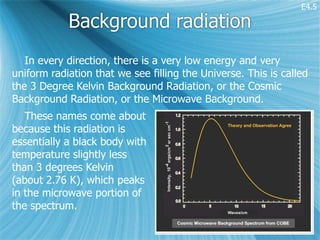
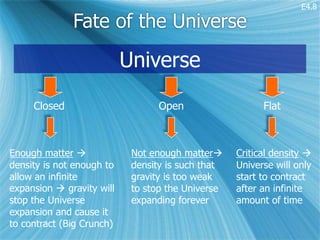
Olber's paradox states that if the universe is infinite and contains an infinite number of stars, each emitting the same amount of light, then the night sky should be uniformly bright, which it is not. Considering an expanding, finite universe explains why the night sky is dark - there is a finite number of stars with finite lifetimes, and the light from distant stars has not had time to reach us due to the universe's finite age. Distant stars are also redshifted into obscurity due to the universe's expansion.