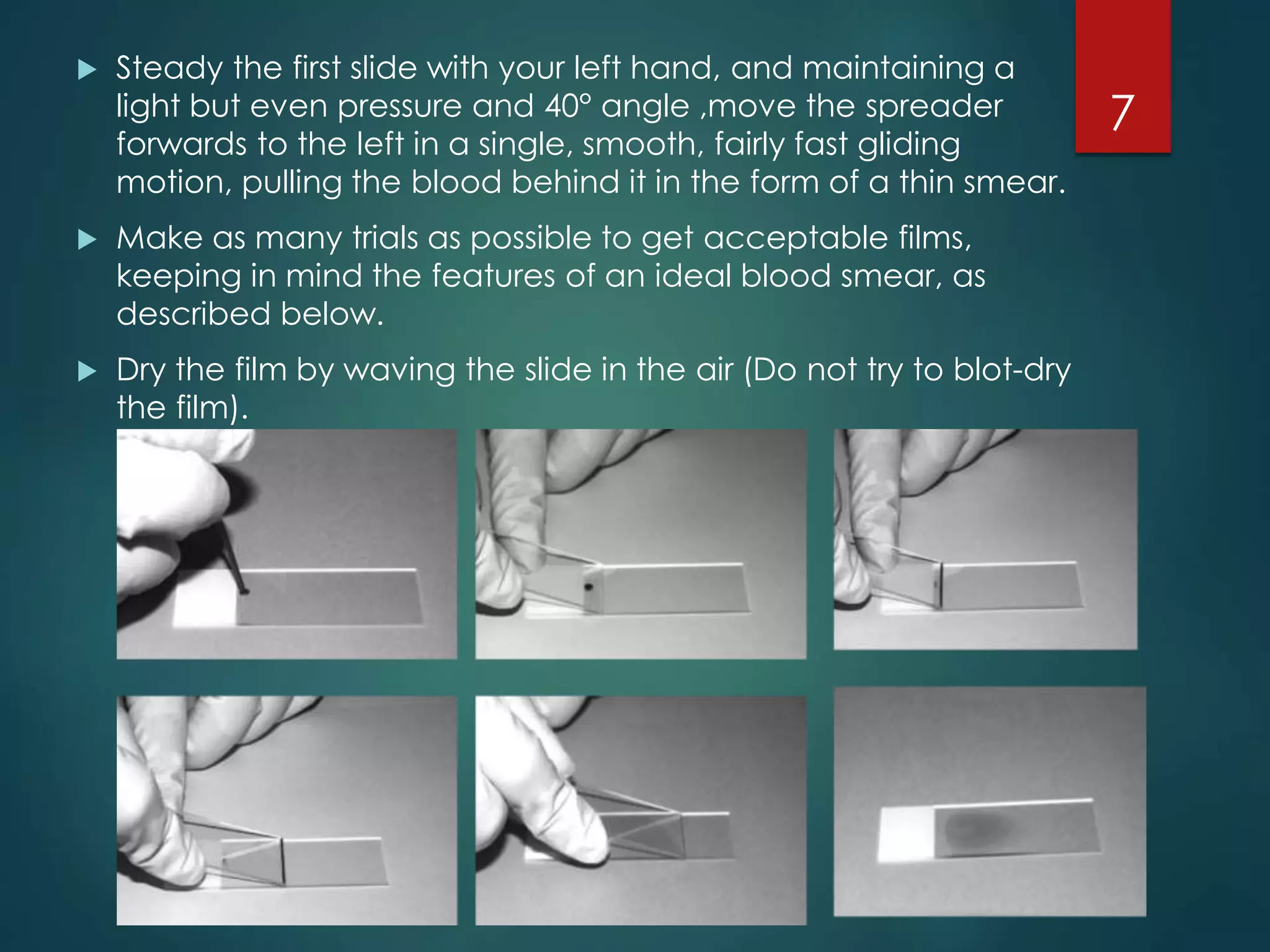
The document describes the key parts and functions of a compound microscope used to examine peripheral blood smears. It outlines the proper procedure for making blood films, including using a spreader slide to create a thin, even smear. An ideal blood smear is translucent and uniformly thick. The process of fixing blood films with Leishman's stain and identifying features of a well-stained smear is also detailed. The major blood cell types—red blood cells, white blood cells including granulocytes and agranulocytes—are defined based on their appearance under different microscope magnifications.