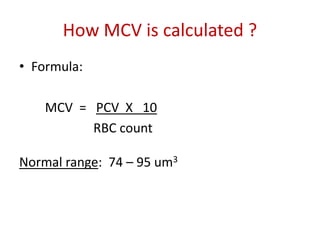
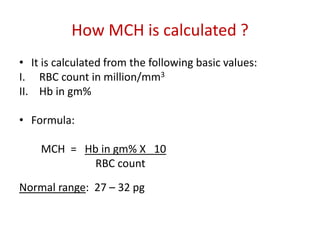
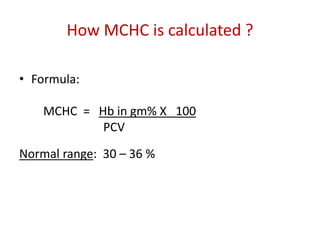
This document discusses the determination of red blood cell indices including packed cell volume (PCV), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). It describes the macrohematocrit or Wintrobe tube method for determining PCV which involves centrifuging a blood sample and measuring the ratio of packed red cells to total blood volume. Formulas are provided for calculating MCV from PCV and RBC count, MCH from hemoglobin and RBC count, and MCHC from hemoglobin and PCV. Normal ranges are listed for each index.