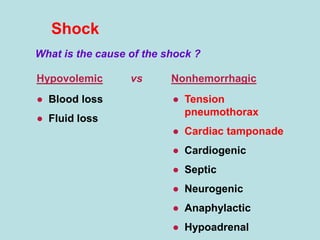
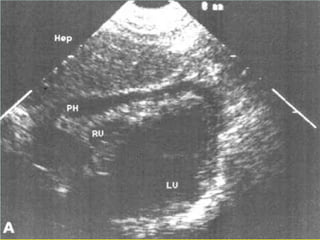
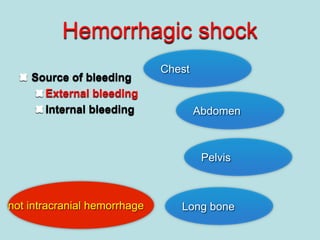
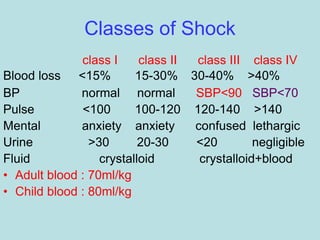
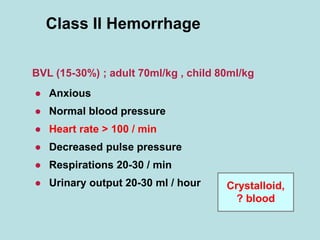
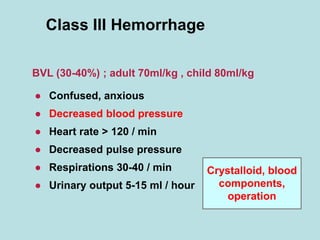
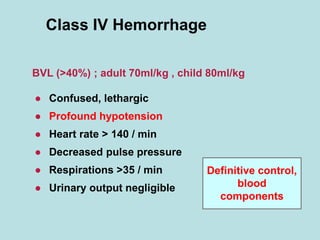
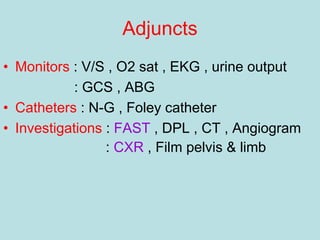
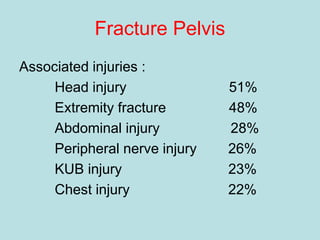
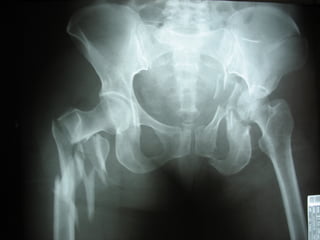
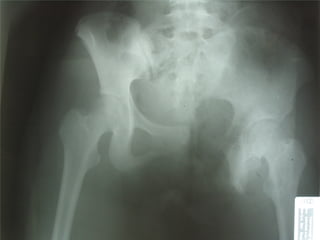
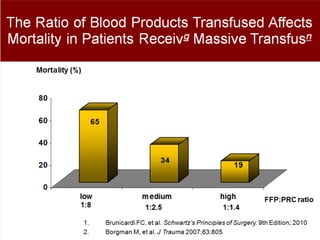
- Shocks occur when there is inadequate tissue perfusion and oxygenation due to problems like blood loss, fluid loss, tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, etc.
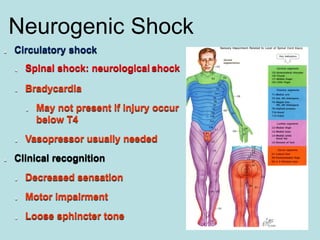
- Clinical signs of shock include anxiety, tachycardia, tachypnea, decreased urine output, pale and cool skin.
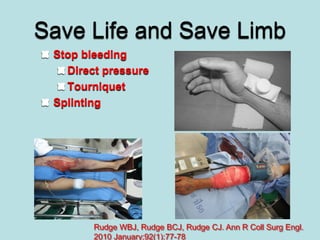
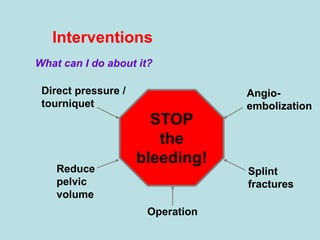
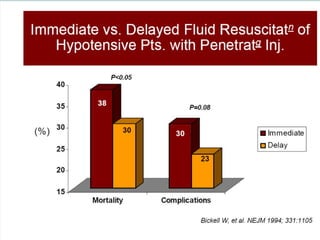
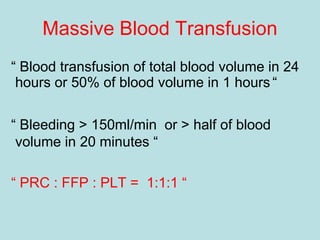
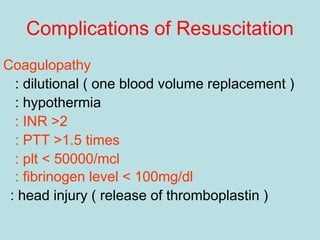
- Treatment of shock involves rapid identification of the cause, stopping any ongoing bleeding, and fluid resuscitation. Blood transfusion may be needed for more severe cases. Care must be taken to avoid complications like hypothermia, acidosis, and coagulopathy during resuscitation.