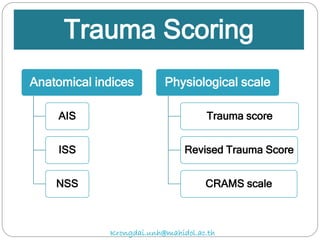
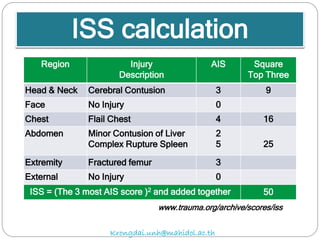
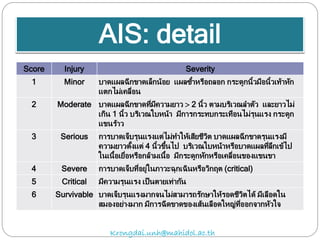
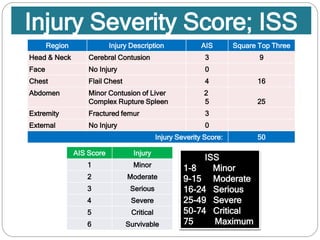
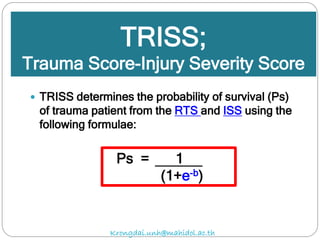
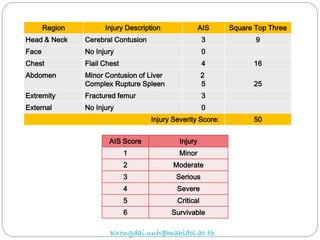
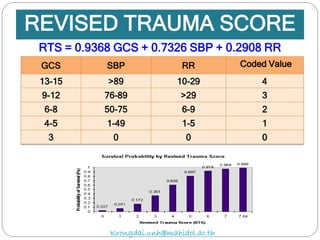
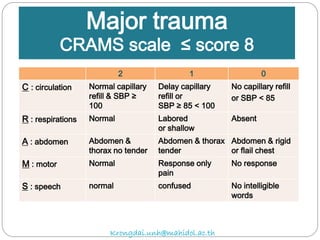
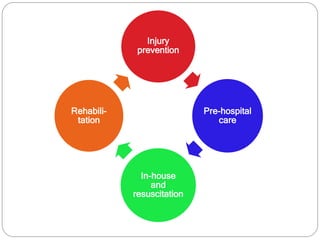
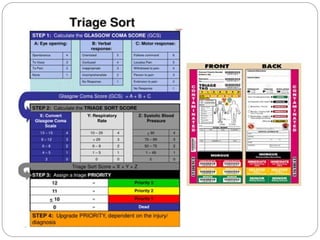
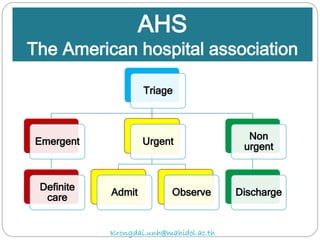
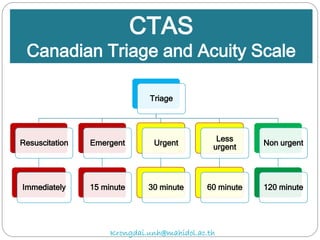
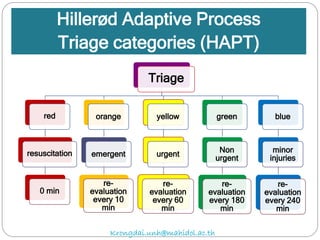
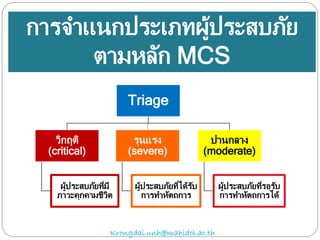
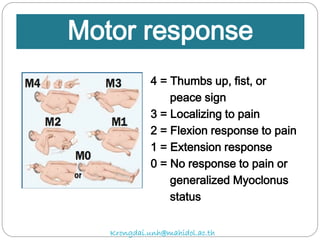
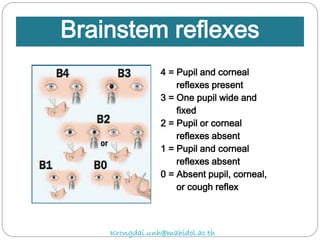
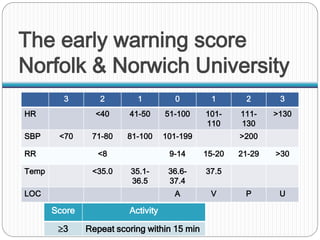
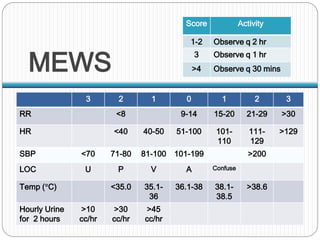
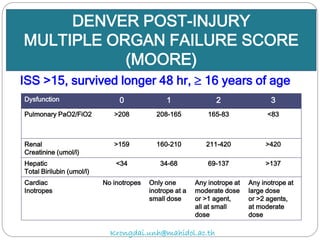
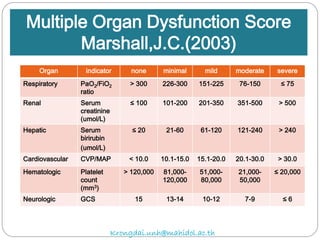
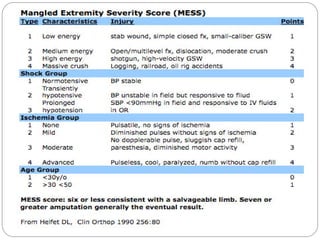
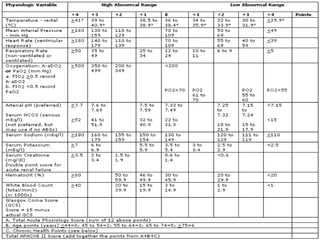
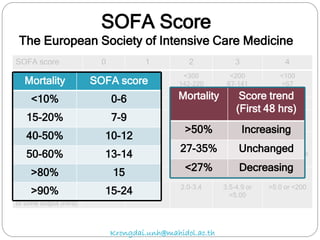
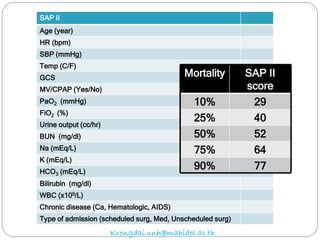
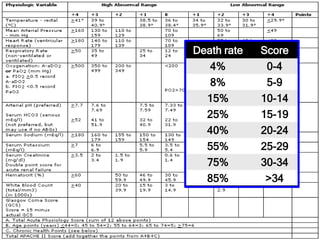
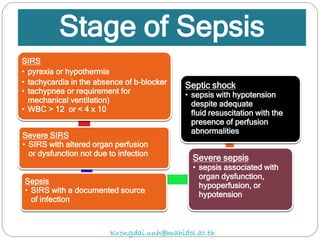
The document discusses various trauma scoring systems used to assess injury severity, predict survival chances, and guide triage and treatment of trauma patients. It describes anatomical indices like the Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) and Injury Severity Score (ISS) which evaluate individual injuries and overall injury burden. It also covers physiological scales like the Trauma Score, Revised Trauma Score, and CRAMS scale. Multiple organ dysfunction scores like SOFA are presented, along with mass casualty triage algorithms like START and SALT.