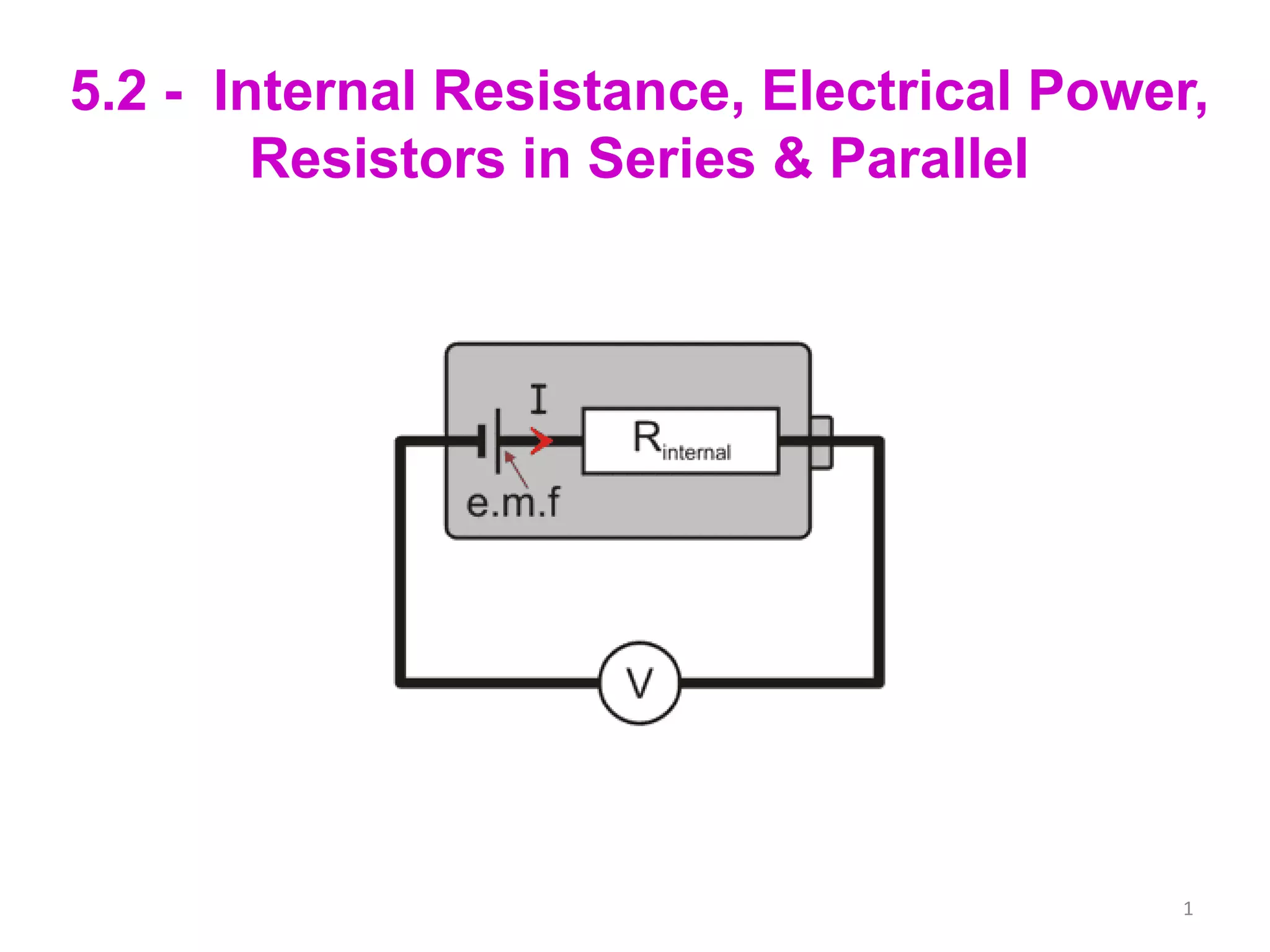
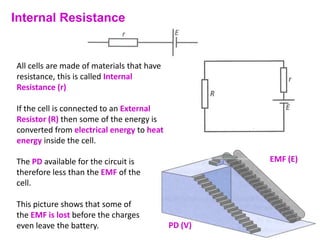
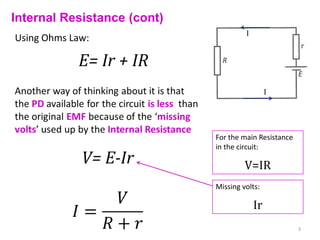
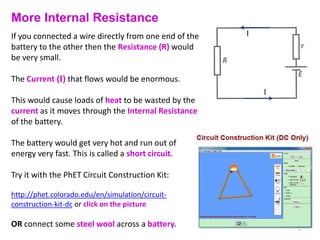
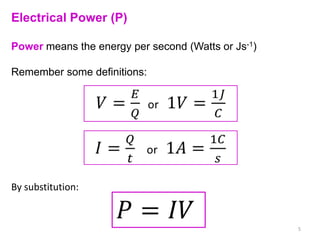
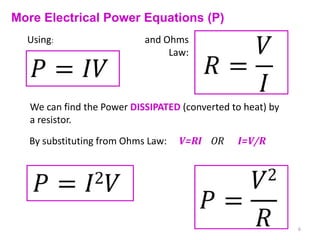
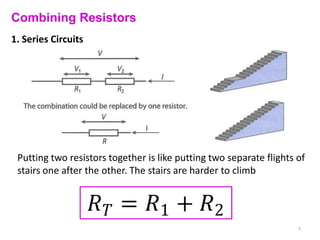
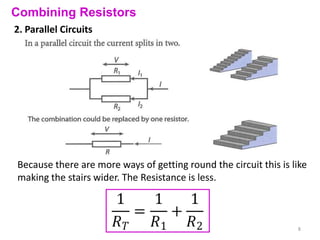
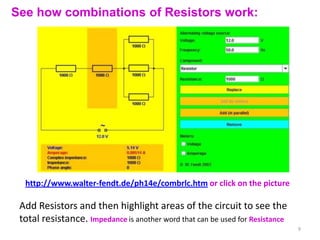
Internal resistance is the resistance of a battery or cell that causes some of the battery's voltage to be dropped internally rather than available to do work. The voltage available for an external circuit (PD) is less than the battery's open circuit voltage (EMF). Power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred, calculated as voltage times current, or the current squared times the resistance. Resistors can be combined in series or parallel circuits. Series circuits add the resistances together while parallel circuits decrease the total resistance.