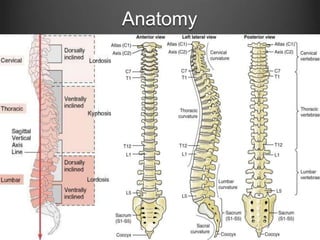
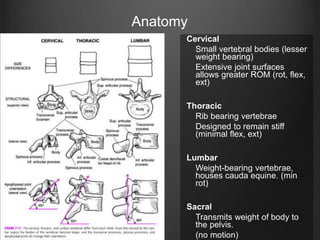
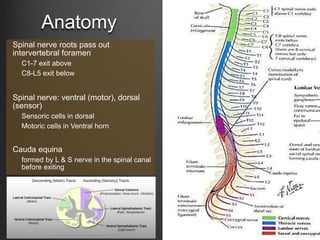
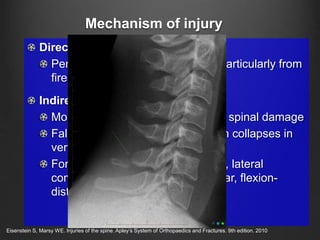
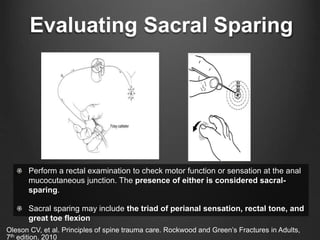
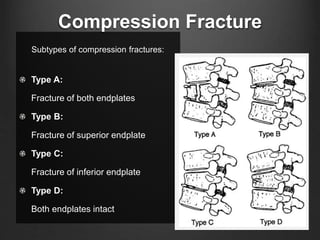
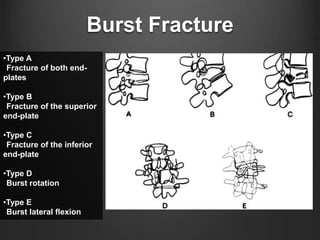
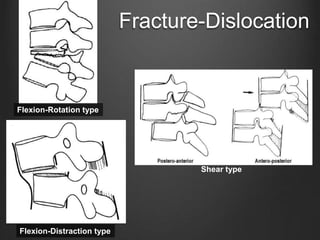
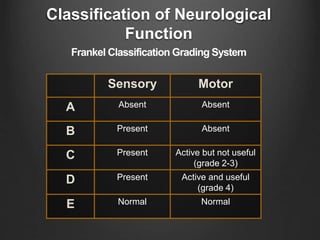
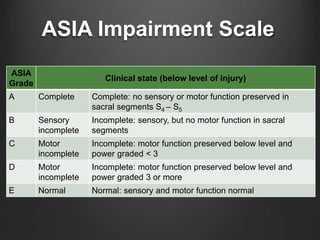
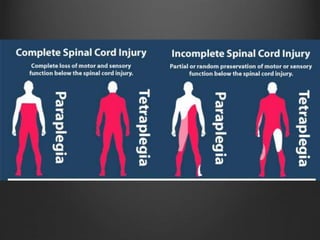
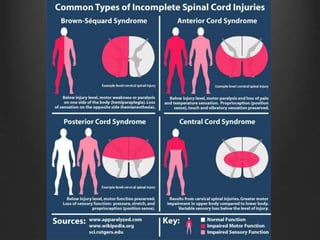
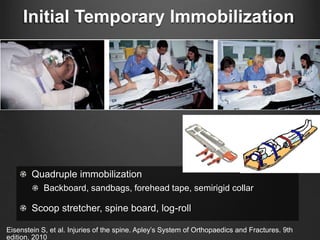
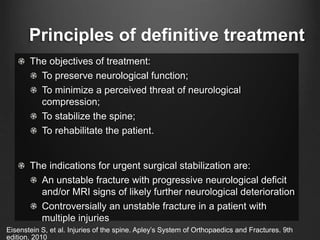
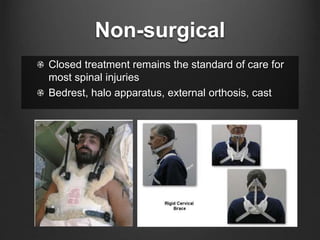
The document summarizes key aspects of spinal anatomy and injuries. It describes the characteristics of the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral regions. Common mechanisms of spinal injury include falls, motor vehicle crashes, and blunt or penetrating trauma. Signs suggestive of spinal injury include neck pain or tenderness, numbness, weakness, and loss of bowel or bladder control. Evaluation involves physical exam including motor and sensory function tests. Imaging with x-rays, CT, and MRI is used for diagnosis. Management principles focus on immobilization, resuscitation, corticosteroid administration in some cases, and surgery for unstable injuries with neurological deficits.