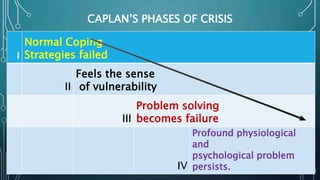
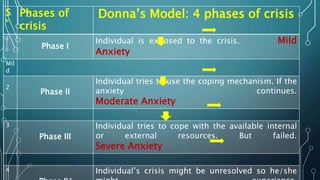
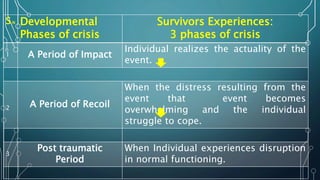
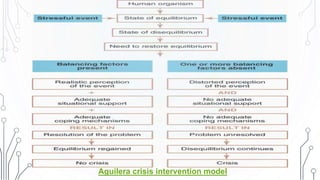
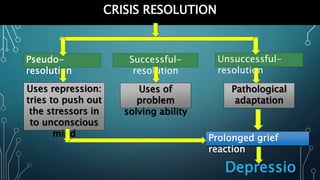
This document discusses crisis intervention. It defines a crisis and lists its characteristics. It describes different types of crises including maturational, situational, sociocultural, and adventitious crises. It discusses factors that can influence a crisis and theories of crisis intervention including Kaplan's crisis sequence theory and Aguilera's crisis intervention model. The document outlines the aims, role, and techniques of crisis intervention for nurses including assessment, diagnosis, implementation through various approaches, and evaluation. It discusses modalities of crisis intervention such as mobile crisis programs and telephone contacts. Finally, it covers signs and symptoms of crisis and resolutions.