Mobile technologies are increasingly accessible and affordable for both institutions and learners. They can be used for numerous teaching functions to improve interaction and reduce distance between learners and teachers. Mobile technologies are also pervasive, novel, and provide quick access to information from anywhere at any time.
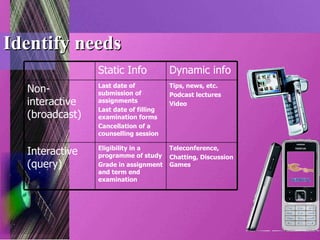
When developing mobile learning programs, it is important to plan purposefully, identify learners' needs, choose appropriate media, implement technology solutions through testing, provide user manuals, run the system with support, and evaluate performance and outcomes. Training stakeholders is also critical for success.