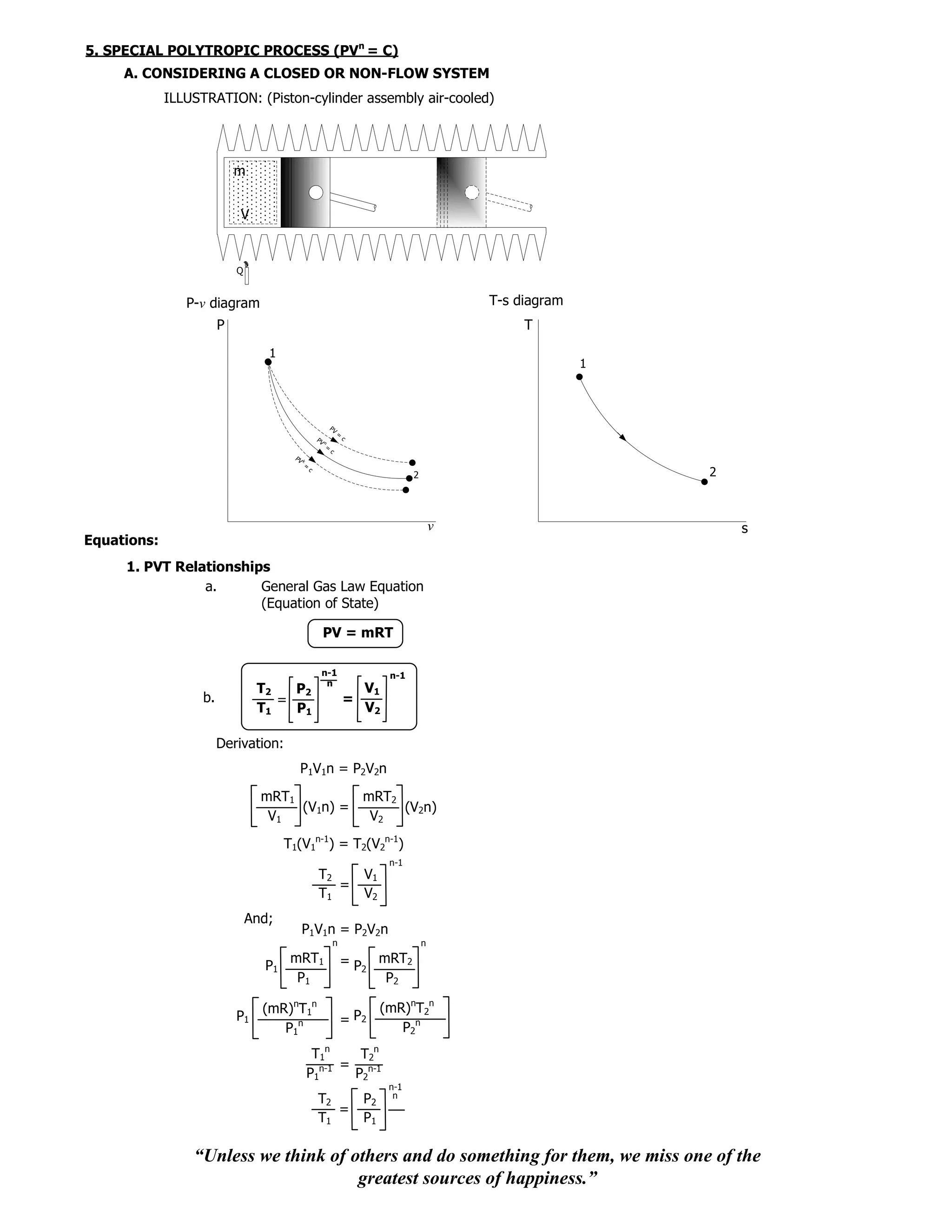
The document discusses various thermodynamic processes including constant temperature, isothermal, isobaric, and adiabatic processes. It provides the equations of state and relationships between pressure, volume, temperature, internal energy, enthalpy, entropy, and work for both closed and open systems undergoing these processes. The summary focuses on defining the key thermodynamic processes and relating the relevant process variables using mathematical equations.
![4. Change in Total Internal Energy, U
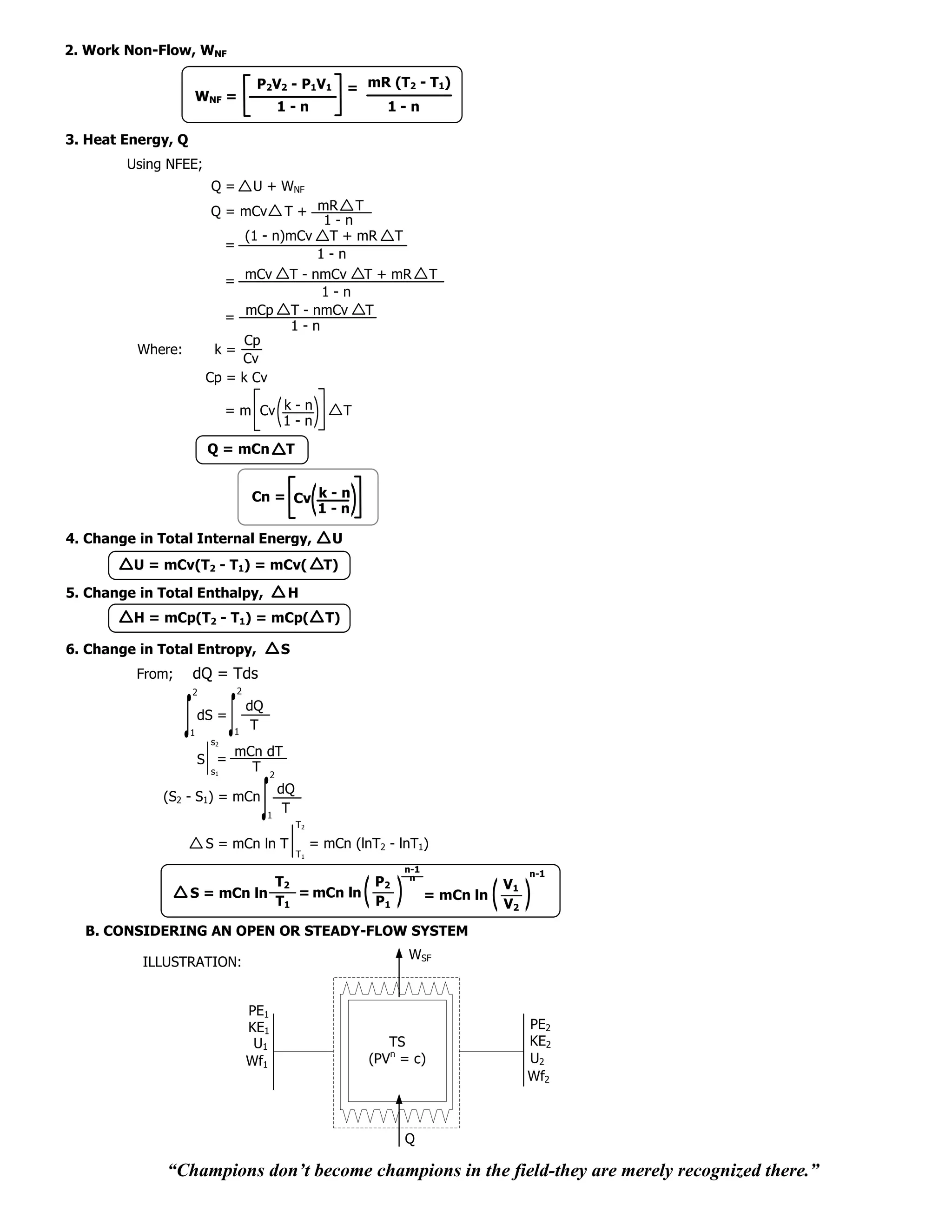
U = mCv(T2 - T1) = mCv( T)
U=0
5. Change in Total Enthalpy, H
H = mCp(T2 - T1) = mCp( T)
H=0
6. Change in Total Entropy, S
From; dQ = Tds
dQ
dS =
2
T
2
dS = 1 dQ = Q
T 1 T
1
V2
mRT1 ln
V1
S2 - S1 =
T
V2 P1
S = mR ln = mR ln
V1 P2
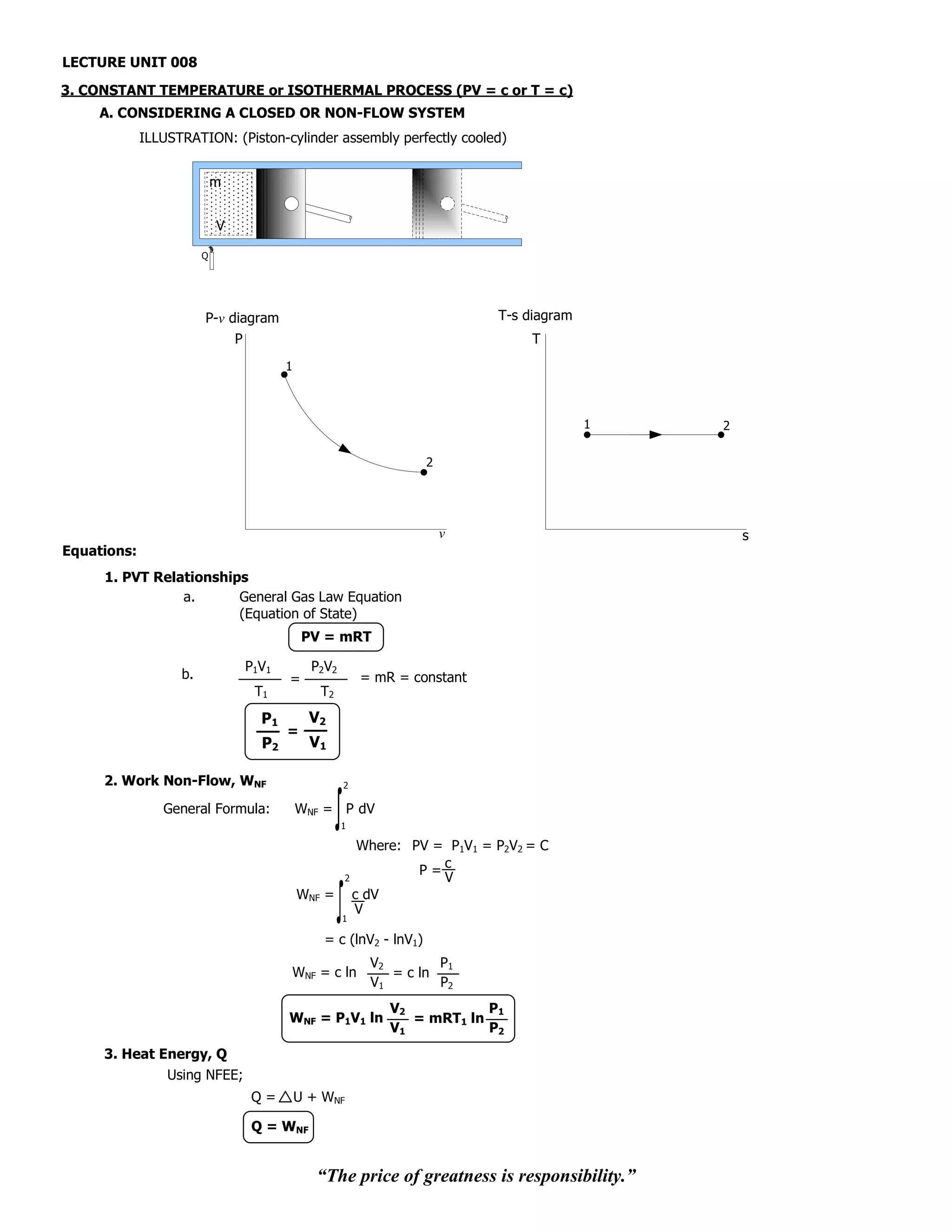
B. CONSIDERING AN OPEN OR STEADY-FLOW SYSTEM
ILLUSTRATION: WSF
PE1 PE2
KE1 KE2
TS
U1 U2
(PV = c)
Wf1 Wf2
Q
[Ein = Eout]
PE1 + KE1 + U1 + Wf1 + Q = PE2 + KE2 + U2 + Wf2 + WSF
Q = (PE1 - PE2) + (KE2 - KE1) + (U2 - U1) + (Wf2 - Wf1) + WSF
Q= PE + KE + U+ Wf + WSF
Recall: H= U+ Wf
Q= PE + KE + H + WSF
When: PE ˜ 0 (z1 ˜ z2)
˜ ˜
KE ˜ 0 (v1 ˜ v2)
˜
Q= H + WSF
But: H=0
Q = WSF
“There is nothing training cannot do. Nothing is above its reach.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/008isothermalisentropicpolytropicprocess-110921083746-phpapp01/75/008-isothermal-isentropic_polytropic_process-2-2048.jpg)
![2. Work Non-Flow, WNF 2
General Formula: WNF = P dV
1
Where: PVk = P1V1k = P2V2k = C
P = c V-k
2
WNF = cV-k dV
1
V2
V-k+1
=c
-k +1
V1
k.
P2V2 V2-k+1 - P1V1k . V1-k+1
=c
-k + 1
P2V2 - P1V1 = mR (T2 - T1)
WNF =
1-k 1-k
3. Heat Energy, Q
2
Q = Tds
1
Q=0
Hence, if we using NFEE, WNF can also be solved by:
Q= U + WNF
WNF = - U
4. Change in Total Internal Energy, U
U = mCv(T2 - T1) = mCv( T)
5. Change in Total Enthalpy, H
H = mCp(T2 - T1) = mCp( T)
6. Change in Total Entropy, S
2
From; Q = Tds
1
2
dQ
S=
1
T
S=0
B. CONSIDERING AN OPEN OR STEADY-FLOW SYSTEM
ILLUSTRATION: WSF
PE1 PE2
KE1 KE2
TS
U1 U2
(PVk = c)
Wf1 Wf2
Q=0
[Ein = Eout]
PE1 + KE1 + U1 + Wf1 + Q = PE2 + KE2 + U2 + Wf2 + WSF
“Leaders always find a way to make things happen.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/008isothermalisentropicpolytropicprocess-110921083746-phpapp01/75/008-isothermal-isentropic_polytropic_process-4-2048.jpg)
![[Ein = Eout]
PE1 + KE1 + U1 + Wf1 + Q = PE2 + KE2 + U2 + Wf2 + WSF
Q = (PE1 - PE2) + (KE2 - KE1) + (U2 - U1) + (Wf2 - Wf1) + WSF
Q= PE + KE + U+ Wf + WSF
When: PE ˜ 0 (z1 ˜ z2)
KE ˜ 0 (v1 ˜ v2)
˜ ˜
Q= H + WSF
WSF = Q - H
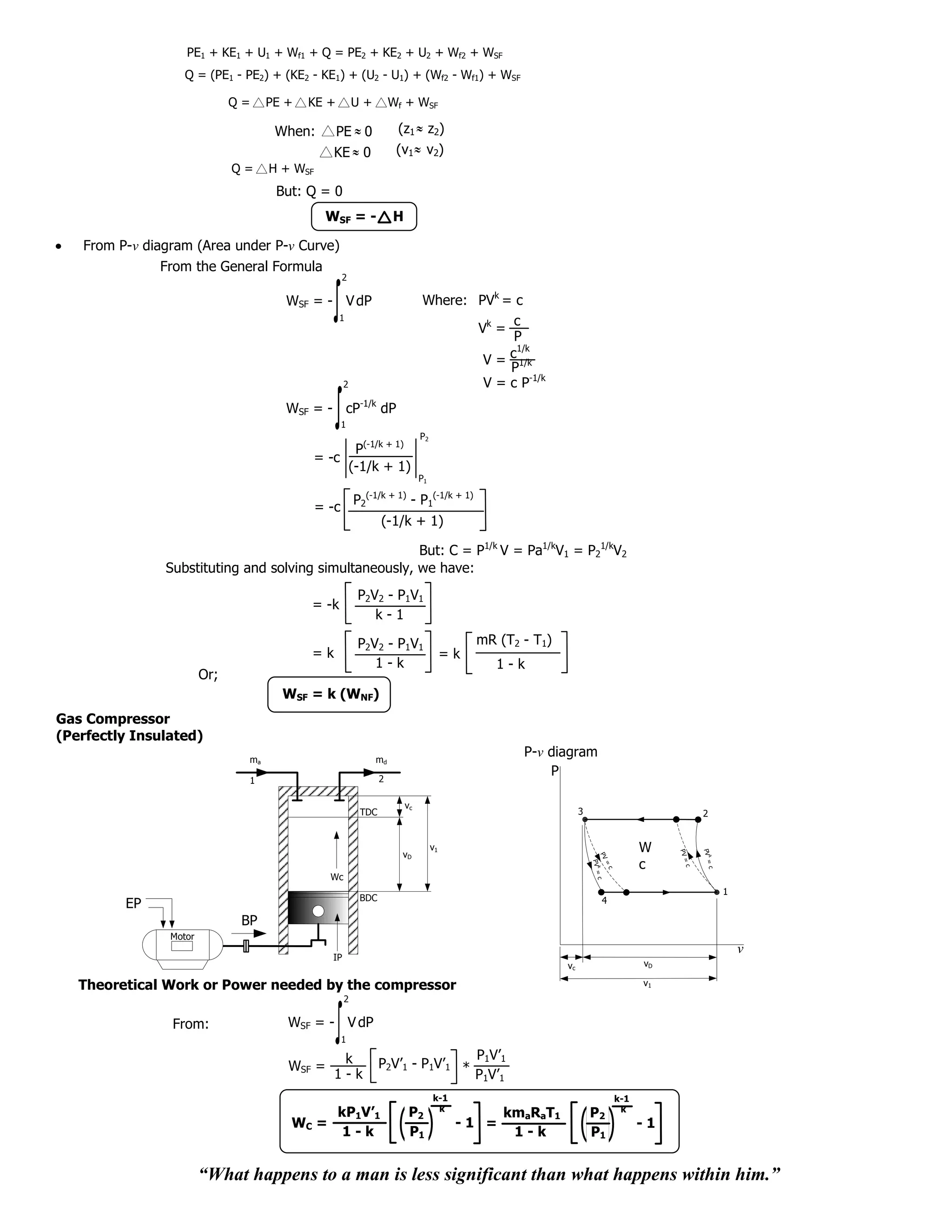
From P-v diagram (Area under P-v Curve)
From the General Formula 2
WSF = - V dP
1
P2V2 - P1V1 mR (T2 - T1)
=n =n
1-n 1-n
Or;
WSF = n (WNF)
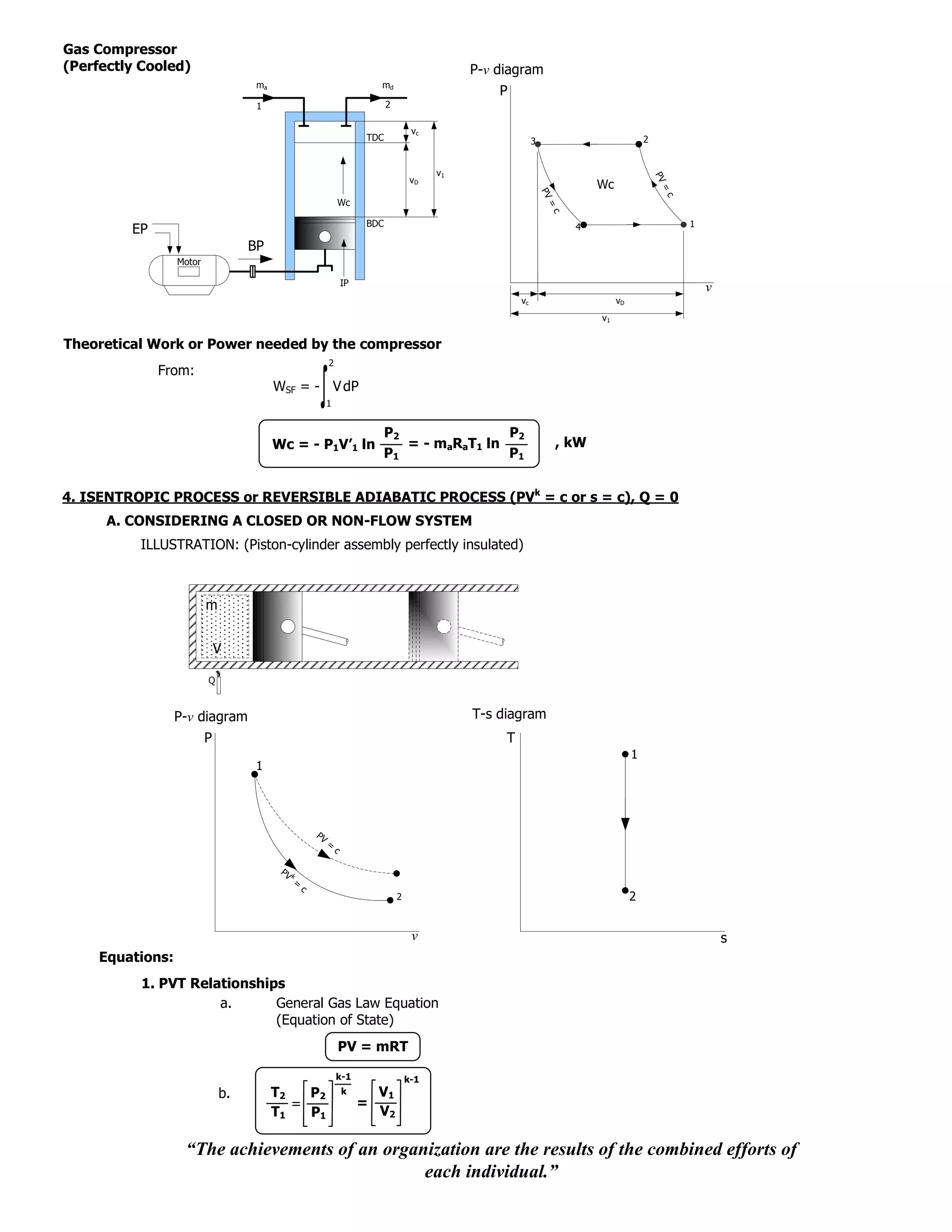
Gas Compressor
ma md
(Air-Cooled) P-v diagram
1 2
P
vc
TDC
3 2
v1
vD
PV =
n
PV =
PV
Wc Wc
PV
k
c
=c
PV =
=
c
k
PV
c
n
BDC
EP
=
c
c
1
BP 4
Motor
IP
v
vc vD
Theoretical Work or Power needed by the compressor
v1
2
From: WSF = - V dP
1
k P1V’1
WSF = P2V’1 - P1V’1 *
1-n P1V’1
n-1 n-1
nP1V’1 n n
P2 nmaRaT1 P2
WC = -1 = -1
1-n P1 1-n P1
Output 1. Motor Efficiency
Efficiency = BP 100%
Input mo=n EP *
2. Mechanical Efficiency
BP
M=n EP *
100%
3. Compression Efficiency
Wc
C=n IP *
100%
Wc = depends on the process involved.
WcT=c = Isothermal process
Wcs=c = Isentropic process
4. Overall Efficiency WcPV n =c = Polytropic process
n = Wc * 100%
o
BP
n = n n * 100%
o C M
“Whoever gives heed to instruction prospers, and blessed is he who trusts in the Lord.”
Proverbs 16:20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/008isothermalisentropicpolytropicprocess-110921083746-phpapp01/75/008-isothermal-isentropic_polytropic_process-8-2048.jpg)