Module 7 (processes of fluids)
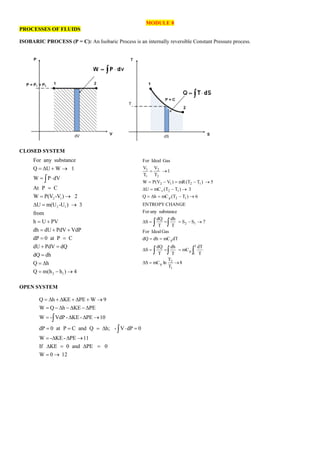
- 1. MODULE 8 PROCESSES OF FLUIDS ISOBARIC PROCESS (P = C): An Isobaric Process is an internally reversible Constant Pressure process. CLOSED SYSTEM OPEN SYSTEM 2 1 2 1 2 1 For any substance Q U W 1 W P dV At P C W P(V -V ) 2 U m(U -U ) 3 from h U PV dh dU PdV VdP dP 0 at P C dU PdV dQ dQ dh Q h Q m(h h ) 4 = + → = = = → = → = + = + + = = + = = = = − → 8 T T ln mC S T dT mC T dh T dQ S dT mC dh dQ Gas Ideal For 7 S S T dh T dQ S substance any For CHANGE ENTROPY 6 ) T T ( mC h Q 3 ) T T ( mC U 5 ) T T ( mR ) V V ( P W 1 T V T V Gas Ideal For 1 2 p 2 1 p p 1 2 1 2 p 1 2 v 1 2 1 2 2 2 1 1 → = = = = = = → − = = = → − = = → − = → − = − = → = Q h KE PE W 9 W Q h KE PE W - VdP - KE - PE 10 dP 0 at P C and Q h; - V dP 0 W - KE - PE 11 If KE 0 and PE 0 W 0 12 = + + + → = − − − = → = = = = = → = = = →
- 2. ISOMETRIC PROCESS (V = C): An Isometric Process is an internally reversible “Constant Volume” process. CLOSED SYSTEM OPEN SYSTEM 3 ) U - m(U Q U Q dU dQ 0 dV PdV dU dQ 2 0 W 0 dV C V At dV P W 1 W U Q substance any For 1 2 → = = = = + = → = = = • = → + = 6 T T ln mC S T dT mC T dQ S CHANGE ENTROPY 5 ) T T ( mCv U Q 4 T P T P Gas Ideal For 1 2 v v 1 2 2 2 1 1 → = = = → − = = → = 1 2 Q h KE PE W 7 W Q h KE PE W VdP KE PE 8 V dP V(P P ) 9 If KE 0 and PE 0 W V dP 10 = + + + → = − − − = − − − → − = − → = = = − →
- 3. ISOTHERMAL PROCESS (T = C or PV = C): An Isothermal Process is an internally reversible “Constant Temperature” Process CLOSED SYSTEM 4 0 U T T But ) T T ( mC U C V P V P V C P or C PV Gas Ideal For 2 1 1 2 v 2 2 1 1 → = = − = = = = = 3 ) U - m(U U 2 dV P W 1 W U Q substance any For 1 2 → = → = → + = 10 Q W e therefor 0, U gas ideal For 9 T Q S S T Q C T At Tds dQ From 8 S - S S substance any For CHANGE ENTROPY 1 2 → = = → = = = = → = 7 P P ln mRT W P P V V 6 V V ln mRT W 5 V V ln V P W V dV C PdV W 2 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 → = = → = → = = =
- 4. OPEN SYSTEM ISENTROPIC PROCESS (S = C): An Isentropic Process is an internally “reversible adiabatic” process in which the entropy remains constant where S = C (for any substance) or PVk = C (for an ideal or perfect gas) 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 and applying laws of logarithm P P VdP PV ln mRT ln 6 P P V VdP mRT ln 7 V If KE 0 and PE 0 P W VdP PV ln 8 P W Q 9 − = = → − = → = = = − = − → = → 2 1 p 2 1 1 2 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 Q h KE PE W 1 W= Q h KE PE W - VdP- KE- PE 2 h m(h h ) 3 For ideal gas h mC (T -T ) but T T h 0 4 W= Q KE PE From C PV C or V P PV P V C dP VdP C P P VdP PV ln 5 P = + + + → − − − = → = − → = = = → − − = = = = − = − − = − → 1 V P V P or V V V V P P antilog taking V V ln V V ln k V V ln k P P ln V dV k P dP n integratio by V dV k P dP PdV VdP k k 2 2 k 1 1 k 2 k 1 k 2 1 1 2 k 2 1 2 1 1 2 1 2 2 1 2 1 → = = = = = − = − = − = − = hence , k dU dh C C but 3 PdV VdP dU dh 2 VdP dh 0 dQ VdP dQ dh 1 PdV dU adiabatic for , 0 dQ PdV dU dQ From v p = = → − = → = = + = → − = = + =
- 5. CLOSED SYSTEM 0 S CHANGE ENTROPY 5 1 P P k 1 V P 1 P P k 1 1 mRT k 1 ) T T ( mR PdV W P P T T From 4 k 1 ) T T ( mR k 1 V P V P PdV W 3 ) T - (T -mC U - W Gas Ideal For 2 U W 1 0 Q W U Q substance any For k 1 k 1 2 1 1 k 1 k 1 2 1 2 k 1 k 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 2 v = → − − = − − = − − = = = → − − = − − = = → = = → − = → = + = − − − OPEN SYSTEM ( ) 8 mRT V P 7 mRT V P 6 PdV k VdP 5 k 1 V P V P k VdP 4 k 1 V P V P PdV egration int By 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 → = → = → = − → − − = − → − − = 3 P C V and V C P C PV From 2 V V P P T T T V P T V P and V P V P C T PV and C PV g sin U k 1 k 1 k k 1 k 2 1 k 1 k 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 k 2 2 k 1 1 k → = = = → = = = = = = − − p 2 1 2 2 1 1 2 1 2 1 Q h KE PE W W Q h KE PE W VdP KE PE Q 0 1 W h KE PE 2 VdP h 3 For Ideal Gas h mC (T -T ) 4 If KE 0 and PE 0 W - VdP - h VdP k PdV k(P V PV ) kmR(T T ) P kmRT1 VdP 1 k 1 k 1 k P = + + + = − − − = − − − = → = − − − → − = − → = → = = = = − = − − − = = = − − − k 1 k 1 k k 1 1 2 1 kPV P 1 1 5 1 k P − − − = − → −
- 6. 17 K KJ T T ln mC S T dT mC T dQ S CHANGE ENTROPY 16 1 P P n 1 V P 1 P P n 1 1 mRT n 1 ) T T ( mR PdV W P P T T From 15 n 1 ) T T ( mR n 1 V P V P PdV W 14 ) T - (T -mC U 13 ) T T ( mC Q 12 U Q W U Q 1 2 n n n 1 n 1 2 1 1 n 1 n 1 2 1 2 n 1 n 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 2 v 1 2 n → = = = → − − = − − = − − = = = → − − = − − = = → = → − = → = + = − − − POLYTROPIC PROCESS (PVn = C): A Polytropic Process is an internally reversible process of an ideal or perfect gas in which PVn = C, where n stands for any constants. CLOSED SYSTEM ( ) 8 mRT V P 7 mRT V P 6 PdV n VdP 5 n 1 V P V P n VdP 4 n 1 V P V P PdV egration int By 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 → = → = → = − → − − = − → − − = 3 P C V and V C P C PV From 2 V V P P T T 1 T V P T V P and V P V P C T PV and C PV g sin U n 1 n 1 n n 1 n 2 1 n 1 n 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 n 2 2 n 1 1 n → = = = → = = → = = = = − − heat specific Polytropic n 1 n k C C 11 ) T - (T mC Q m g Considerin 10 ) T T ( C Q dT C dQ n 1 n k C C : let dT n 1 n k C n 1 n k dT C dQ n 1 1 k n 1 dT C n 1 1 k 1 dT C dQ v n 1 2 n 1 2 n n v n v v v v → − − = → = → − = = − − = − − = − − = − − + − = − − + = − − + = − − + = = − = − + = + = → − = − − = − − = = → + = n 1 1 k CvdT CvdT dQ n 1 dT C dT kC dT C dQ kC C C C R n 1 RdT dT C dQ dW dU dQ 10 n 1 RdT dW n 1 ) T T ( R n 1 P P Pd W 9 W U Q From v v v v p v p v 1 2 1 1 2 2
- 7. OPEN SYSTEM ISOENTHALPIC PROCESS or THROTTLING PROCESS (h = C): An Iso-enthalpic Process is a steady state, steady flow, process in which W = 0, KE = 0, PE = 0, and Q = 0, where the enthalpy h remains constant. h1 = h2 or h = C IRREVERSIBLE OR PADDLE WORK m U Q W WP = = = − − = − − = − − = − − = − → − = → = − = + = + = → − − − = → − − − = → + + + = − − VdP - W 0 PE and 0 KE If 1 P P n 1 V nP 1 P P n 1 nmRT n 1 ) T T ( nmR n 1 ) V P V P ( n VdP 22 ) T T ( mC Q 1 2 ) T - (T mC h U h ) PV ( ) PV ( U h PV U h 20 PE KE h Q W 19 PE KE VdP W 18 W PE KE h Q n 1 n 1 2 1 1 n 1 n 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 2 n 1 2 p work Paddle or le Irreversib Wp : Where W W U Q P − − + =
- 8. 3 3 1 1 3 2 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 m V 6 L x 0.006 m 1000L P 100 KPa V 2 L 0.002 m PV C PV P V C C P V PV P 900 KPa V P V PV W PdV 1 n W 1.2 KJ W 1.2 KJ work is done on the system = = = = = = = = = = = − = = − = − = → SAMPLE PROBLEMS PURE SUBSTANCE & PROCESSES 1. If 6 L of a gas at a pressure of 100 KPa are compressed reversibly according to PV2 = C until the volume becomes 2 L, Find the final pressure and the work. P V dV 2 1 − = dP V Area C PV2 = 2. An ideal gas with R = 2.077 KJ/kg-K and a constant k= 1.659 undergoes a constant pressure process during which 527.5 KJ are added to 2.27 kg of the gas. The initial temperature is 38C. Find the S in KJ/K. Given: R = 2.077 KJ/kg-K; k = 1.659 Q = 527.5 KJ; m = 2.27 kg T1 = 38 + 273 = 311 K Process: P = C Q = mCp(T2 – T1) ; p Rk C 5.72KJ / kg K k 1 = = − − K 352 T mCp Q T 1 2 = + = K / KJ 6 . 1 T T ln mCp S 1 2 = = 3. A perfect gas has a molecular weight of 26 kg/kgm and a value of k = 1.26. Calculate the heat rejected when 1 kg of the gas is contained in a rigid vessel at 300 KPa and 315C, and is then cooled until the pressure falls to 150 KPa. (- 361 KJ)
- 9. KJ -91.5 61.5 - -30 W - Q U KJ 5 . 61 ) 14 . 0 55 . 0 ( 150 W ) V - P(V dV P W C P at PdV W W U Q 1 2 = = = = − = = = = = + = (rejected) KJ 2 . 361 Q ) 588 294 ( 23 . 1 ( 1 ) T T ( mC Q 294 300 ) 588 ( 150 T T P T P C V At 588 273 315 T 23 . 1 1 k R C 32 . 0 26 3143 . 8 R 1 2 v 2 2 2 1 1 1 v = − = − = = = = = = + = = − = = = 4. A closed gaseous system undergoes a reversible process in which 30 KJ of heat are rejected and the volume changes from 0.14 m3 to 0.55 m3 . The pressure is constant at 150 KPa. Determine the change in internal energy of the system and the work done. 5. An ideal gas has a mass of 1.5 kg and occupies 2.5 m3 while at a temperature of 300K and a pressure of 200 KPa. Determine the ideal gas constant for the gas. Given: m = 1.5 kg V = 2.5 m3 T = 300K P = 200 KPa 6. A cylinder fitted with a frictionless piston contains 5 kg of superheated water vapor at 1000 KPa and 250C. The system is now cooled at constant pressure until the water reaches a quality of 50%. Calculate the work done and the heat transferred. From h = u + PV dh = du + PdV + VdP but dQ = du + PdV dh = dQ + VdP K kg KJ 11 . 1 ) 300 ( 5 . 1 ) 5 . 2 ( 200 mT PV R mRT PV − = = = = 2 1 for a cons tan t pressure process, P C dP 0; therefore dh dQ; and by int egration dh h and dQ Q Q h m(h - h ) 5(1768.57 - 2942) Q -5867.2 KJ Q 5867.2 KJ (Heat is rejected) = = = = = = = = = =
- 10. 2 2 1 1 2 1 Q = ΔU + W KJ W = PdV at P = C; W = P(υ - υ ) in KJ kg W = m P(υ - υ ) = -676.43 KJ W = 676.43 KJ (Work is done on the system) From table or software at 1000 KPa and 250C h1 = 2942 KJ/kg: 1 = 0.233 m3 /kg At P = 1000 KPa and quality x = 0.50 h2 = 1768.57 KJ/kg; 2 = 0.097714 m3 /kg 7. A throttling calorimeter is connected to the de-superheated steam line supplying steam to the auxiliary feed pump of a ship. The line pressure measures 2.5 MPa (2500 KPa). The calorimeter pressure is 110 KPa and the temperature is 150C. Determine the line steam quality. From Superheated table, at 110 KPa and 150C, h2 = 2775.6 KJ/kg From Saturated liquid and saturated vapor table hf1 = 962.11 KJ/kg; hfg = 1841.0 KJ/kg h1 = hf1 + x1(hfg1) h1 = h2 1 f1 1 fg1 1 h -h 2775.6-962.11 x 0.985 h 1841.0 x 98.5 % = = = = Thank You
