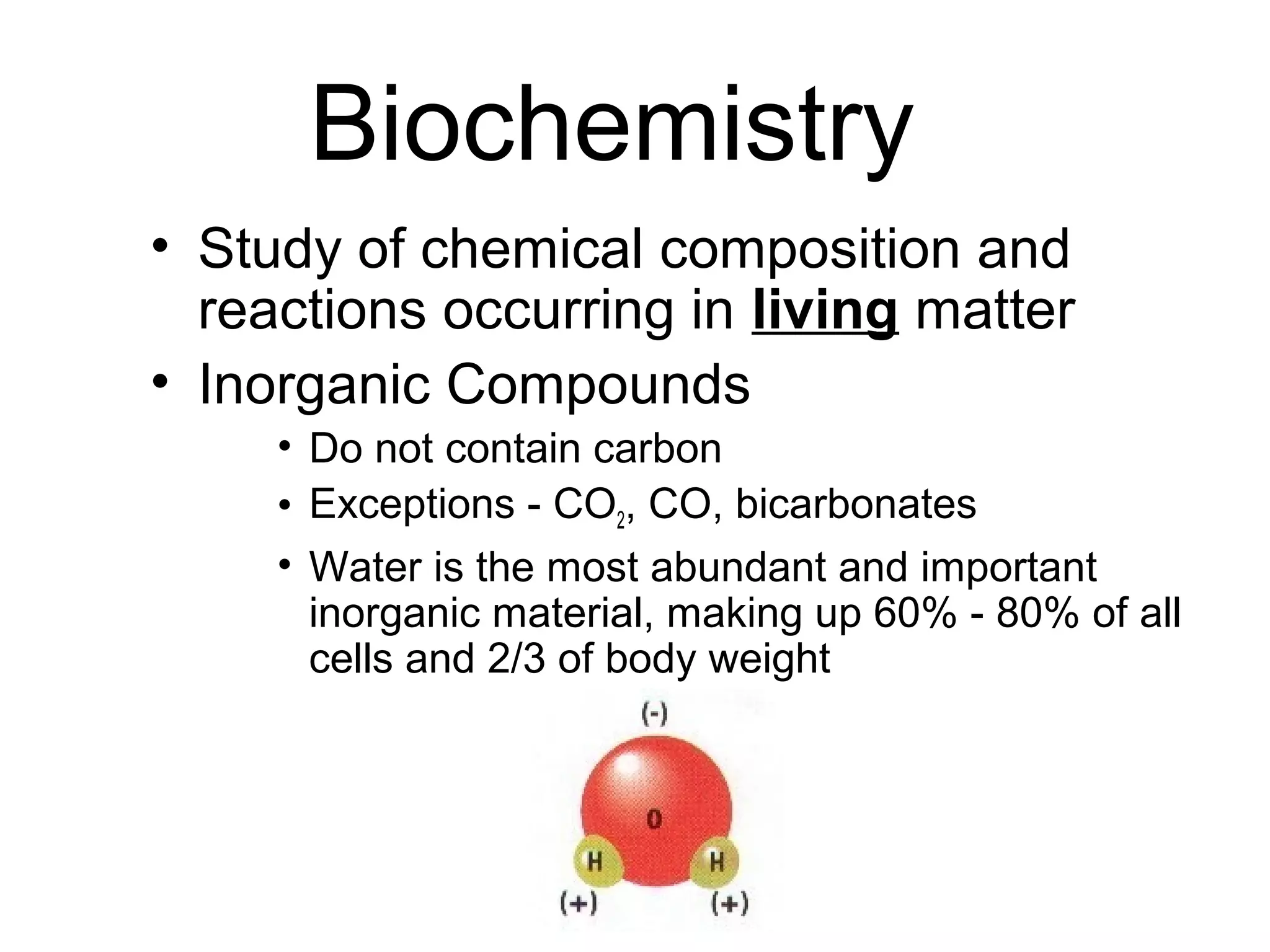
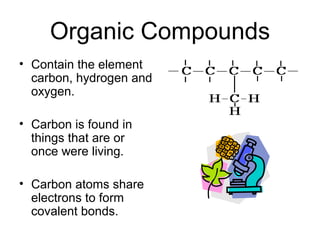
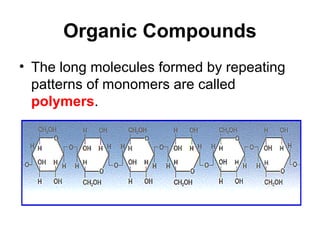
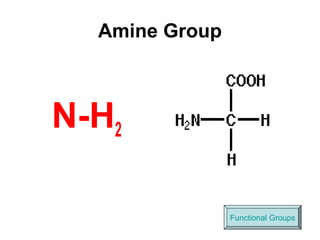
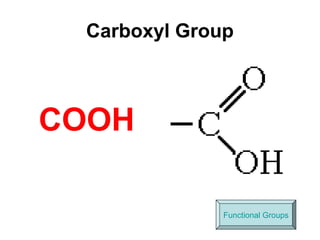
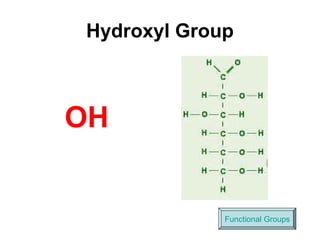
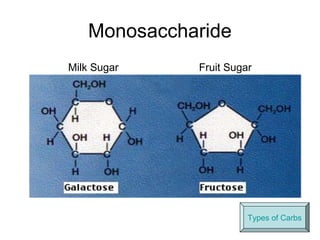
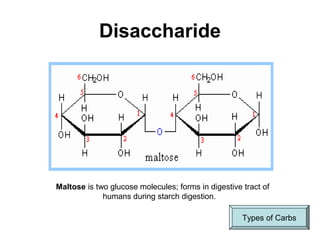
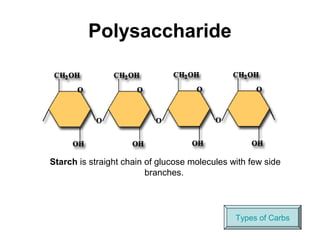
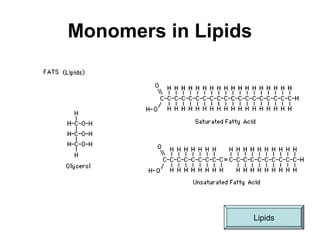
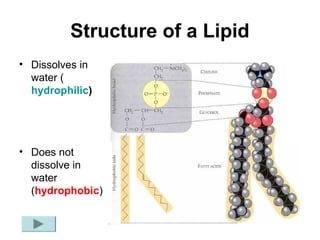
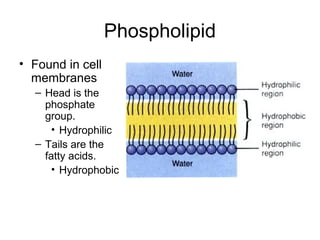
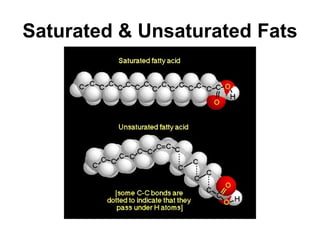
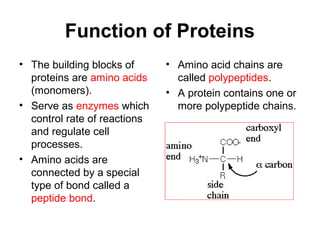
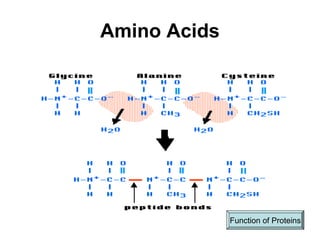
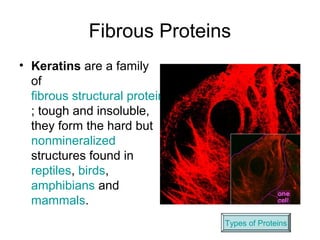
Biochemistry is the study of chemical composition and reactions in living matter. It includes inorganic compounds like water and CO2, as well as organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Organic compounds are made of polymers of monomers like carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These macromolecules are essential to life processes in cells and provide structure, energy storage, homeostasis, and genetic information.