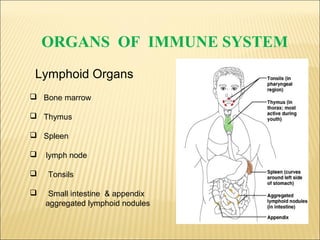
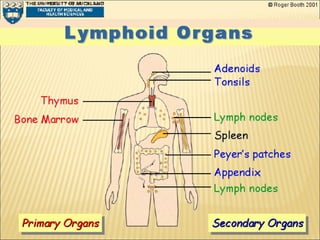
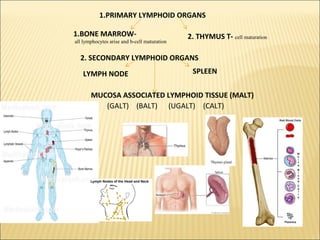
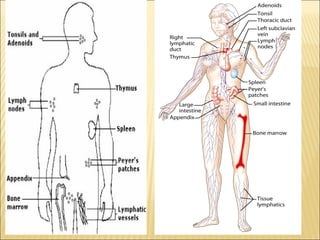
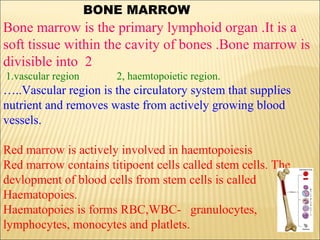
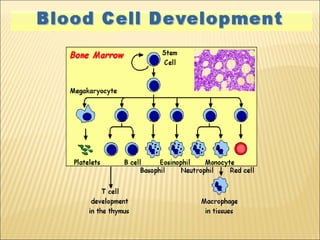
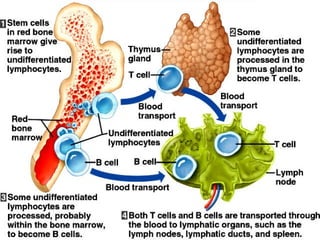
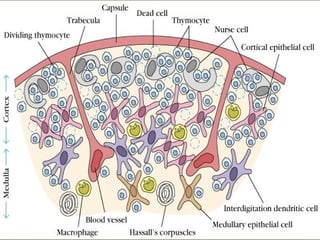
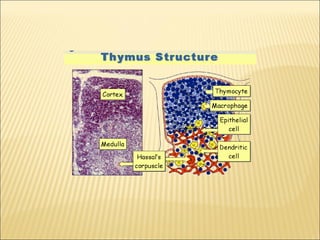
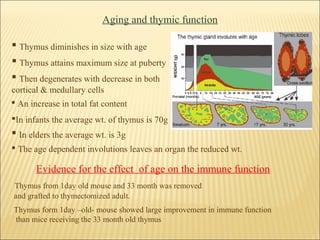
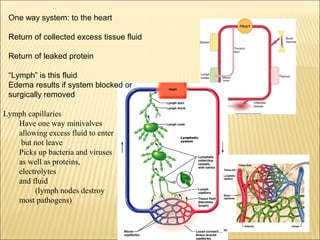
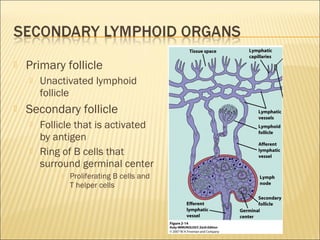
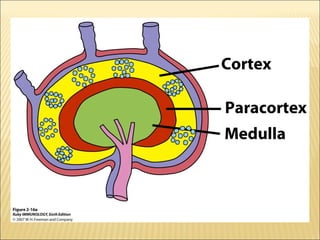
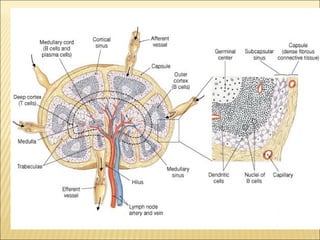
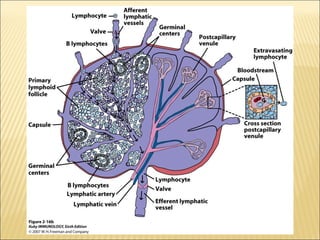
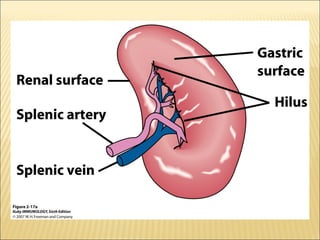
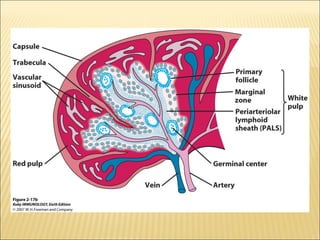
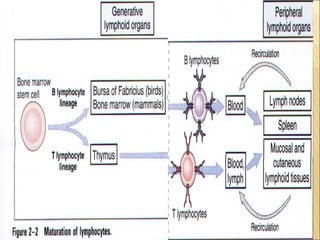
The document discusses the lymphoid organs of the immune system. It describes the bone marrow and thymus as the primary lymphoid organs, where lymphocytes develop and mature. The bone marrow is the site of generation for all blood cells including B lymphocytes, and is where B cell maturation occurs. The thymus is the site of T cell maturation and selection. Secondary lymphoid organs include the lymph nodes, spleen, and mucosal-associated lymphoid tissues, which harbor mature lymphocytes.