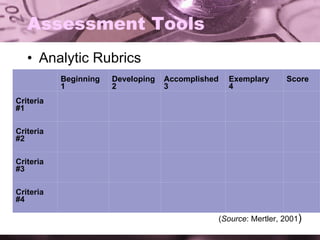
The document discusses various alternative assessment techniques that can be used instead of traditional testing methods. It describes techniques like self-assessment, peer assessment, portfolios, reflective journals, projects and oral presentations. It also provides details on how to implement these techniques, including providing training to students, defining clear criteria, and using tools like rubrics to evaluate performance. The key benefits highlighted are developing skills like self-reflection, collaboration and lifelong learning.