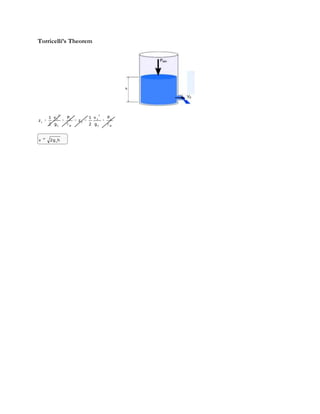
1) Conservation of mass states that the mass entering a system must equal the mass leaving the system. This can be expressed as an equation where the mass flow rate in equals the mass flow rate out.
2) The continuity equation relates mass flow rates, velocities, and cross-sectional areas of different parts of a system based on the law of conservation of mass.
3) Bernoulli's principle applies conservation of energy between two points in a fluid system and relates pressure, elevation, and velocity based on assumptions of incompressible, frictionless flow. It results in an equation equating total mechanical energy at different points.
![The Bernoulli’s Principle
Assumptions:
1. The flow is incompressible, therefore the specific weight of the fluid is constant.
2. The fluid is ideal or no viscosity is considered.
3. There are no mechanical devices such as pumps or turbines in between point 1 and point 2
of the system.
4. The flow is steady
5. No heat removed or added in between point 1 and point 2 of the system.
Applying the Law of Conservation of Energy
[E IN E OUT ]
PE 1 KE 1 Wf1 U1 PE 2 KE 2 Wf2 U2
If we assume that the temperature from the suction and discharge of the pump are
almost equal, t t , then we can say that the change in internal energy is negligible,
1 2
. .
U 0 . We can also assume a steady state pumping process for the pump, V1 V2 .
. .
.
go 1 mW 2
. .
go 1 mW 2
.
mW z1 v1 V W P1 mW z2 v2 V W P2
gC 2 gC gC 2 gC
gC
Multiplying both sides of the equations by .
.
m W go
2 2
1 v1 P1 1 v2 P2
z1 z2
2 gC W
2 gC W](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bernoullisequation-121114014457-phpapp01/85/Bernoulli-s-equation-2-320.jpg)