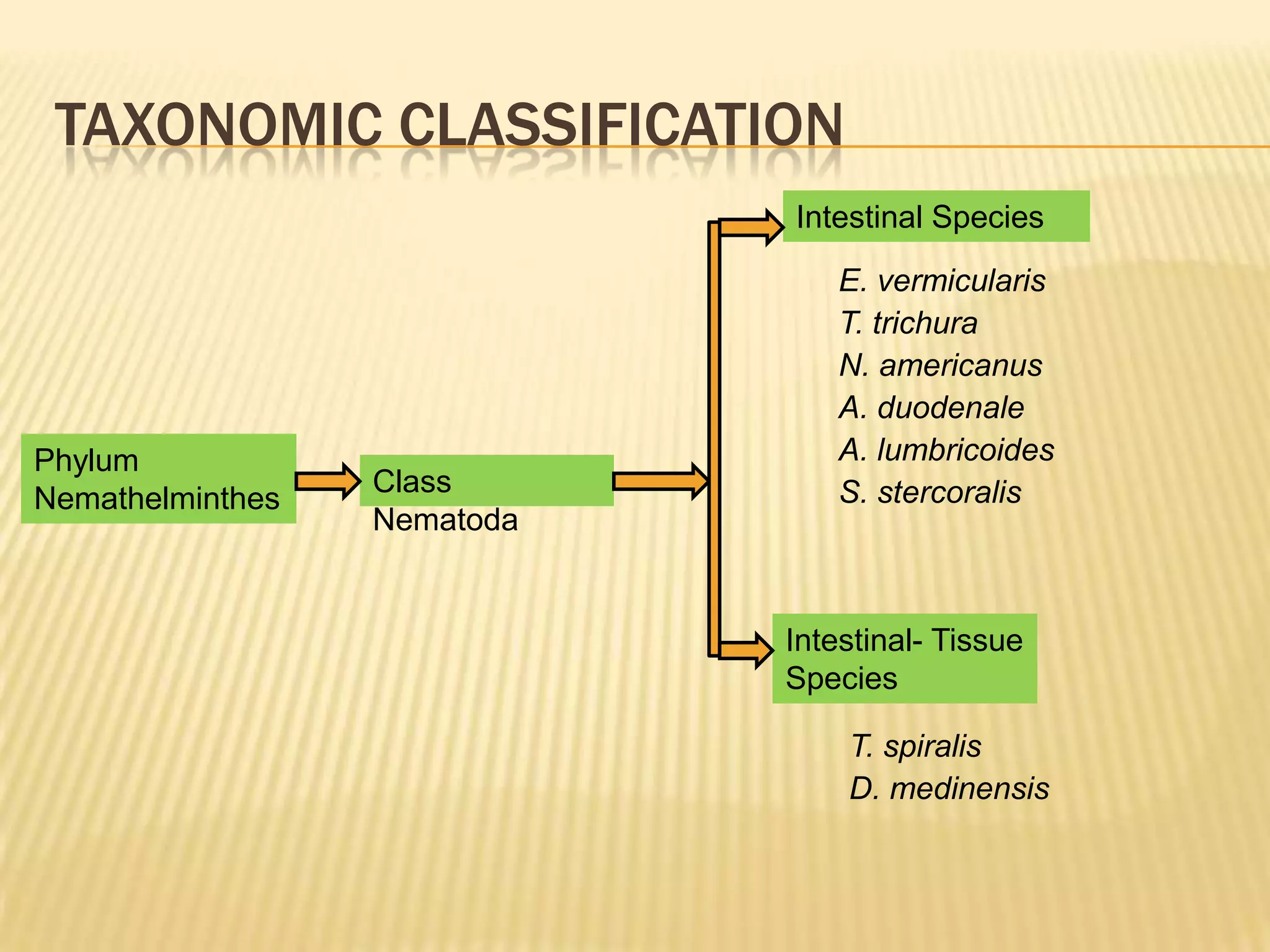
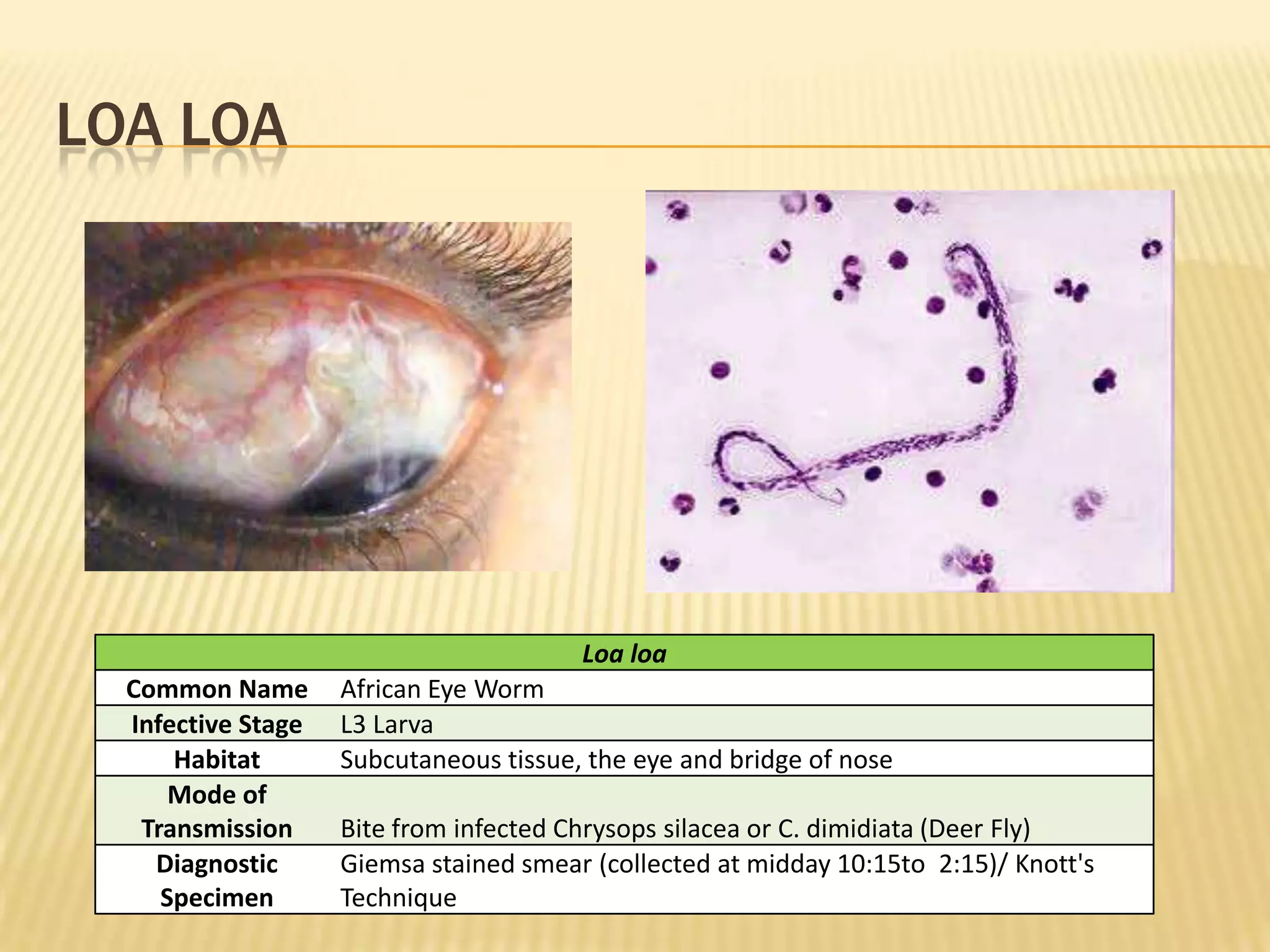
The document discusses various nematodes that can infect humans such as Ascaris lumbricoides and Enterobius vermicularis, describing their characteristics, life cycles, and diagnostic methods. It also outlines techniques for diagnosing nematode infections from stool samples, including the Kato-Katz method, concentration techniques like acid ether concentration, and culture methods like Harada Mori.