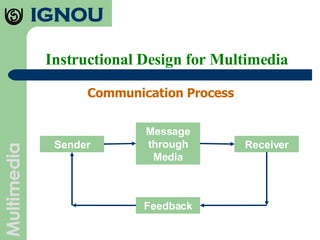
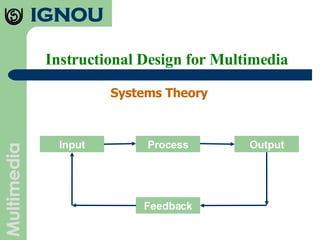
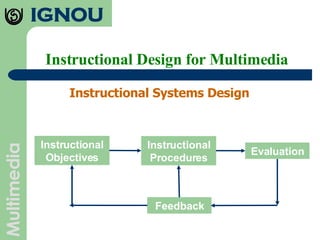
The document discusses principles of instructional design for multimedia. It outlines seven principles: multimedia principle, contiguity principle, modality principle, redundancy principle, coherence principle, personalization principle, and practice principle. It also discusses instructional design as a process, discipline, and science. Key aspects of instructional design discussed include needs analysis, material development, implementation, and evaluation.