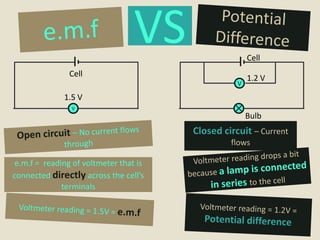
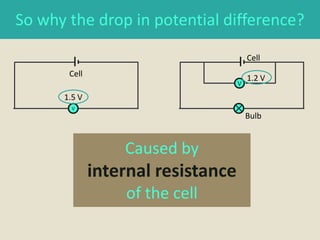
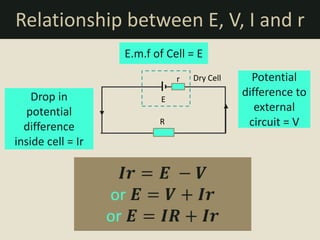
The document defines electromotive force (e.m.f) as the work done by a source to drive one coulomb of charge around a complete circuit. It states that the e.m.f of a cell or battery refers to the electrical energy produced for each coulomb that passes through it. However, the potential difference, or voltage, across the external terminals is usually lower than the e.m.f due to the internal resistance of the cell or battery, which causes a drop in potential and some of the energy to be lost as heat. The relationship between e.m.f, potential difference, current, and internal resistance is explained.