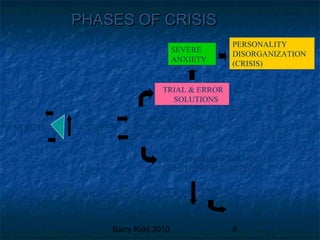
This document defines crisis and crisis intervention. It begins by defining a crisis as an overwhelming reaction to a threatening situation where a person's usual problem solving strategies fail, resulting in disequilibrium. It then outlines three types of crises: developmental, situational, and adventitious. Next, it provides an overview of crisis intervention, noting that a crisis is time-limited, occurs for everyone, and one's perception determines if an event is a crisis. It describes balancing factors that determine the outcome of a crisis and outlines the phases of a crisis. The document concludes by describing the assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation and evaluation steps involved in crisis intervention.