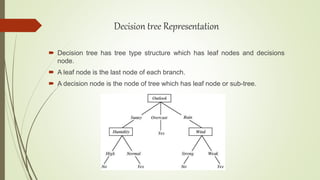
The document discusses decision tree induction, which is a popular tool for classification and prediction. It describes how decision trees work by having internal decision nodes that split the data into branches, which end at leaf nodes that provide a class label or prediction. It also covers different algorithms for building decision trees like ID3, C4.5, and CART. The key steps in decision tree induction include selecting attributes to split on using metrics like information gain or Gini index, and pruning the fully grown tree to avoid overfitting.