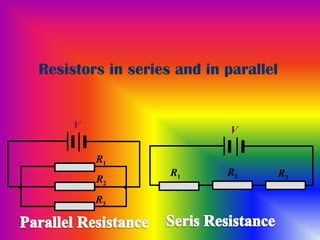
Resistors in series and parallel circuits were discussed. In a series circuit, the total resistance is equal to the sum of the individual resistances. In a parallel circuit, the total resistance is lower than the individual resistances. Examples of circuit analysis problems involving calculating equivalent resistances and currents/voltages in various components were provided. The effects of the internal resistances of ammeters, voltmeters and cells on circuit measurements were also explained.










![3 Resistors in parallel
I.e.
R1
R2
R3
V
• •
I1
I2
I3
I
R [= (R1
–1
+ R2
–1
+ R3
–1
)–1
]
V
I =
= I1 + I2 + I3
V
R](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dhimandebnathrollno1023-151005163555-lva1-app6892/85/Dhiman-debnath-rollno1023-12-320.jpg)





































