
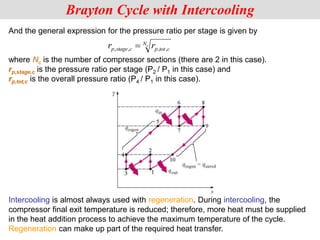
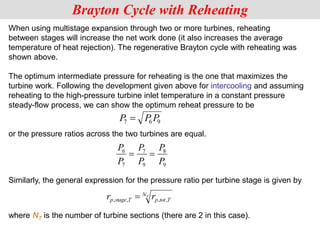
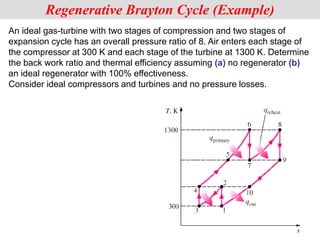
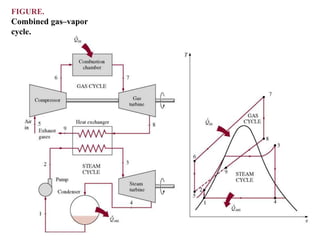
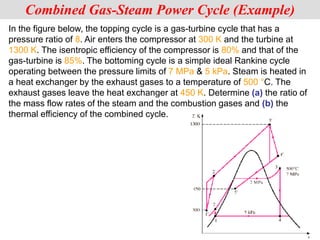
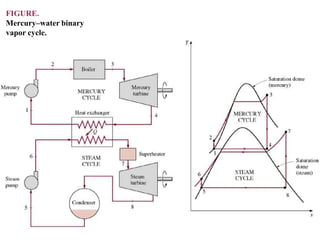
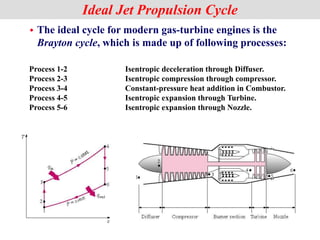
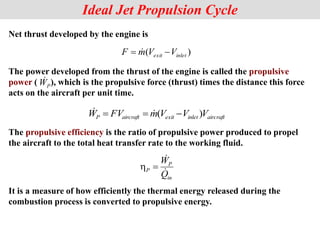
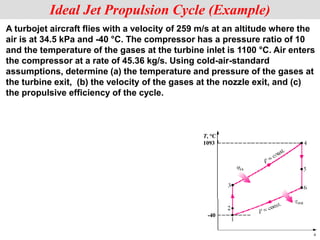
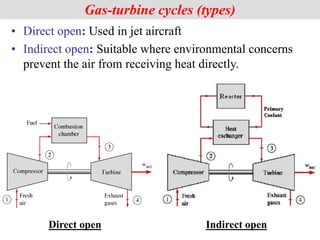
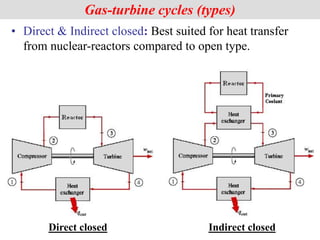
The document discusses different types of gas turbine cycles including direct open, indirect open, direct closed, and indirect closed cycles. It then focuses on the ideal Brayton cycle and how the net work output varies with pressure ratio, reaching a maximum at a specific pressure ratio. The regenerative Brayton cycle is introduced as an improvement where heat is recouped through a regenerator. Intercooling and reheating are also discussed as ways to further improve the cycle performance. Combined cycles, which use both gas and steam turbines, provide higher efficiencies than gas turbines alone. The ideal jet propulsion cycle for aircraft is described, where the turbine power is only used to drive the compressor.

![Let's take a closer look at the effect of the
pressure ratio on the net work done.
w w w
C T T C T T
C T T T C T T T
C T
r
C T r
net turb comp
p p
p p
p
p
k k p p
k k
( ) ( )
( / ) ( / )
( ) ( )
( )/
( )/
3 4 2 1
3 4 3 1 2 1
3 1 1
1
1 1
1
1
1
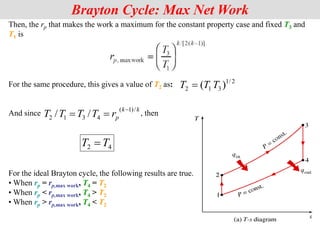
For fixed values of Tmin and Tmax, the net work of the Brayton cycle first increases with the
pressure ratio, then reaches a maximum at rp=(Tmax/Tmin)k/[2(k-1)], and finally decreases. What
happens to th and wnet as the pressure ratio rp is increased? Consider the T-s diagram
for the cycle and note that the area enclosed by the cycle represents the net work
done.
Brayton Cycle: Max Net Work](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9lecturebraytoncycle-210503174820/85/Brayton-cycle-Gas-Cycle-Introduction-4-320.jpg)
![Note that the net work is zero when
/( 1)
3
1
1
k k
p p
T
r and r
T
For fixed T3 and T1, the pressure ratio that makes the work a maximum is obtained
from:
dw
dr
net
p
0
This is easier to do if we let X = rp
(k-1)/k
w C T
X
C T X
net p p
3 1
1
1
1
( ) ( )
dw
dX
C T X C T
net
p p
3
2
1
0 1 1 0 0
[ ( ) ] [ ]
Solving for X ,
Brayton Cycle: Max Net Work](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9lecturebraytoncycle-210503174820/85/Brayton-cycle-Gas-Cycle-Introduction-5-320.jpg)
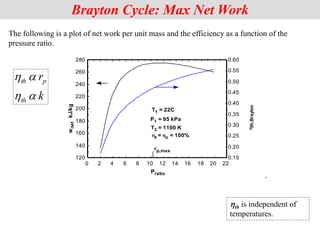

![The net power of the cycle, for constant specific heats,
k
k
p
C
k
k
p
T
p
net
r
r
T
T
T
c
m
W /
)
1
(
/
)
1
(
1
3
1
1
1
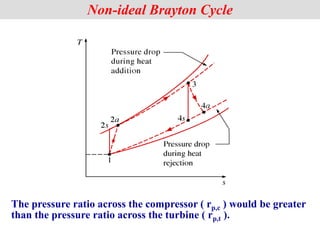
Non-ideal Brayton Cycle
]
)
(
)
[(
)]
(
)
[( 1
2
4
3
1
2
4
3
C
s
T
s
p
p
net
T
T
T
T
c
m
T
T
T
T
c
m
W
in
net
th
Q
W
and in terms of the min and max temperatures and pressure ratio,
The heat added in the cycle, for constant specific heats, is given by
C
k
k
p
p
in
p
r
T
T
T
c
m
T
T
c
m
Q
1
)
(
)
(
/
)
1
(
1
1
3
2
3
The efficiency of the cycle can then be obtained by dividing the
above two equations,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9lecturebraytoncycle-210503174820/85/Brayton-cycle-Gas-Cycle-Introduction-10-320.jpg)